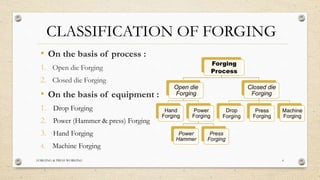
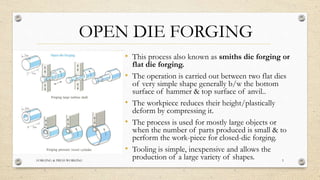
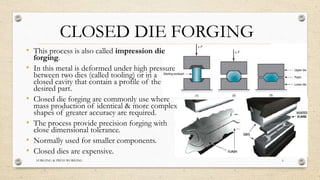
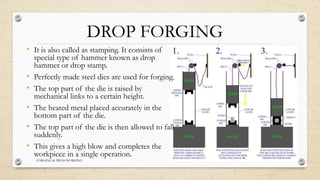
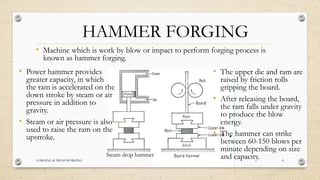
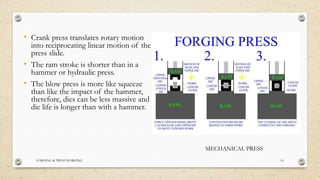
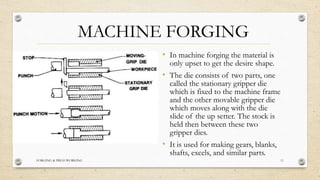
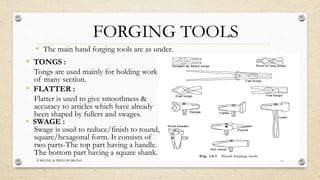
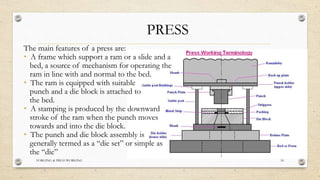
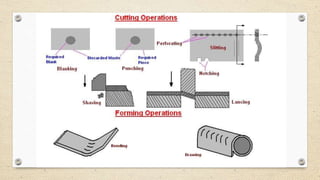
This document provides an overview of forging and press working processes. It defines forging as plastically deforming metal under compressive force at elevated temperatures using tools like hammers or presses. Forging is classified as open die or closed die based on the tools used, and as hammer, press, drop or machine forging based on the equipment. Press working involves shaping sheet metal between dies in a press machine. Common press working operations include cutting via blanking, punching and forming through bending and drawing.