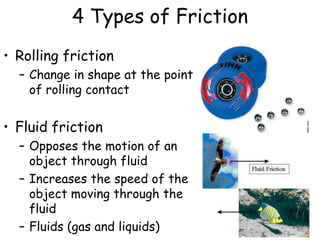
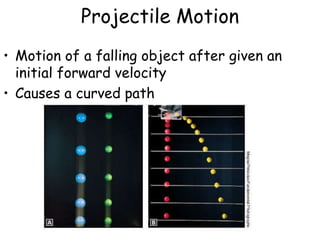
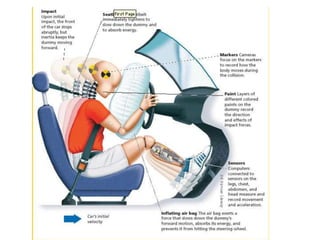
1. Forces can cause objects to move, change speed, or change direction. They are measured in Newtons and represented by arrows.
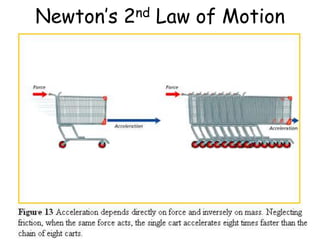
2. Newton's Second Law states that acceleration is produced when a net force acts on an object, and is directly proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the object's mass.
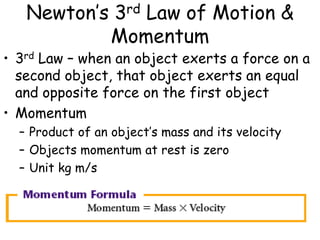
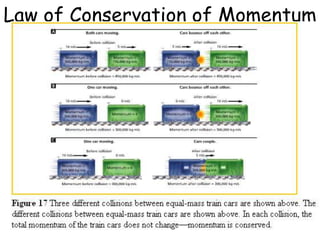
3. Newton's Third Law states that for every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force. The total momentum of a system remains constant if no external forces act on it.