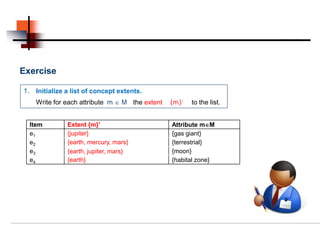
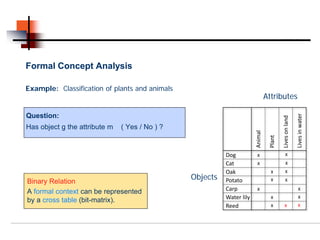
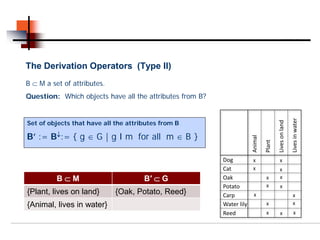
Cat x x
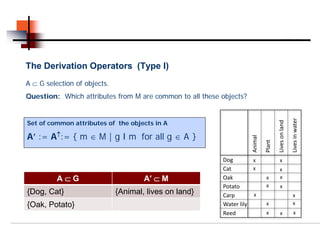
A⊂G A′ ⊂ M Oak x x
Potato x x
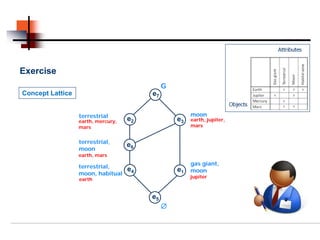
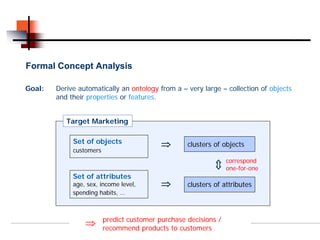
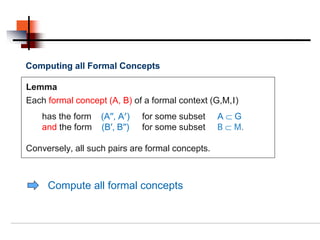
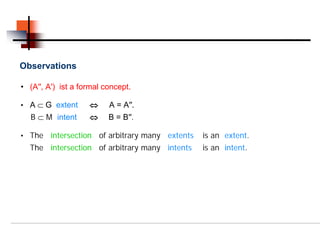
Formal concept analysis studies how objects can be grouped hierarchically based on their common attributes. It models concepts as units consisting of an extension (objects belonging to the concept) and an intension (attributes common to those objects). Formal contexts represent relationships between objects and attributes, and derivation operators identify the attributes common to a group of objects or the objects sharing a group of attributes.



































![Conceptual Hierarchy
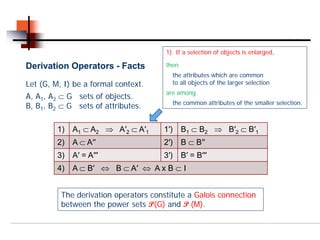
Let (A1, B1) and (A2, B2) be formal concepts of (G,M,I).
(A1, B1) sub-concept of (A2, B2) :⇔ A1 ⊂ A2 [⇔ B2 ⊂ B1 ].
Animal
Dog, Cat, Carp
• (A2, B2) is a super-concept of (A1, B1).
• Notation: (A1, B1) ≤ (A2, B2)
Animal, lives on land
Dog, Cat](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamining-formalconceptanalysis-110909115443-phpapp02/85/Formal-Concept-Analysis-47-320.jpg)


![Conceptual Hierarchy
Let (A1, B1) and (A2, B2) be formal concepts of the context (G,M,I).
(A1, B1) proper sub-concept of (A2, B2) [ (A1, B1) < (A2, B2)]
:⇔ (A1, B1) ≤ (A2, B2) and (A1, B1) ≠ (A2, B2) .
(A2 , B2)
(A1 , B1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamining-formalconceptanalysis-110909115443-phpapp02/85/Formal-Concept-Analysis-51-320.jpg)

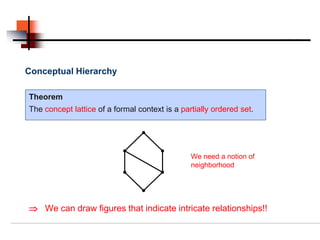
![Conceptual Hierarchy
Proper sub-concepts can be used to define a notion of neighborhood.
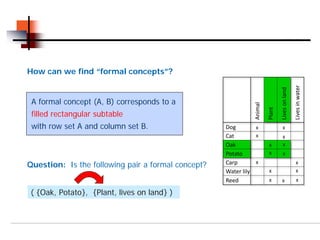
Let (A1, B1) and (A2, B2) be formal concepts of the context (G,M,I) (A2 , B2)
and (A1, B1) is a proper sub-concept of (A2, B2).
(A1, B1) is a lower neighbor of (A2, B2) [(A1, B1) (A2, B2)], (A , B )
if no formal concept (A, B) exists with
(A1 , B1)
(A1, B1) < (A, B) < (A2, B2).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamining-formalconceptanalysis-110909115443-phpapp02/85/Formal-Concept-Analysis-53-320.jpg)