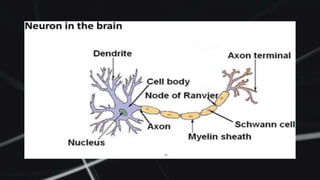
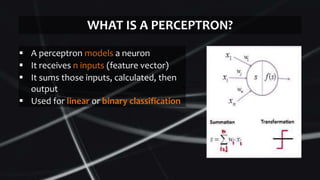
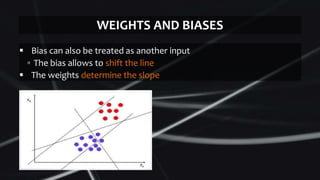
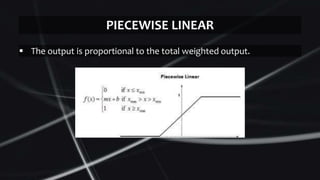
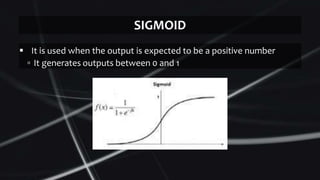
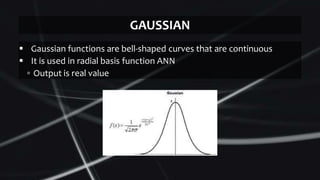
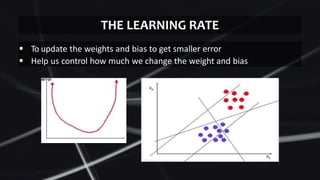
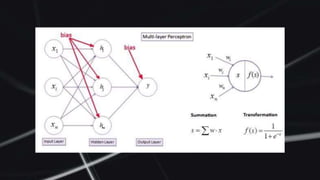
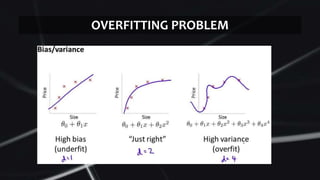
Feed forward neural networks use multiple perceptrons arranged in layers to perform increasingly complex functions. They take a weighted sum of inputs and pass them through an activation function to produce an output. The network learns through a backpropagation algorithm which calculates error rates to adjust weights between layers to minimize errors. Overfitting can occur if the network learns patterns specific to the training data and does not generalize well to new data.