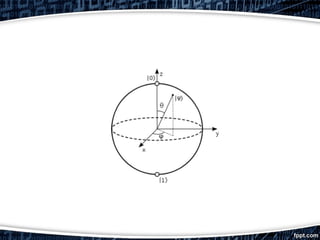
Artificial intelligence (AI) simulates human intelligence processes such as learning and reasoning, while quantum artificial intelligence aims to enhance these processes through quantum computing. Quantum bits (qubits) can store information more efficiently than classical bits, offering significant speed advantages in computational tasks. Quantum computing promises to revolutionize data processing by enabling instant access and analysis of large datasets, potentially exceeding the capabilities of today's computers.