The document describes a laboratory experiment to determine the empirical formula of copper(II) oxide. The experiment involves heating copper(II) oxide in a combustion tube under a hydrogen gas flow. The apparatus is weighed before and after heating to calculate the mass of copper and oxygen. The ratio of moles of copper to oxygen gives the empirical formula. Precautions like removing air from the tube and repeating heating/cooling cycles until a constant mass is reached help ensure complete reaction. The empirical formula is determined from the simplest whole number ratio of moles of copper to oxygen.



![Chapter 3: Chemical Formulae and Equations
A. Knowledge ( Definition, Meaning and Facts )
1. State the meaning of relative atomic mass based on carbon-12 scale.
- the ratio of the average mass of one atom of an element to
1
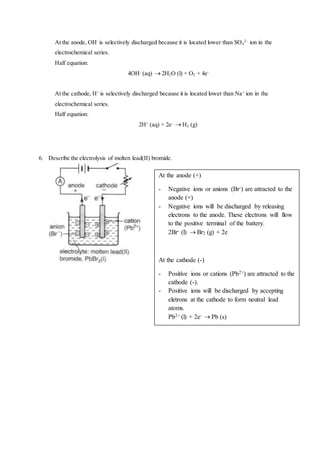
12
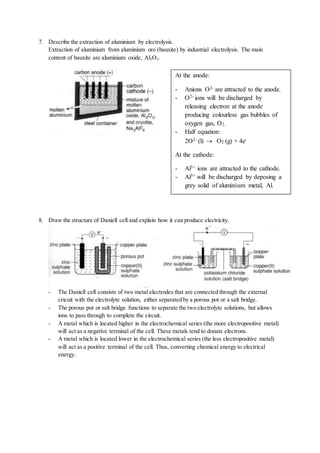
of the mass of an atom
of carbon-12.
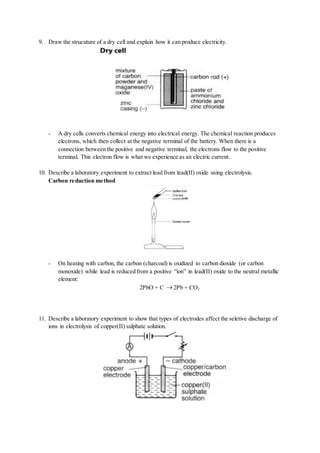
Relative Atomic Mass
(RAM) of an element
= The average mass of 1 atom of an element
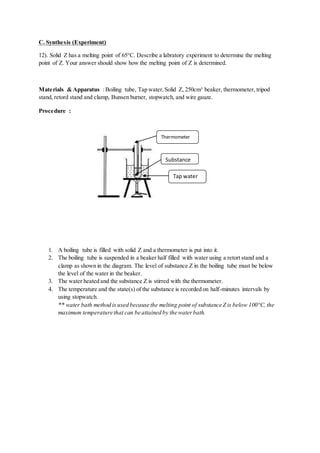
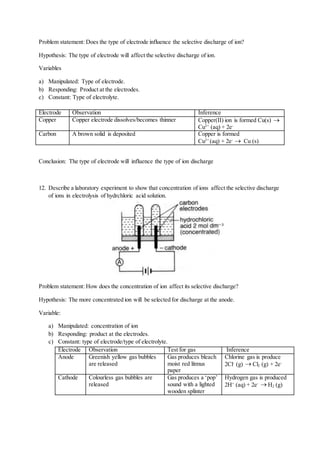
1
12
× the mass of one carbon− 12
2. Define mole.
- One mole is defined as the number of particles equal to that in exactly 12.00g of carbon-12
isotope.
3. State the meaning of molar mass
- Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance. (unit g mol−1)
4. State the meaning of molar volume of gas.
- Molar volume of gas means the volume occupied by 1 mole of any gas. (unit dm3 mol−1)
[ i.e. 22.4 dm3 mol−1 at STP or 24 dm3 mol−1 at room conditions ]
5. State the meaning of empirical formula
- The chemical formula that shows the simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in
the compound.
6. State the meaning of molecular formula
- The chemical formula that shows the actual number of atoms of each element in the
compound.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/form4chemistryproject-150120011331-conversion-gate01/85/Form-4-Chemistry-Project-Radioactive-9-320.jpg)
![B. Understanding / Application / Analysis
7. Explain why we could not determine the empirical formula of copper (ll) oxide by heating
copper powder in a crucible.
- Copper is less almost not a reactive metal
8. Compare and contrast empirical formula with molecular formula using ethane as an example.
Empirical formula Molecular formula
C2H6 C2H6
9. Vinegar is a dilute ethanoic acid with a molecular formula of CH3COOH.
(a) Find the empirical formula of ethanoic acid.
(b) Find the percentage composition by mass of carbon in ethanoic acid.
(a) CH2O
(b) 40 %
10. 3.6 g of carbon reacted with 0.8 g of hydrogen to form a compound.
(a) Determine the empirical formula of the compound formed.
(b) Given that the relative molecular mass of the compound is 88 g, find its molecular formula.
[Relative atomic mass : C, 12 ; H, 1 ]
(a)
(b)
Element Carbon , C Hydrogen , H
Mass (g) 3.6 0.8
Number of moles 0.3 0.8
Most simplest ratio 1 3
Empirical formula : CH3
n (CH3) = 88
n (12+ 3) = 88
15n = 88
n = 6
Molecular formula : C6H18
11. Hydrogen gas is reacted with 20 g of hot copper (ll) oxide powder to produce solid copper and
water.
(a) Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
(b) Calculate the maximum mass of solid copper formed.
[Relative atomic mass : Cu, 64 ; O, 16 ; H, 1]
(a) Hydrogen (g) + copper (ll) oxide (s) copper (s) + water (l)
(b) H2 + CuO CuO + H2O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/form4chemistryproject-150120011331-conversion-gate01/85/Form-4-Chemistry-Project-Radioactive-10-320.jpg)
![i. No. of moles of CuO
=
mass
RMM
=
20 g
80
= 0.25 mol
ii. 1 mol of CuO 1 mol of Cu
0.25 mol of CuO 0.25 mol of Cu
iii. Mass of solid copper
= mol × RAM
= 0.25 × 64
= 16 g
C. Synthesis (Experiment)
12. Describe a laboratory experiment to determine the empirical formula of magnesium oxide. Your
answer should include all the precautions and calculations involved.
[Relative atomic mass : Mg, 24; O, 16 ]
Material : Magnesium ribbon, sandpaper
Apparatus : Crucible with lid, Bunsen burner, pipe-clay triangle, chemical balance, tripod stand.
Procedure :
1. A crucible and its lid are weighed.
2. A 10cm length of magnesium ribbon is cleaned with sandpaper to remove the oxide layer on
its surface.
3. The ribbon is coiled loosely and placed in the crucible. The crucible with its lid and content
are weighed.
4. The apparatus is set up as shown in the diagram.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/form4chemistryproject-150120011331-conversion-gate01/85/Form-4-Chemistry-Project-Radioactive-11-320.jpg)
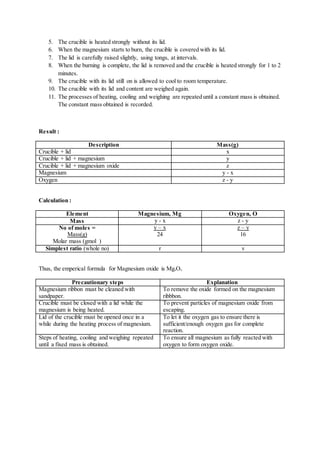
![Discussion :
1. Magnesium reacts with oxygen in the air to form white fumes, magnesium oxide.
Magnesium + Oxygen magnesium oxide
Conclusion :
The emperical formulae of magnesium oxide is MgO.
C. Synthesis (Experiment)
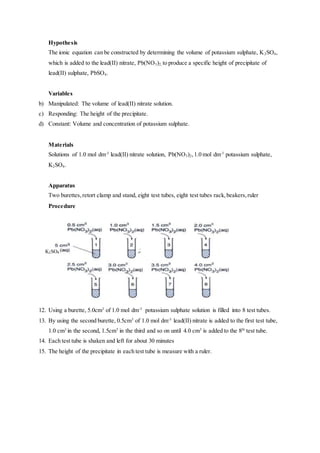
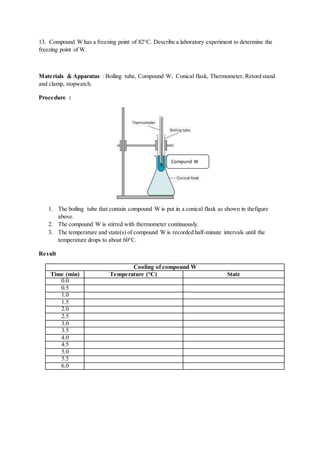
13. Describe a laboratory experiment to determine the emperical formula of copper(ll) oxide.Your
answer should include all the precautions and calculations involved.
[Relative atomic mass: Cu, 64; O, 16]
Material : Copper oxide powder, zinc pieces, dilute hydrochloric acid, anhydrous calcium chloride.
Apparatus : Round bottomed flask, combustion tube with small opening at its end, stopper with
delivery tube, chemical balance, retort stand with clamp, thistle funnel,U-tube.
Procedure :
1. Combustion tube mass with the porcelain dish in it is weighed.
2. A spatula full of copper(ll) oxide is added to the porcelain dish. The tube is weighed again.
3. The apparatus is set up as shown in the diagram.
4. Hydrogen gas is allowed to flow into the set of apparatus for 5 to 10 minutes to remove all the
air in the tube.
5. To determine whether all the air has been removed from the tube, the gas that has comes out
from the small hole is collected in the a test tube. Then ,the gas is tested with a lighted](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/form4chemistryproject-150120011331-conversion-gate01/85/Form-4-Chemistry-Project-Radioactive-13-320.jpg)

![Chapter 4 : Periodic Table ofElements.
A. Knowledge (Definition, meaning and facts)
1. State the basic principle of arranging the elements in the periodic table from its proton number.
The elements are arranged according to the ascending proton numbers of the
electrons.
2. State the physical properties of Group 1.
good conductor of heat & electricity.
soft & cut easily with knife.
are grey in colour (silvery & shiny surfaces)
low melting/boiling points
low densities, float on water.
3. State the physical properties of Group 17.
non-metal, non-conductors of heat & electricity.
the colour becomes darker when going down the group.
low boiling points.
4. State the changes in the atomic size and electronegativity of elements across the Period 3.
Atomic size decreases across Period 3.
Electronegativity increases across Period 3.
5. State three special properties of transition elements?
a) Form coloured compounds :
Fe2+
(green solution)
Fe3+
(brown solution)
Ni2+
(green solution)
Mn2+
(pink solution)
Cu2+
(blue solution)
b) Shows different oxidation number in their compounds.
Iron(II) chloride, FeCl2
Iron(III) chloride, FeCl3
Copper(I) oxide, Cu2O
Copper(II) oxide, CuO
c) Are useful catalysts
fine iron powder – haber process(ammonia)
platinum, Pt – Ostwald process(nitric acid)
nickel, Ni – manufacture margarine
vanadium (V) oxide, V2O5 – contact process (sulphuric acid)
d) Form complex ions
hexamine chromium (III) ion [Cr(NH3)6]3+
hexacyanoferrate(II) ion [Fe(CN)6]4-
hexacyanoferrate(III) ion [Fe(CN)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/form4chemistryproject-150120011331-conversion-gate01/85/Form-4-Chemistry-Project-Radioactive-15-320.jpg)



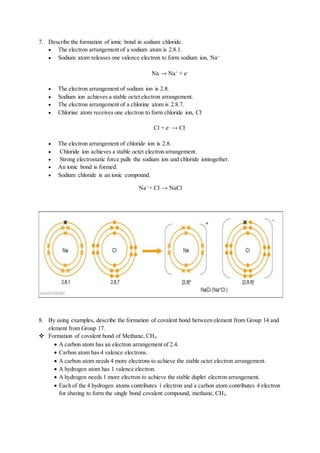
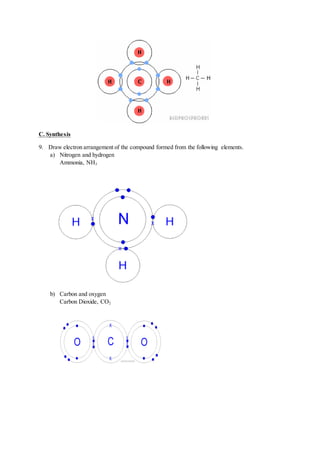
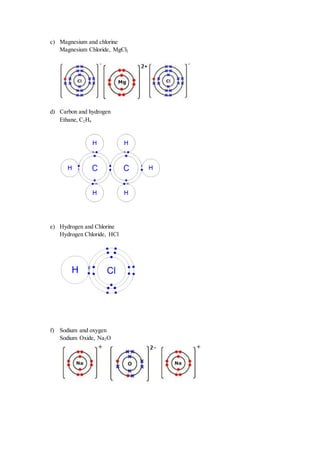
![Chapter 5: Chemical Bonds
A.Knowledge [Definition, Meaning and Facts]
1. What is anion?
- Anion is a negatively charged ion that would be attracted to anode in electrolysis.
- Anion is formed when an atom receives electron.
- Anion are attracted to cation by strong electrostatic force of attraction in ionic bond.
2. What is cation?
- Cation is a postively charged ion that would be attracted to cathode in electrolysis.
- Cation is formed when an atom releases electron.
- Cation are attracted to anion by strong electrostatic force of attraction in ionic bond.
-
3. State two physical properties of ionic compound :
- High melting or boiling point
- Conducts electricity in liquid and in aqueous solution.
4. State two physical properties of covalent compound:
- Low melting or boiling point
- Does not conduct electricity in any state
B. Understanding, Aplication, Analysis
5. Exlain why Sodium Chloride can conduct electricity in aqueous state but cannot conduct
electricity in solid state.
- In aqueous state, sodium chloride dissolvesin water and dissociates to produce Na
and Cl
ions.
These ions can move freely in the solution and conducts electricity.
- In solid state,sodium chloride’s ion are bond together tightly and cannot move freely to conduct
electricity
6. Magnesium chloride and hydrogen chloride are two compunds of chlorine. At room temperature,
magnesium chloride existed as solid but hydrogen chloride exist as a gas. Explain why.
Magnesium Chloride Hydrogen Chloride (HCl)
- Ionic bond are formed between Mg 2
and
Cl
ions.
(ionic compound)
- Magnesium is a metal and chlorine is non
metal.
- Has high melting and boiling point.
- Hydrogen and chlorine atoms share
electrons through covalent bonding.
(Covalent compound)
- Both elements are non metals
- Has low melting and boiling point.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/form4chemistryproject-150120011331-conversion-gate01/85/Form-4-Chemistry-Project-Radioactive-19-320.jpg)


![Conclusion:
a. In a concentrated electrolyte solution, ions that are more concentrated,that is chloride ions, are
selected for discharge at the anode to form chlorine gas.
b. At the cathode, ions that are lower in the electrochemical series are selected for discharge to form
hydrogen gas.
13. You are given magnesium ribbon, copper plate, magnesium nitrate solution, copper(II) sulphate
solution, connecting wires with crocodile clips, 250cm3
beaker, voltmeter and porous pot.
Construct a voltaic cell by using the above materials. Explain how the voltaic cell can produce
electricity. Your answer must include observations and half equations for reaction at anode and
cathode.
- A porous pot has fine pores that allowions to flow through but can prevent the two different
aqueous solutions from mixing.
- As magnesium is more reactive than copper, magnesium becomes the negative terminal. It
release 2 electrons to come Mg2+
ions.
Anode[Oxidation]:
Mg Mg2+
+ 2e-
-
At the positive terminal, Cu2+
ions in the copper(II) sulphate solution accept 2 electrons to
form copper.
Cathode[Reduction]:
Cu2+
+ 2e- Cu
Overall equation:
Mg + Cu2+ Mg2+
+ Cu
14. Describe a laboratory experiment to construct the electrochemical series of magnesium, copper,
zinc and lead based on the potential difference in a voltaic cell.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/form4chemistryproject-150120011331-conversion-gate01/85/Form-4-Chemistry-Project-Radioactive-29-320.jpg)






![Chapter 8 : Salts
A. Knowledge [Definition, meaning and facts]
1. What is salt?
A salt is a compound formed from the replacement of hydrogen ions, H+
, in an acid by a metal ion or
ammonium ion, NH4
+
.
2. What is double decomposition reaction?
3. A double decompostion reaction is a reaction involving ion exchange to produce insoluble salts
(precipitate).
4. State one uses of salts in agriculture, medical field and food preparation.
Salts Uses
Food
11. Table salt, (NaCl) Monosodium glutamate,
C5H8NO4Na
12. Sodium benzoate, (NaC7H5O2) & sodium
nitrite, NaNO2
Food flavouring
Food preservatives
Medicine
Calcium sulphate sesquihydrate,
2CaSO4.H2O
Milk of Magnesia (magnesium hyrdroxide),
Mg(OH)2
Barium sulpate, BaSO4
Plaster of Paris
Antacid
Barium meal for patients
Agriculture
Ammonium sulphate, (NH4)2SO4
Ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3
Ammonium phosphate, (NH4)3PO4
Fertilisers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/form4chemistryproject-150120011331-conversion-gate01/85/Form-4-Chemistry-Project-Radioactive-36-320.jpg)