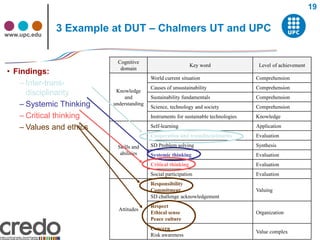
The document discusses competencies in sustainability for engineering education. It defines competencies and lists taxonomies that classify competencies into categories like knowledge, skills, attitudes, and ethics. Engineering graduates are expected to have competencies like critical thinking, systemic thinking, and interdisciplinarity. Analysis of competency frameworks from different universities found that competencies are introduced at varying levels, from basic knowledge to complex problem solving and valuing sustainability challenges. The document also outlines the University of Polytechnic Catalonia's framework for its generic sustainability competency.