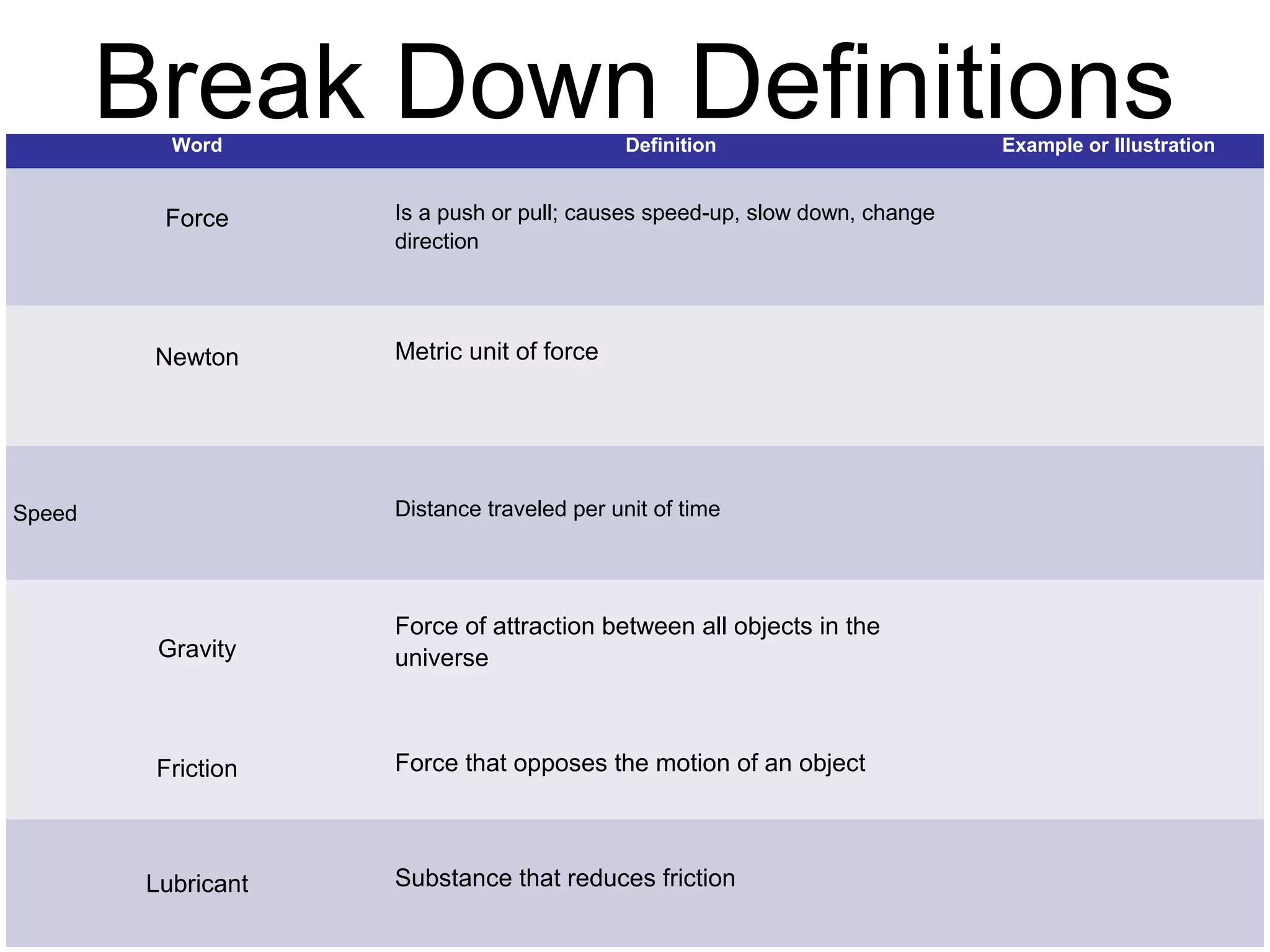
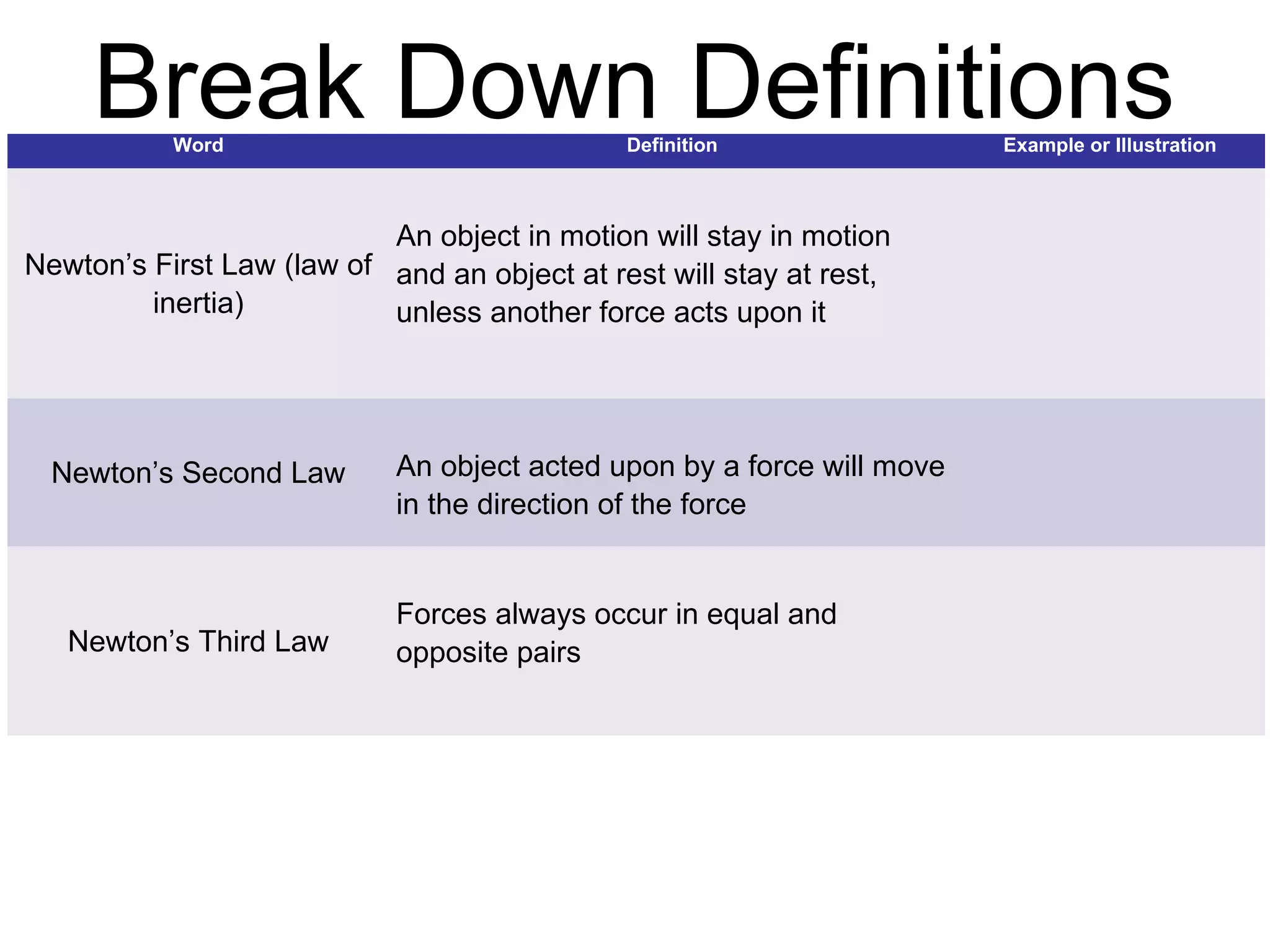
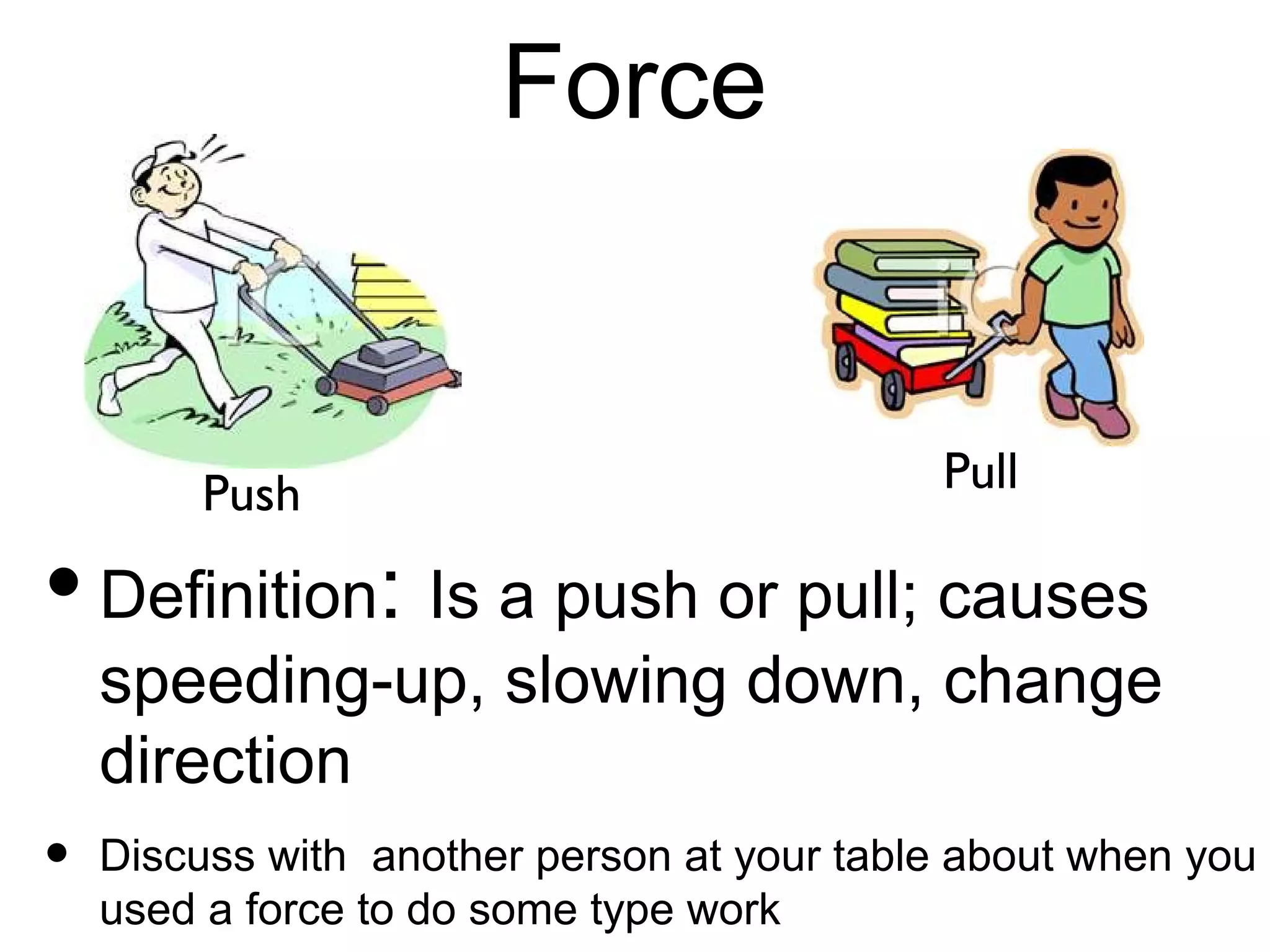
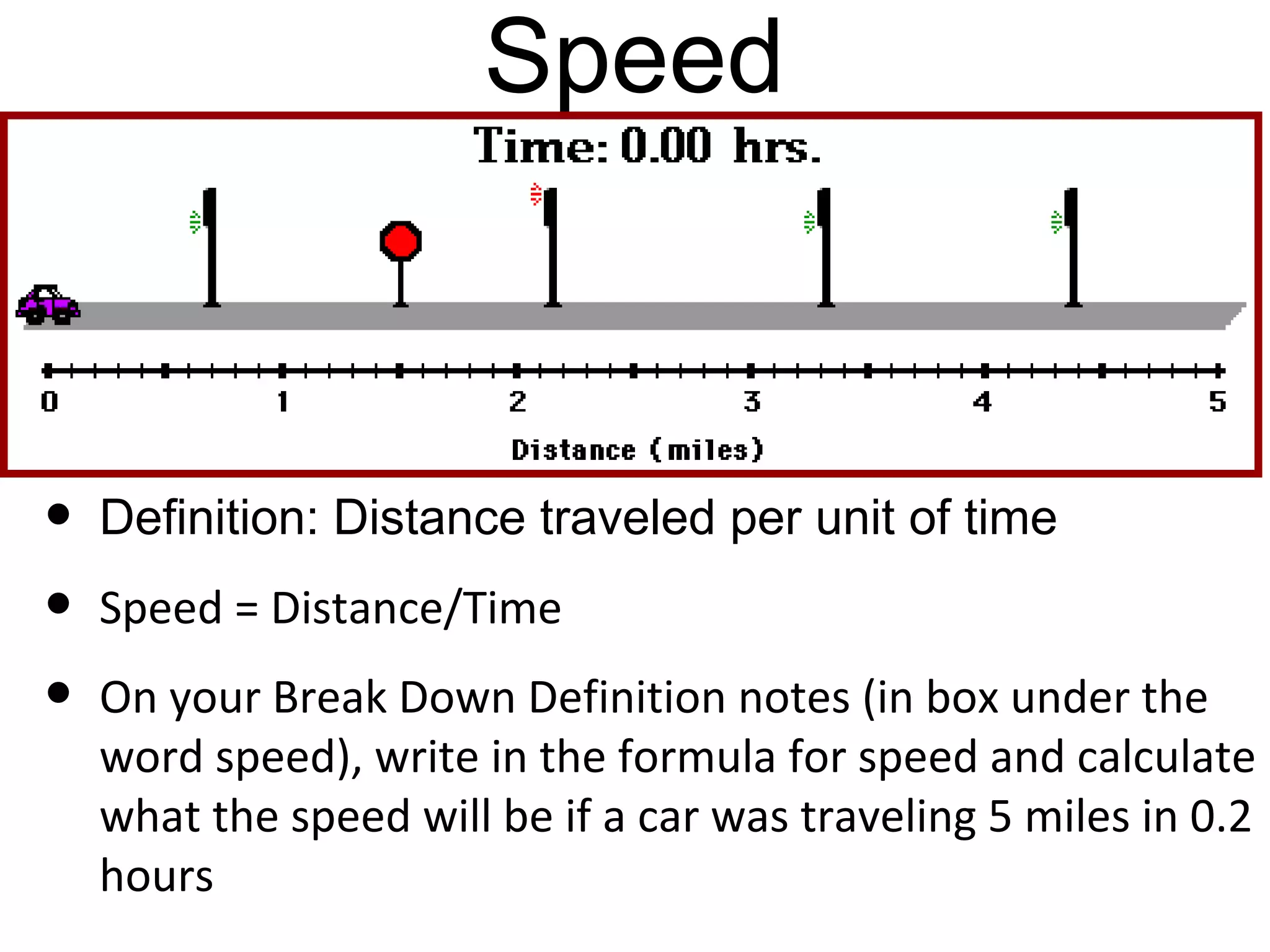
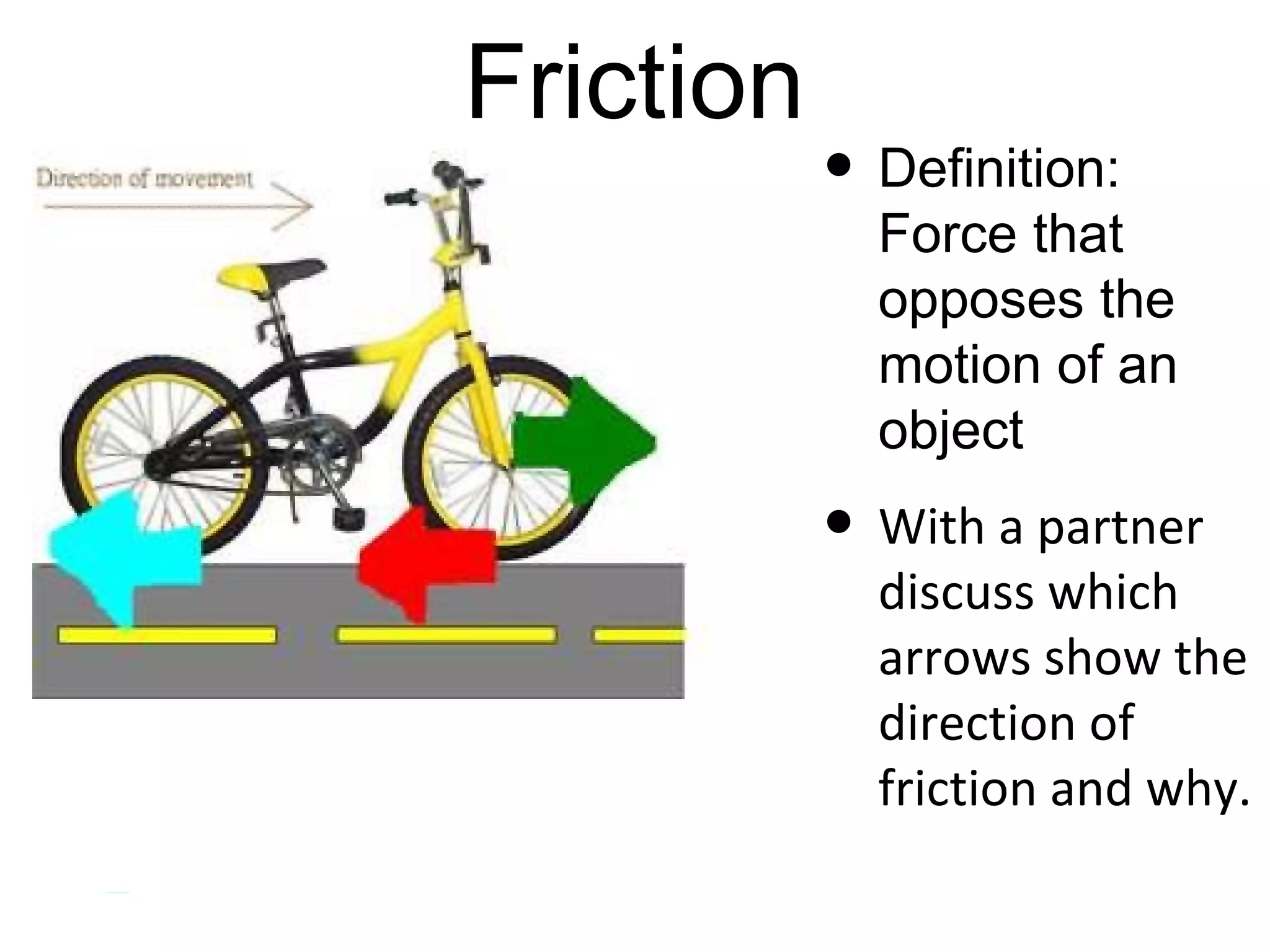
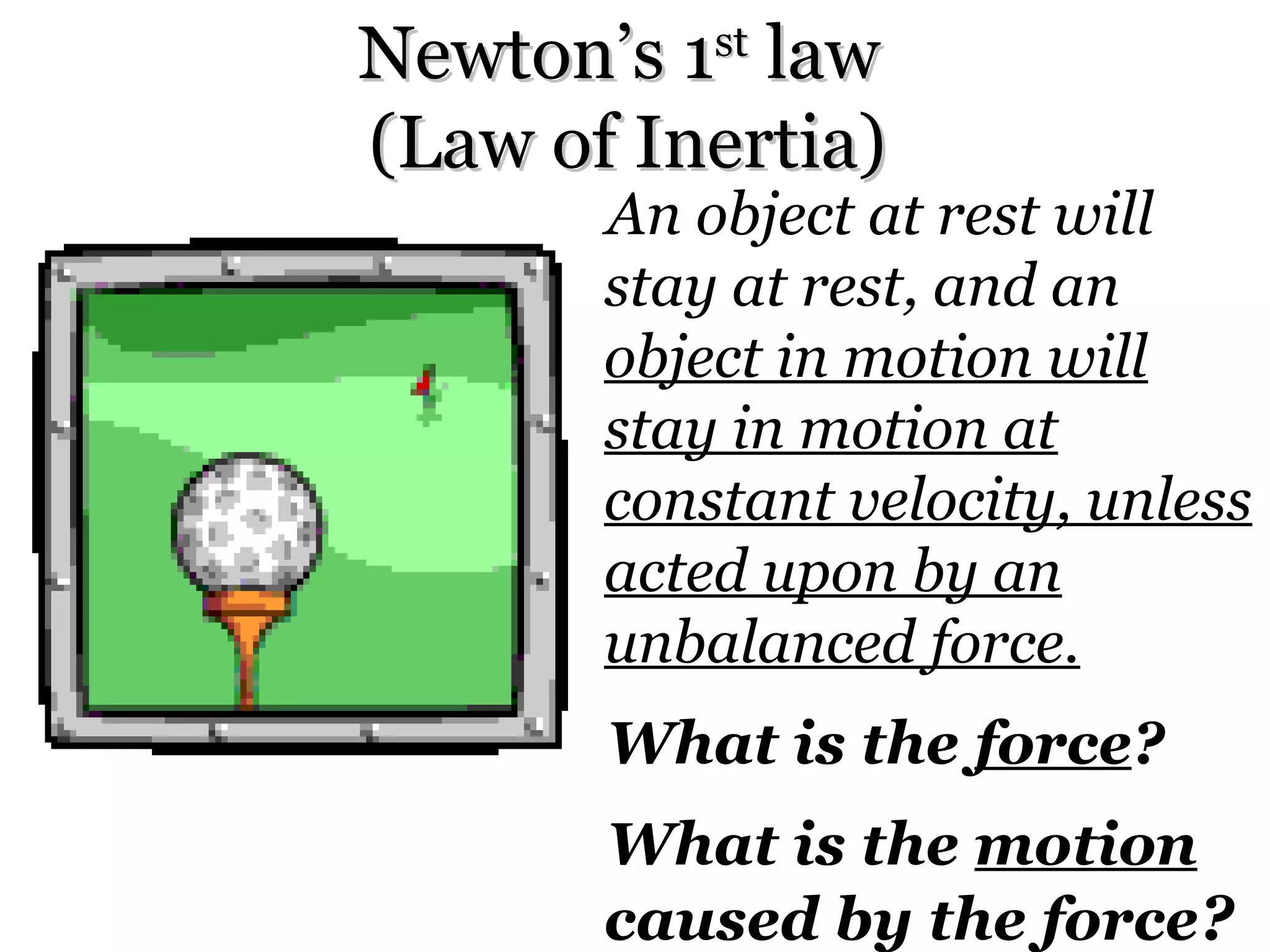
The document discusses force and motion through examples and explanations of key concepts like Newton's laws. It explains Newton's first law of inertia through an example of a pencil sitting still on a table. It also demonstrates Newton's third law of equal and opposite reaction through an example of hitting a balloon, feeling a push back from the balloon. The document uses examples, diagrams, and questions to help teach students about important force and motion concepts.