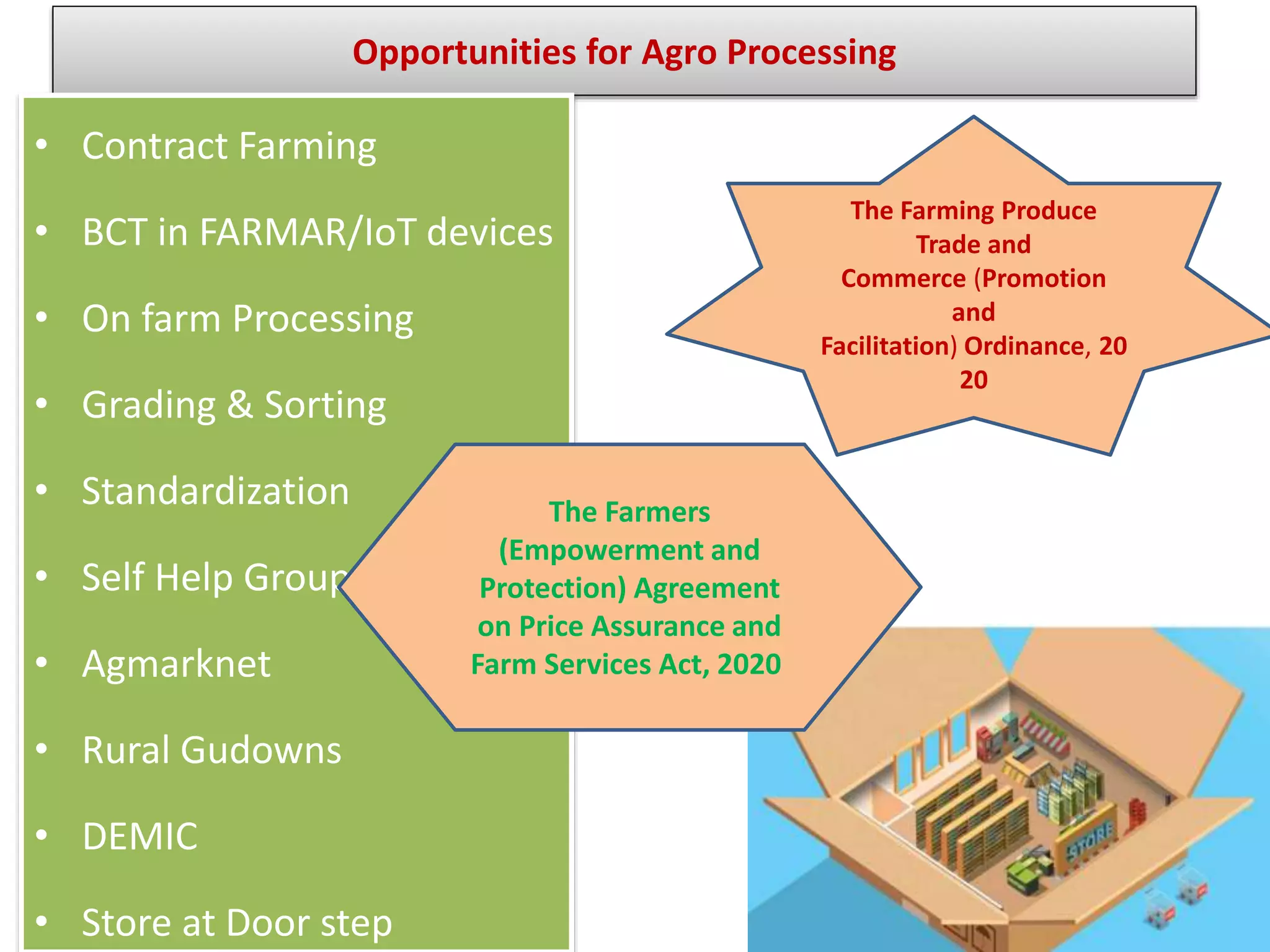
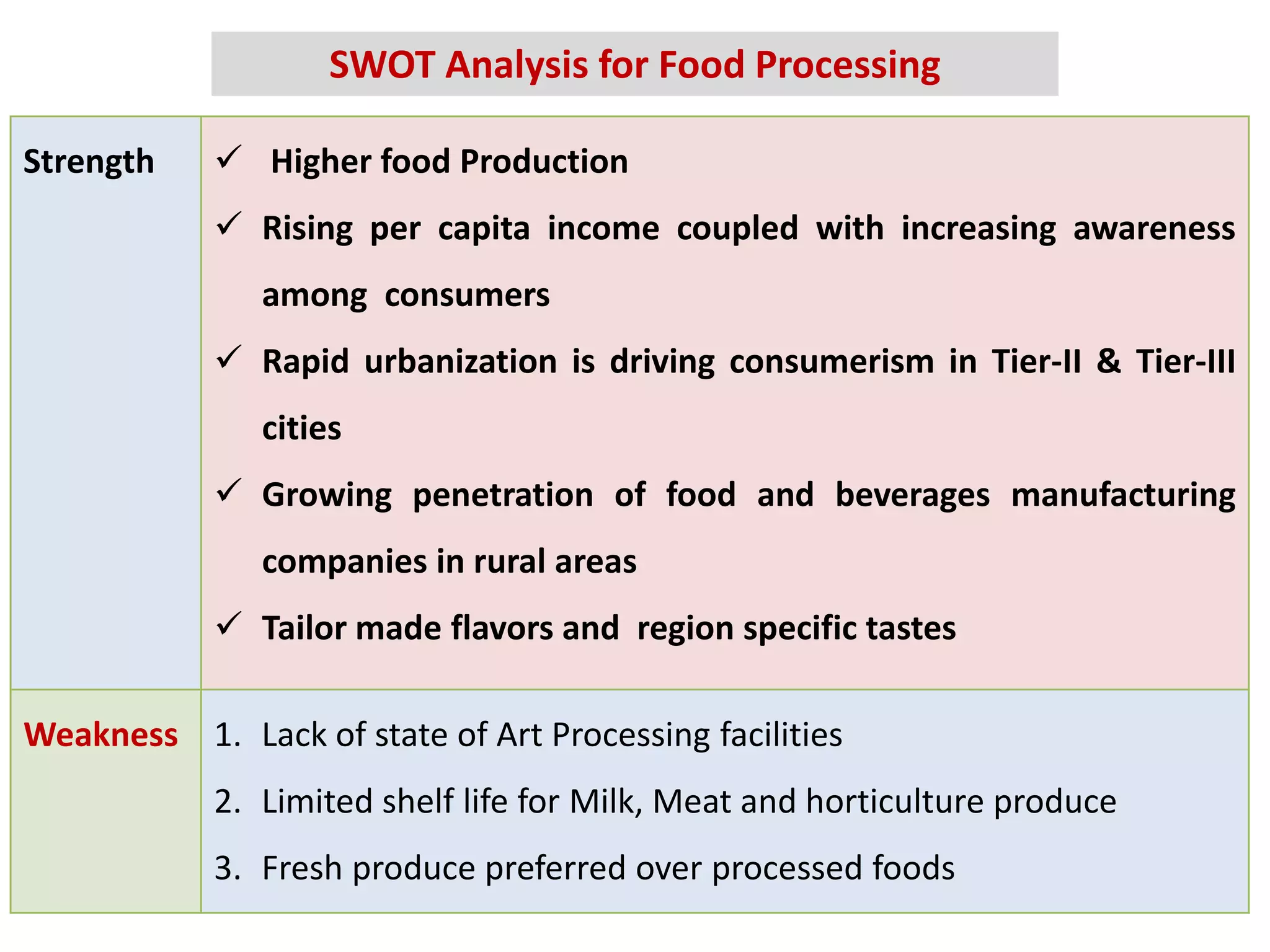
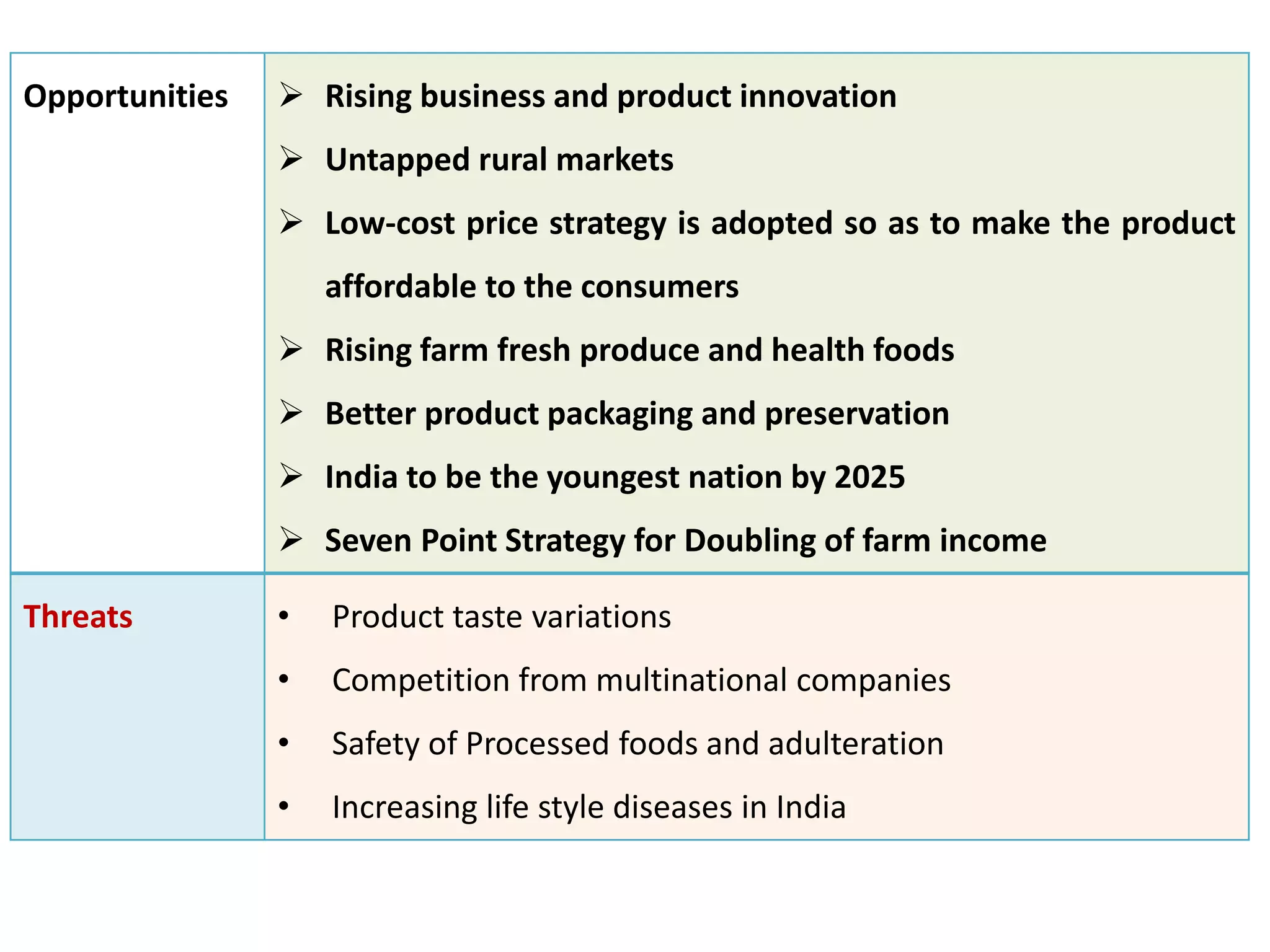
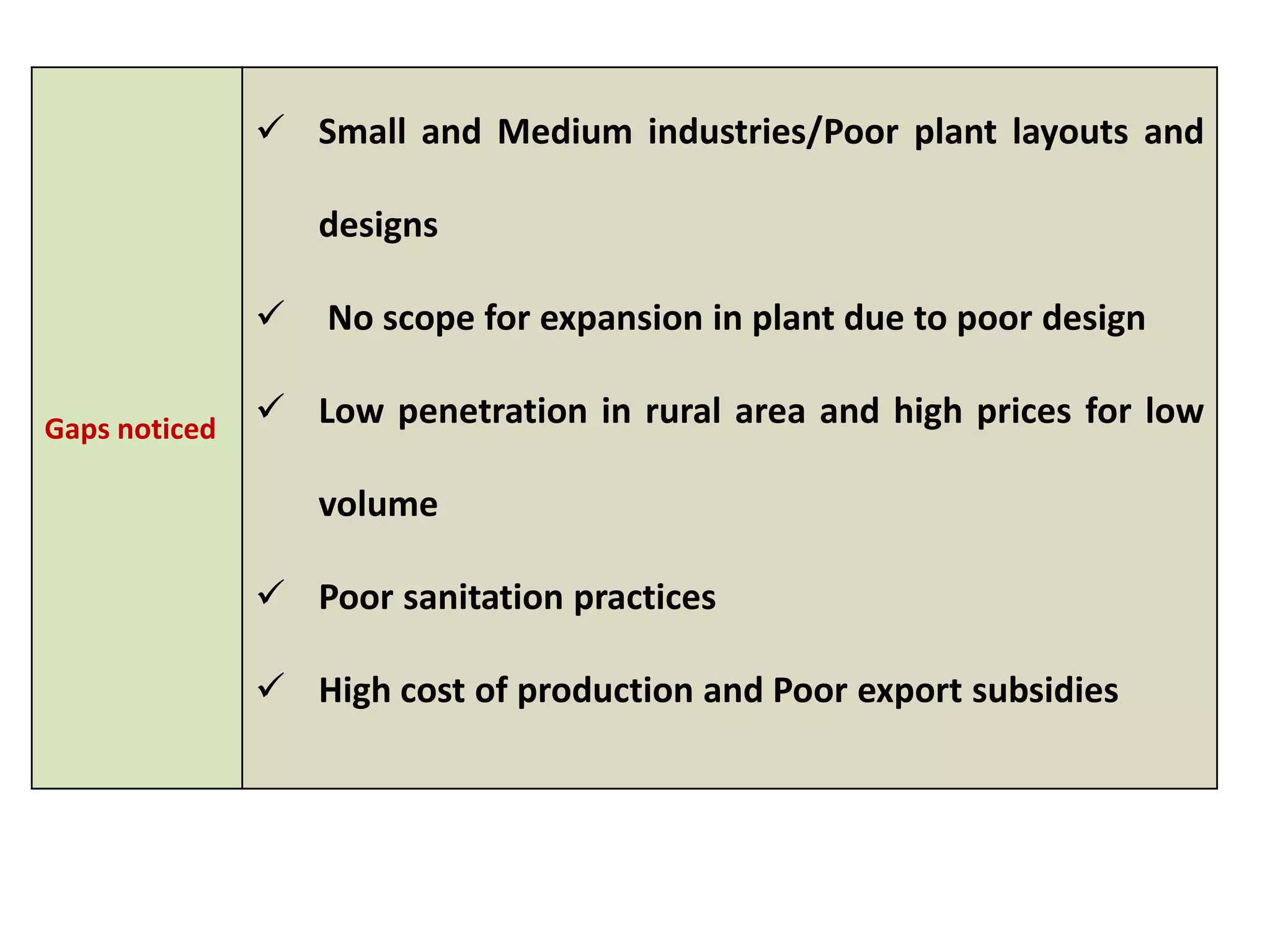
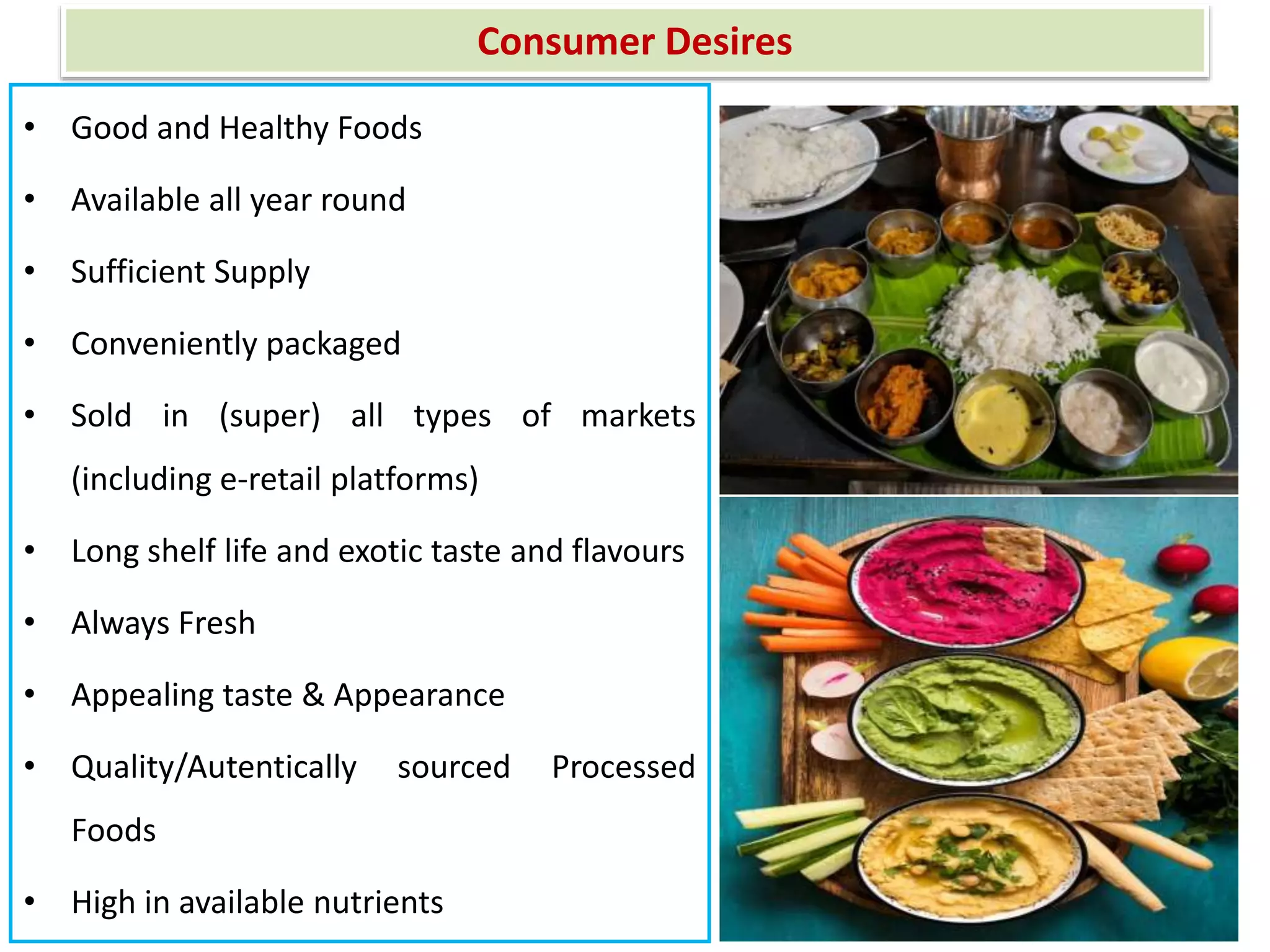
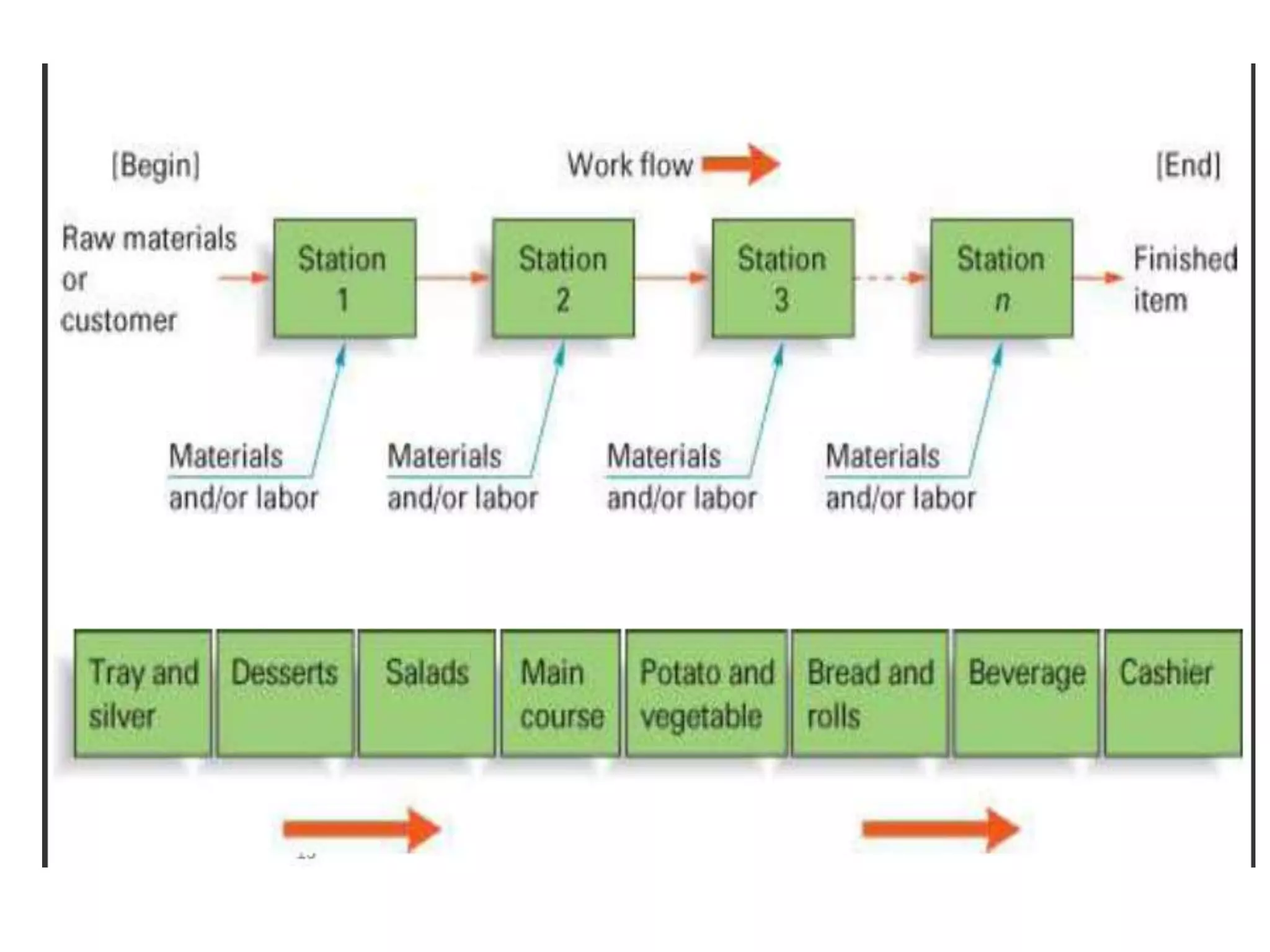
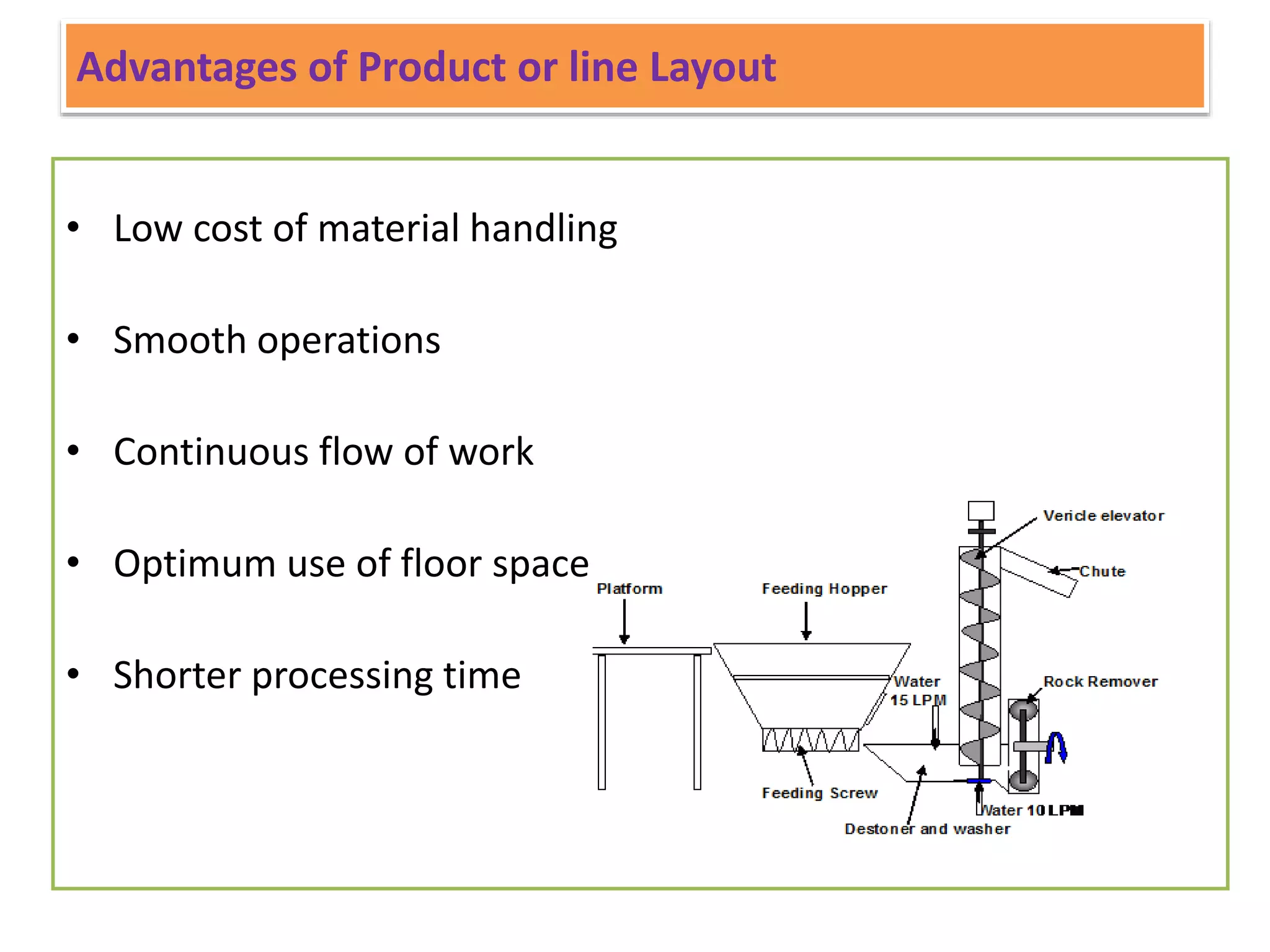
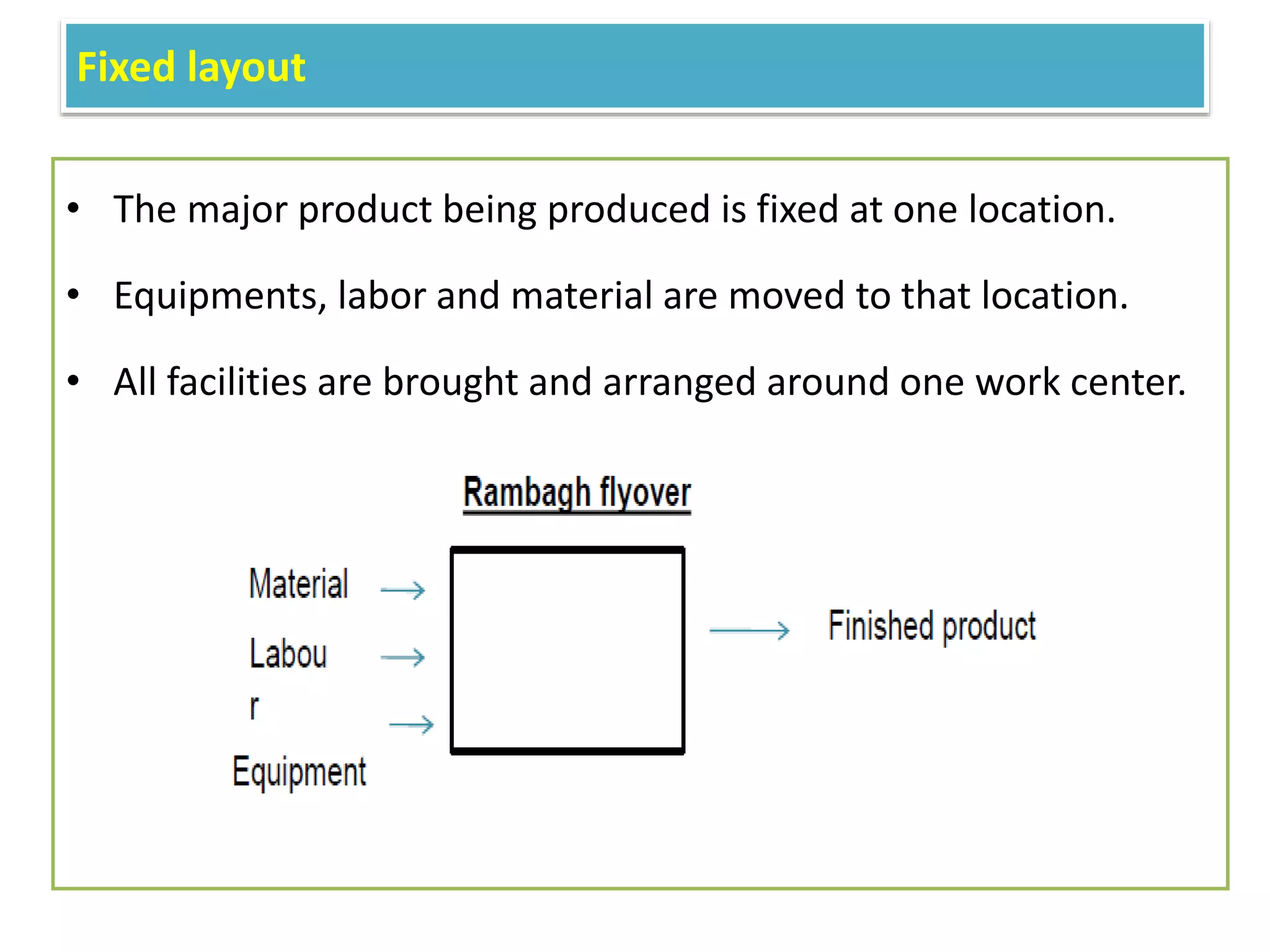
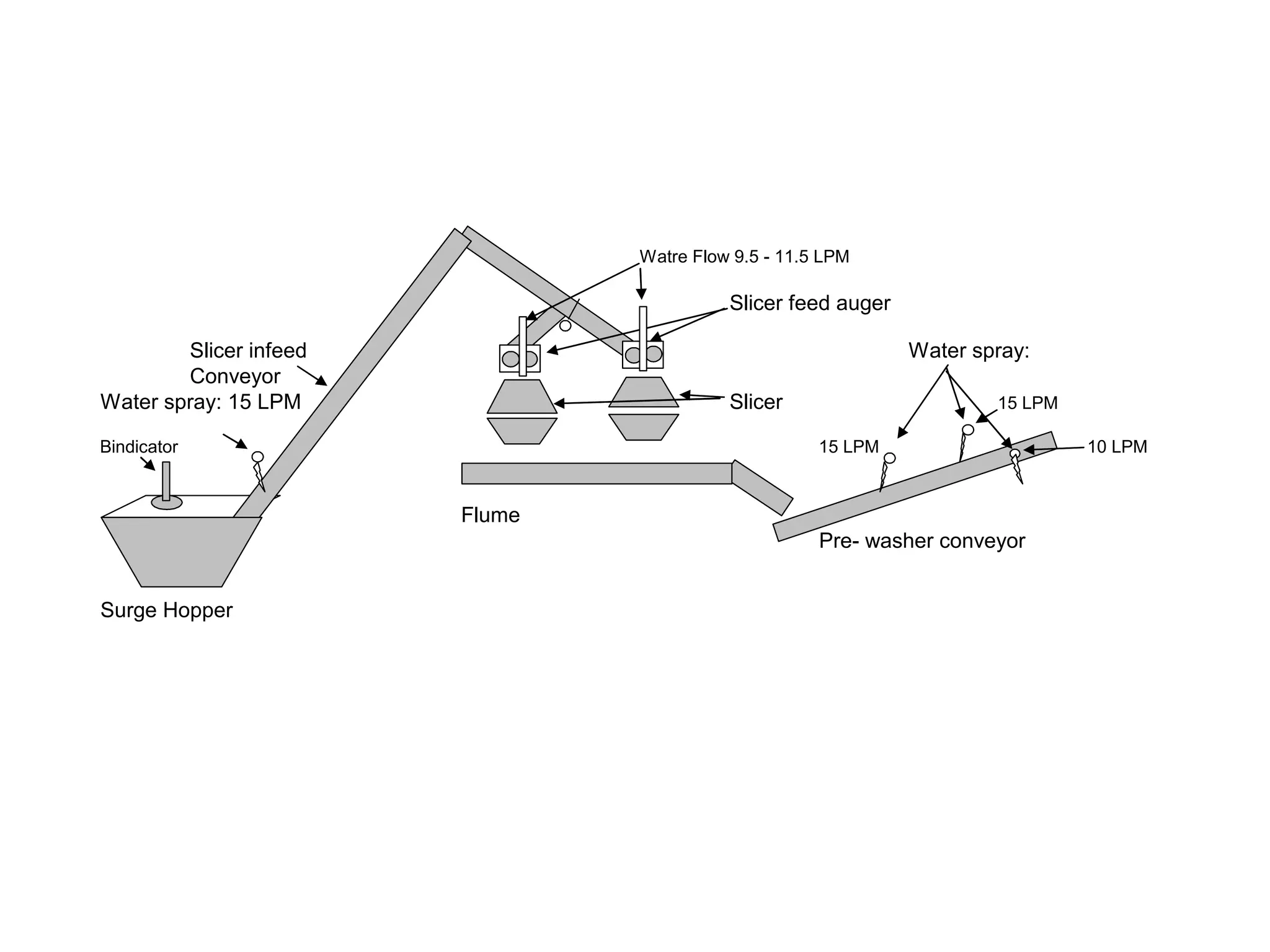
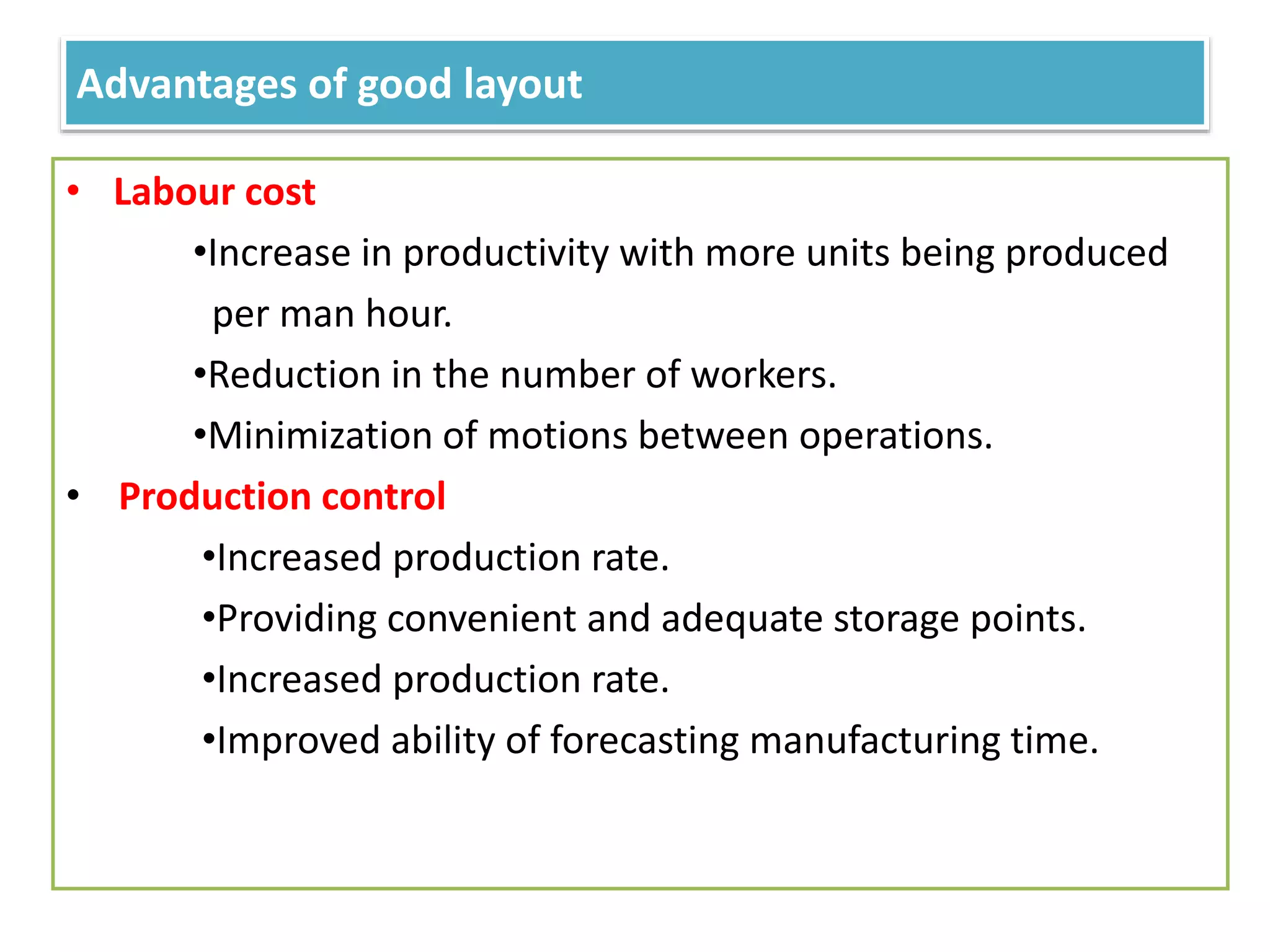
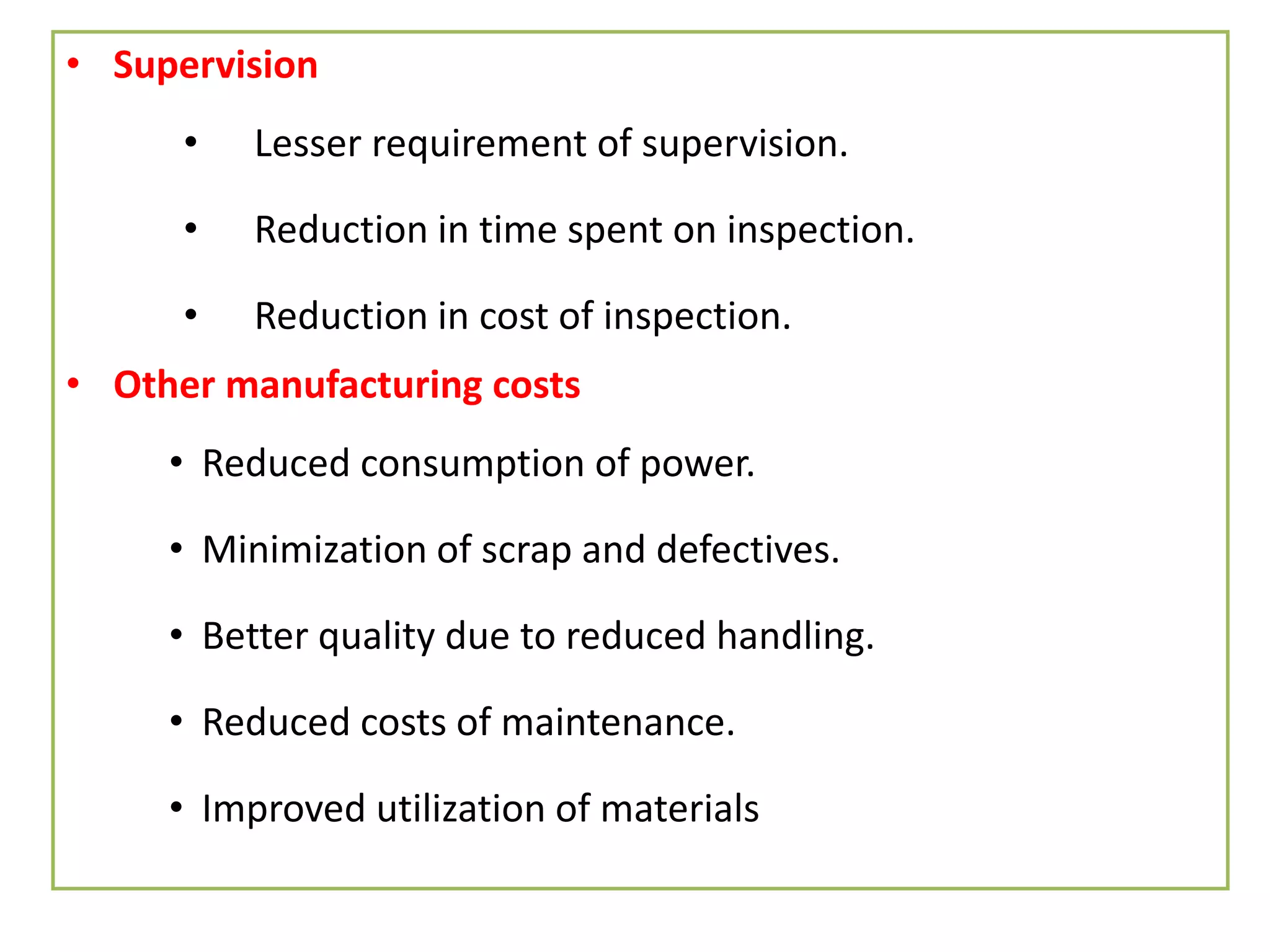
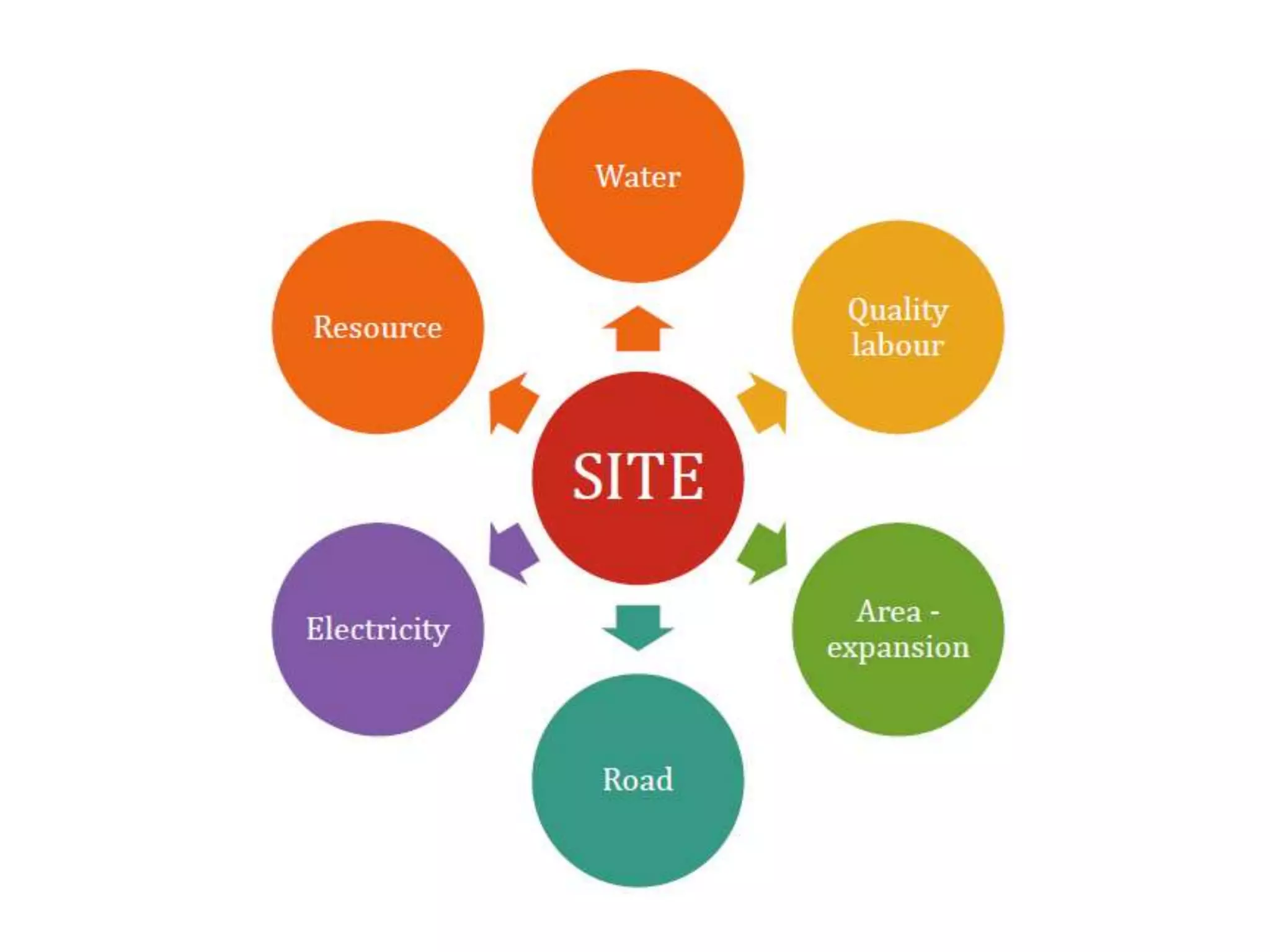
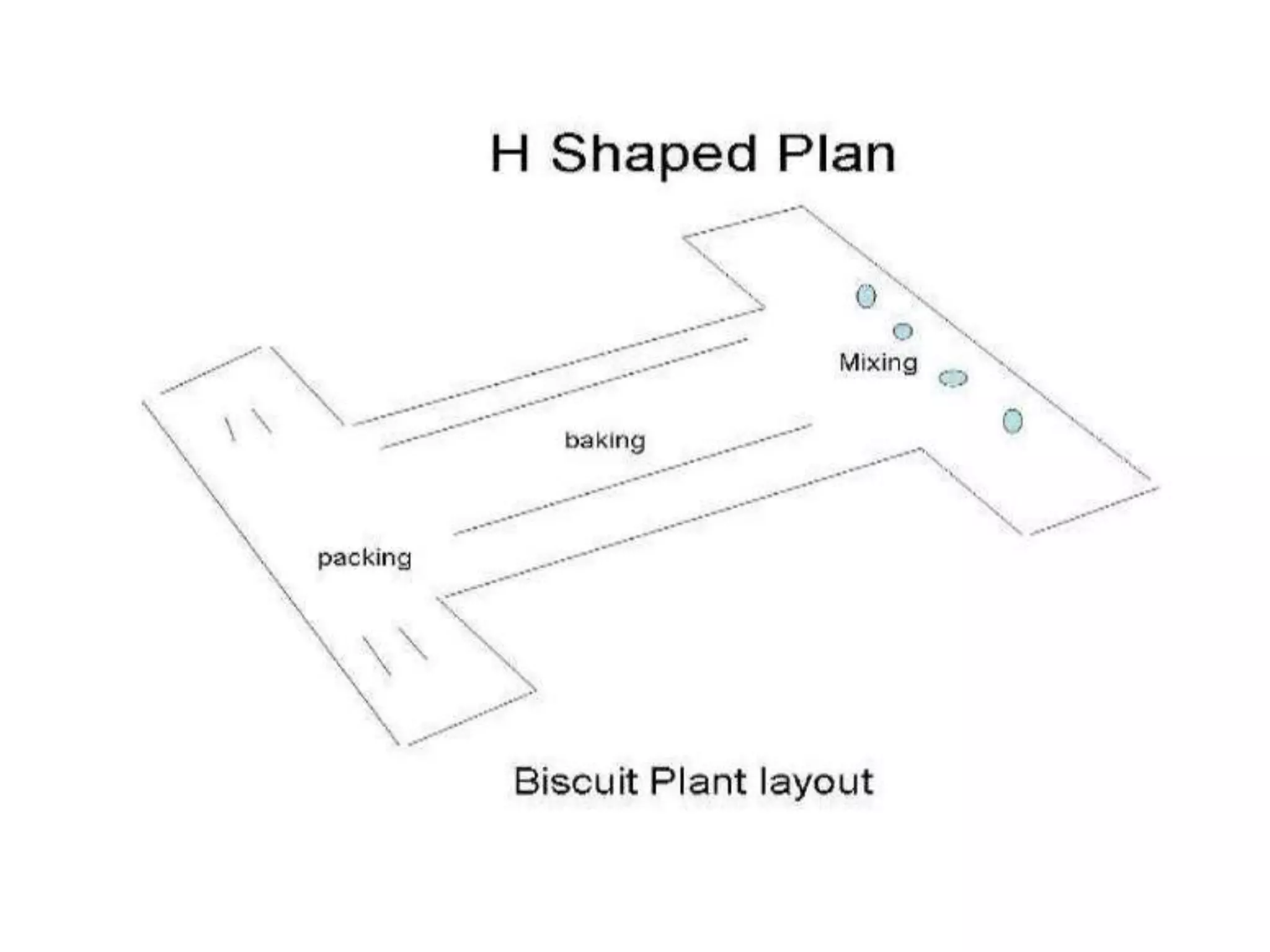
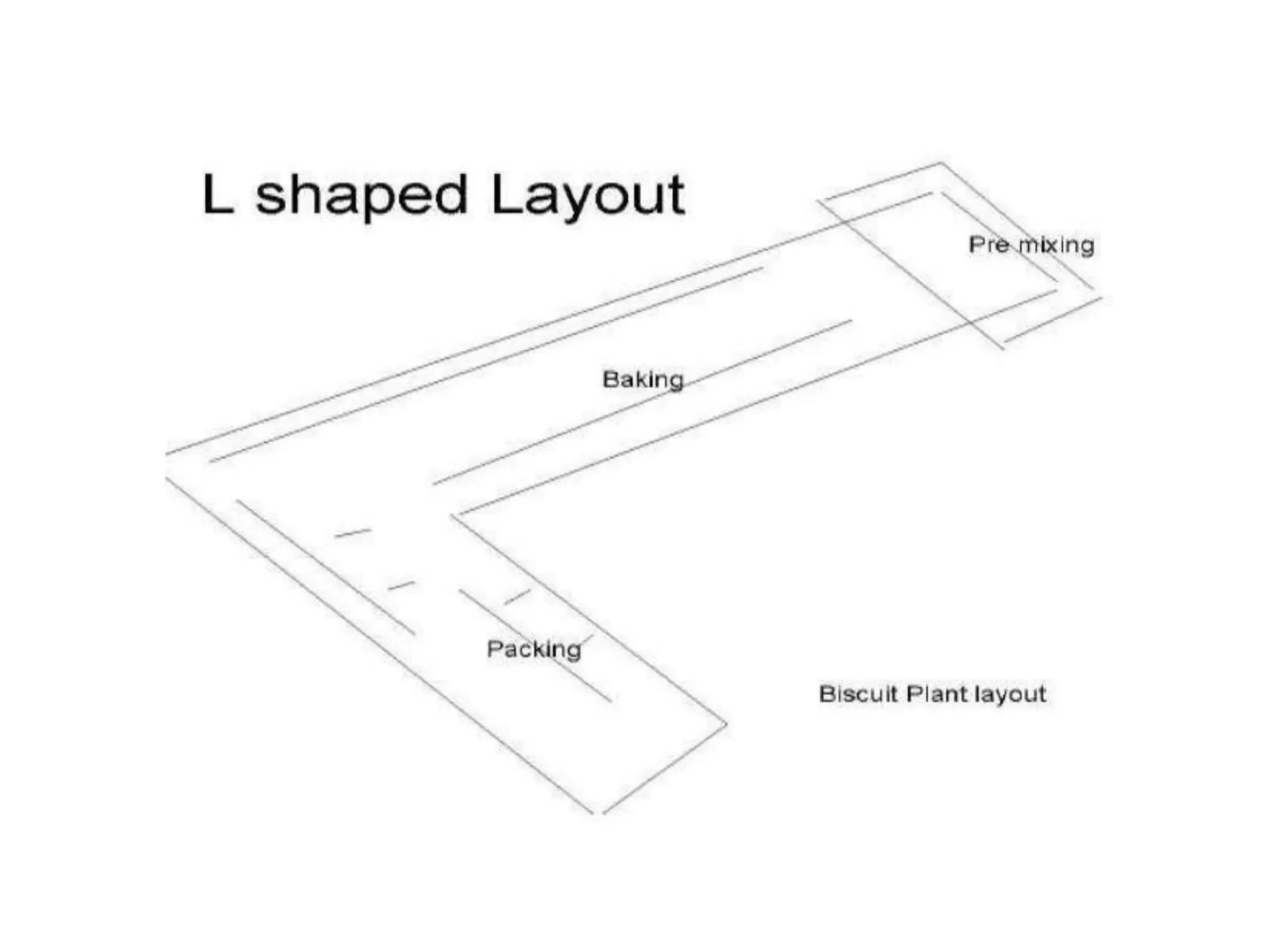
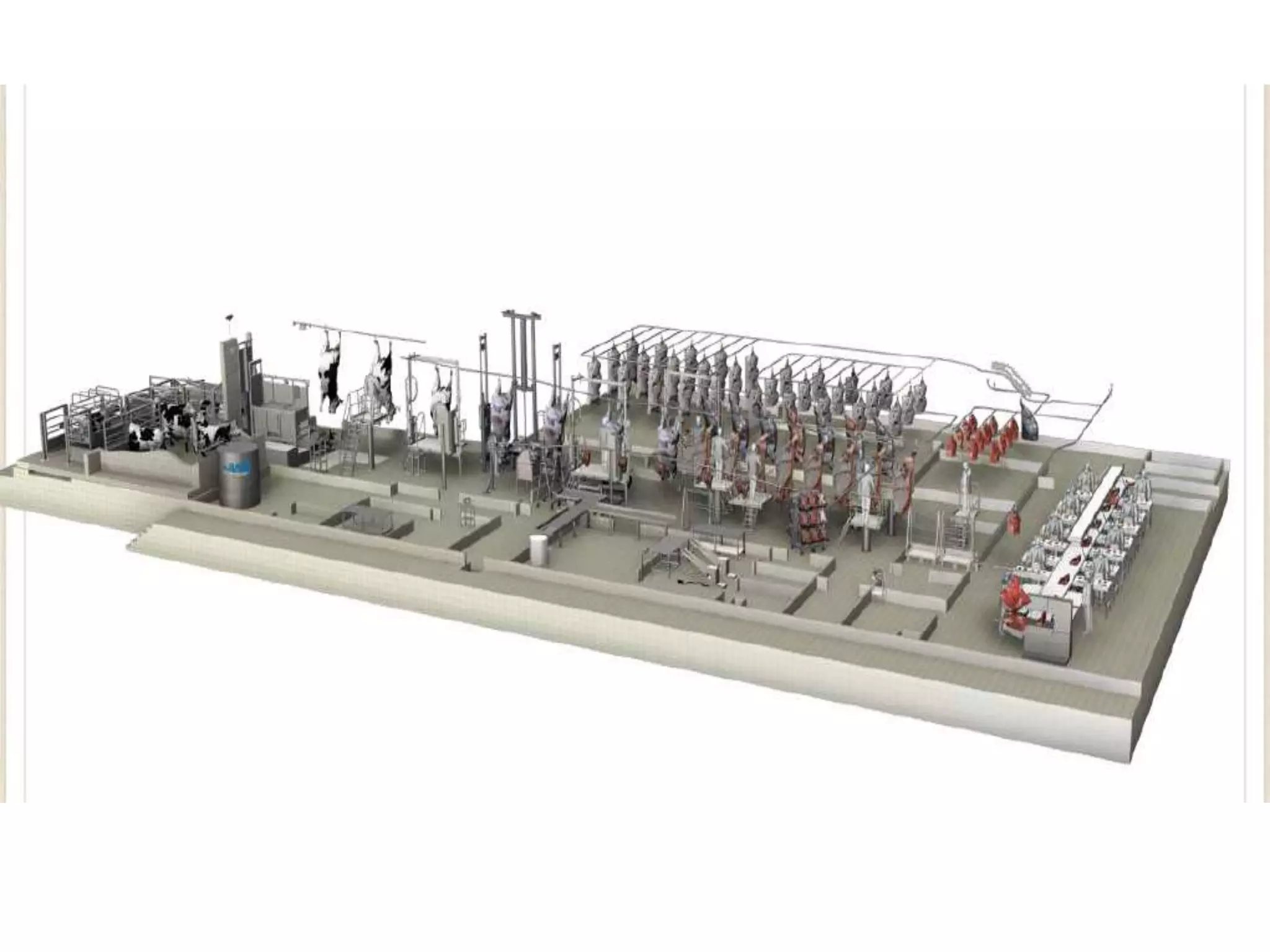
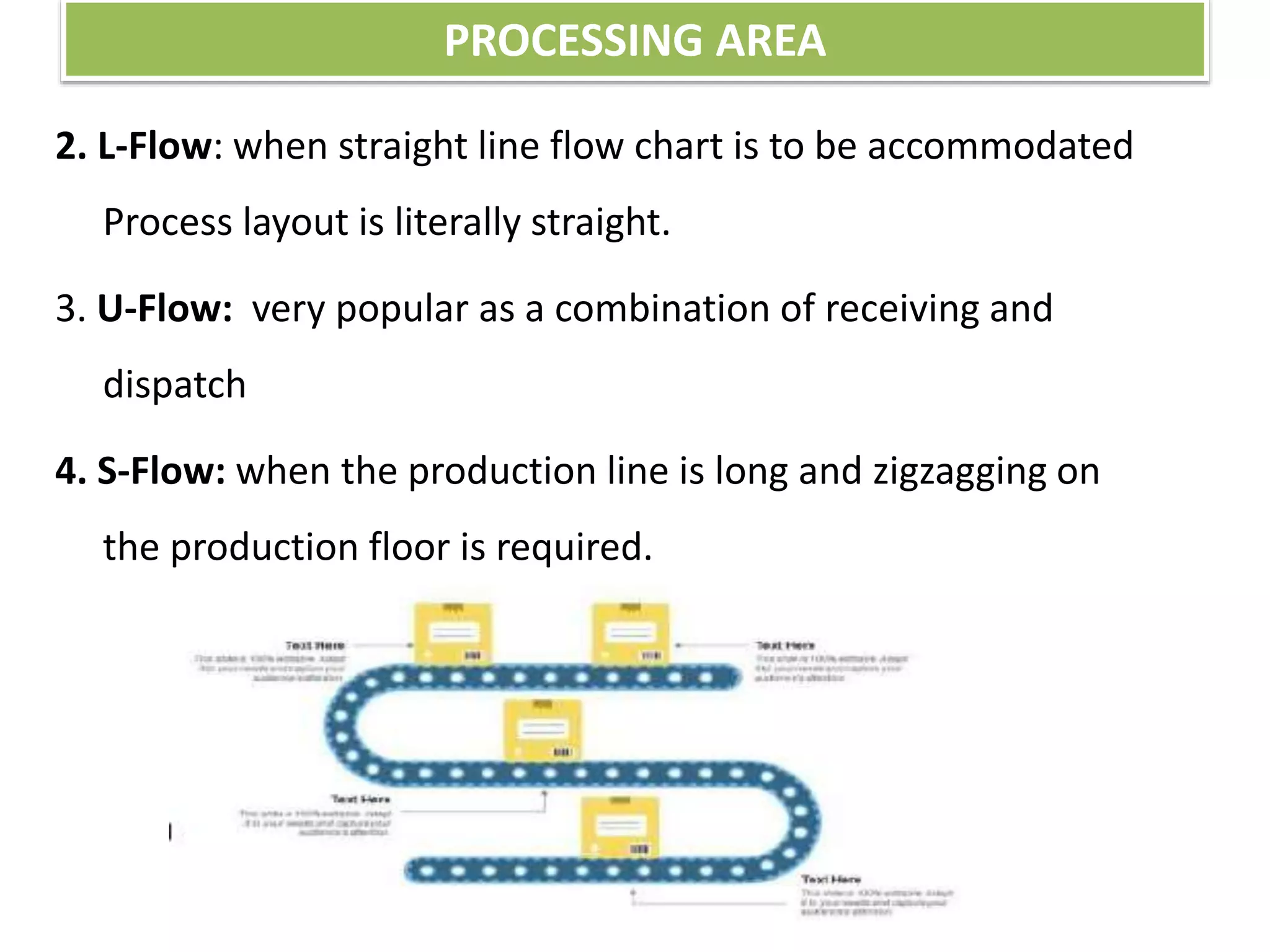
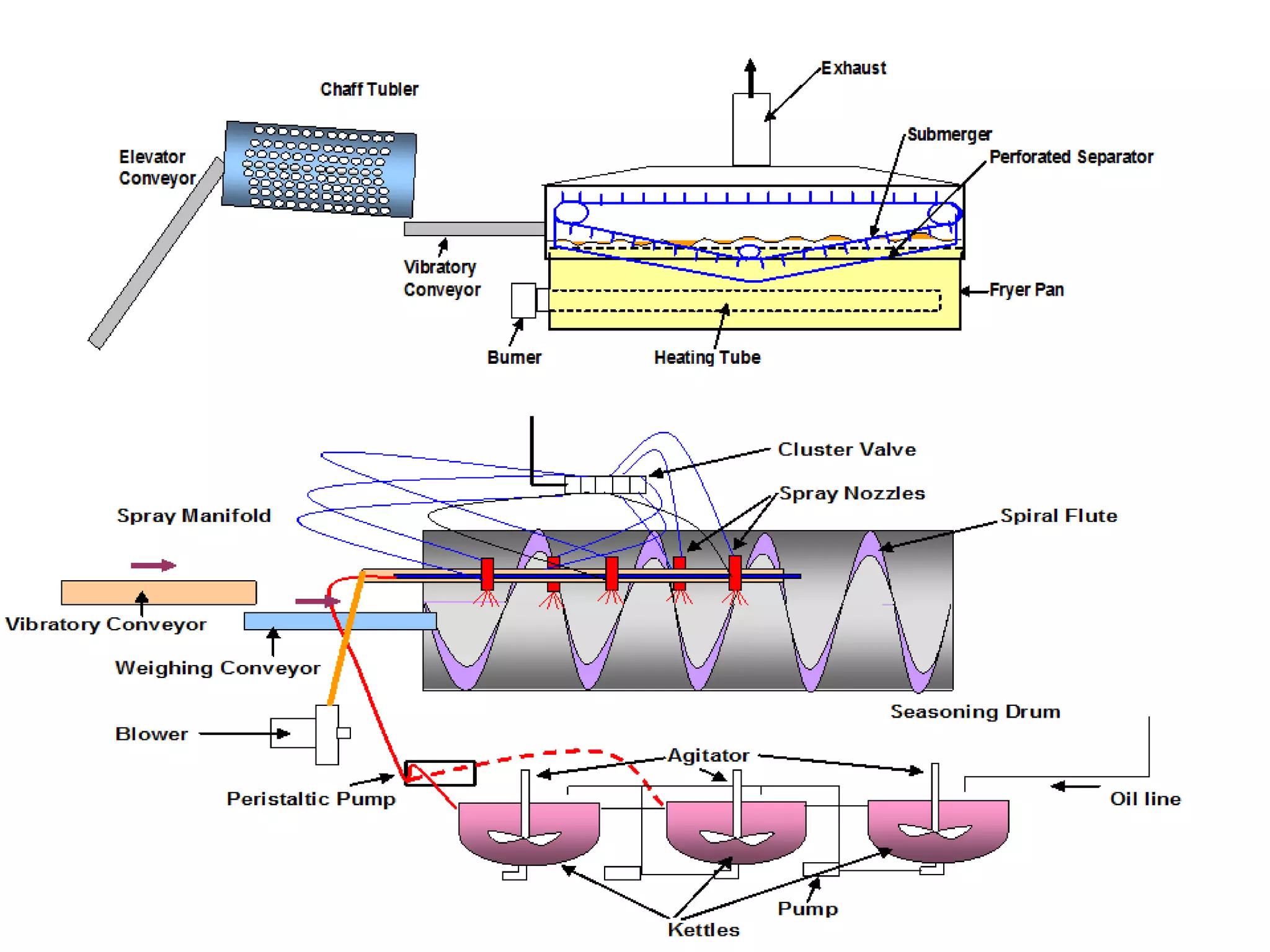
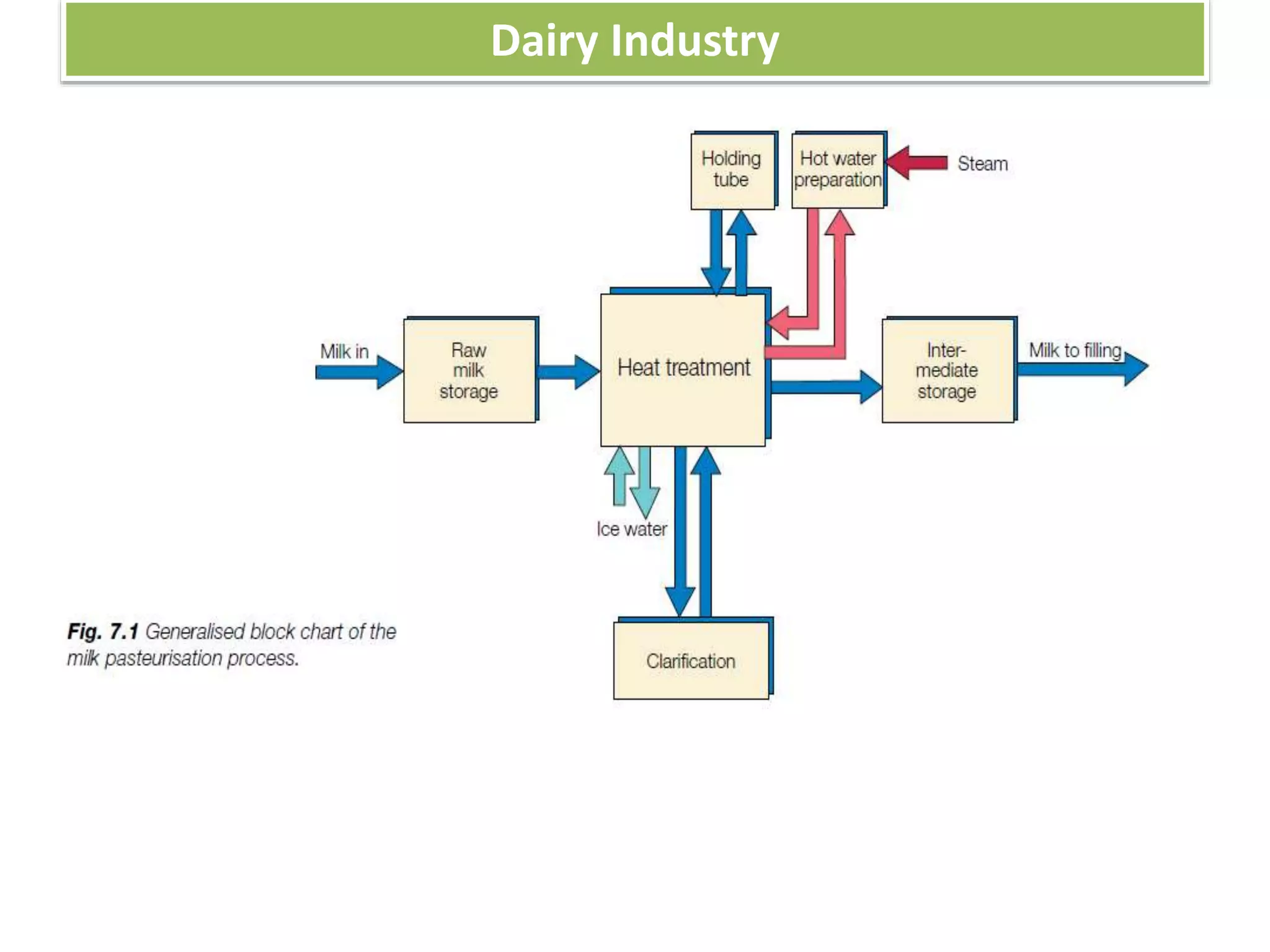
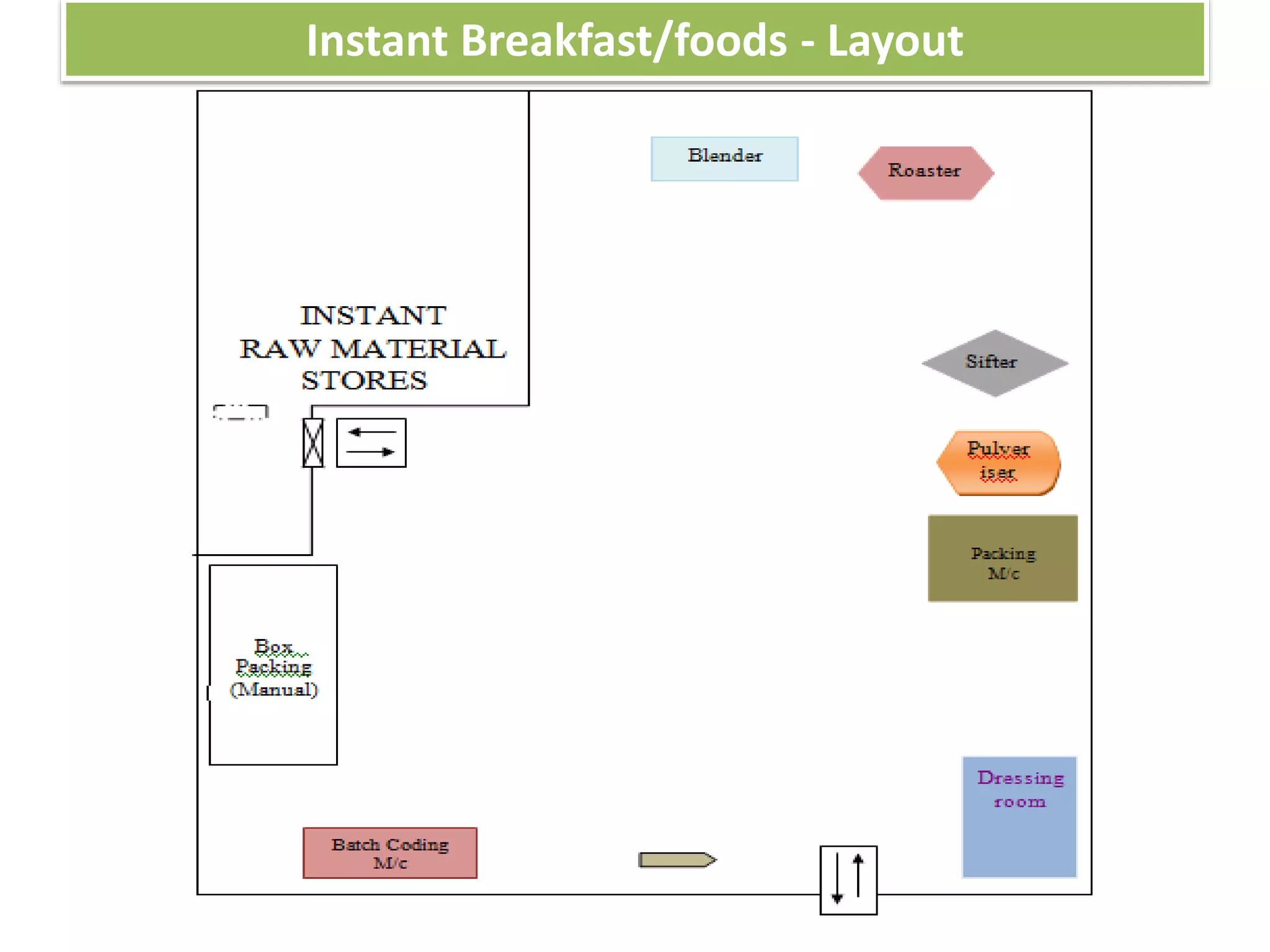
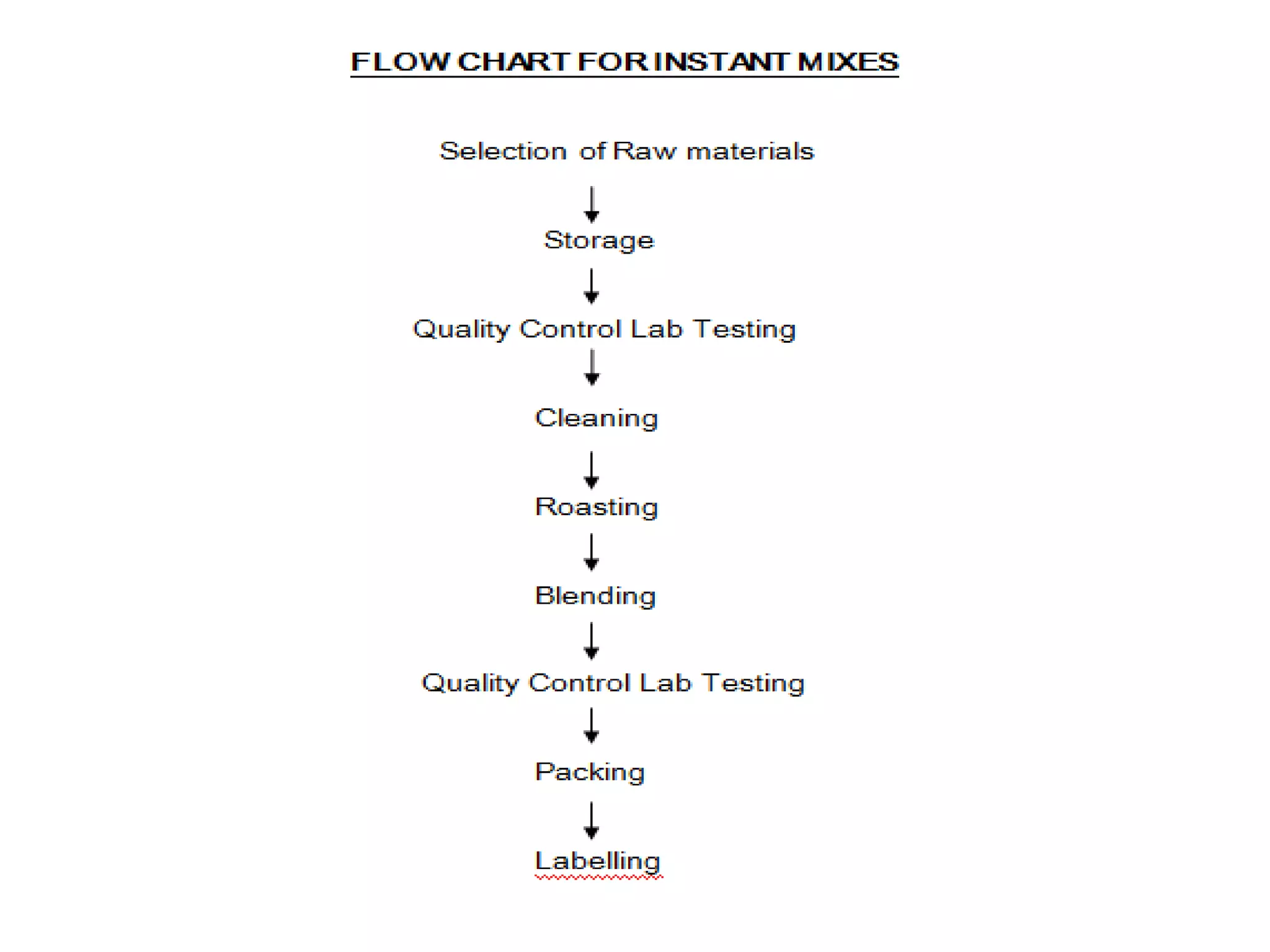
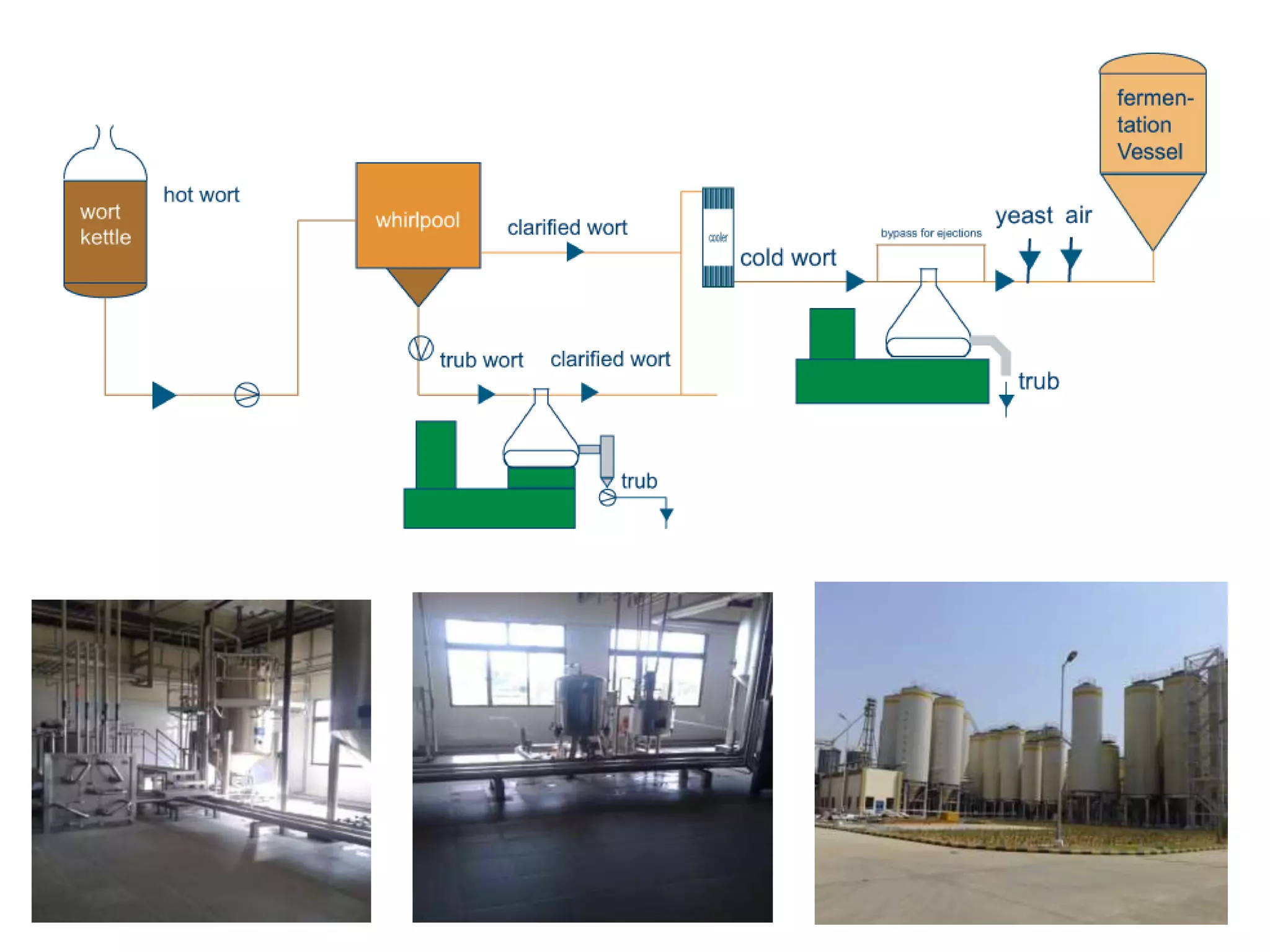
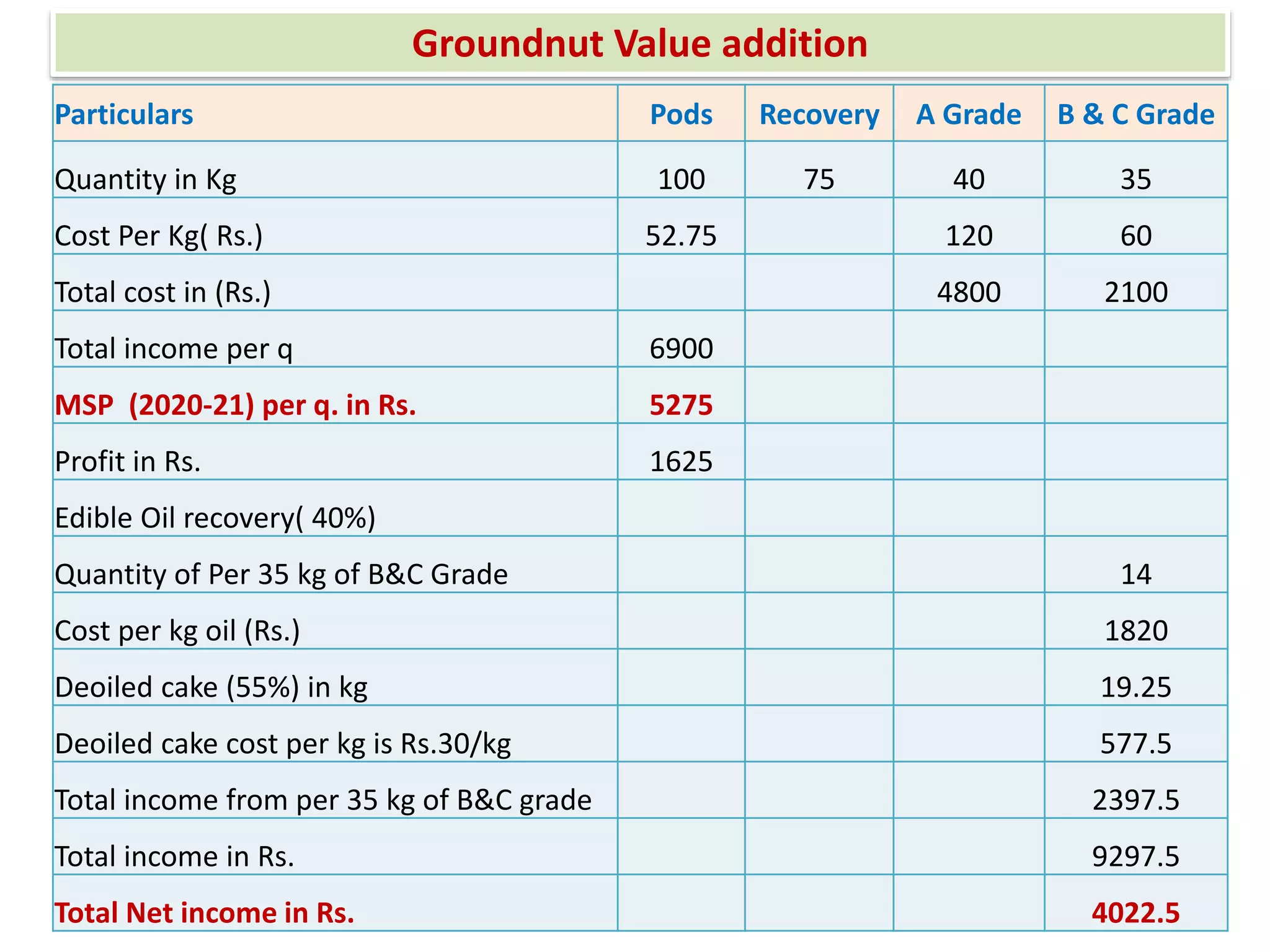
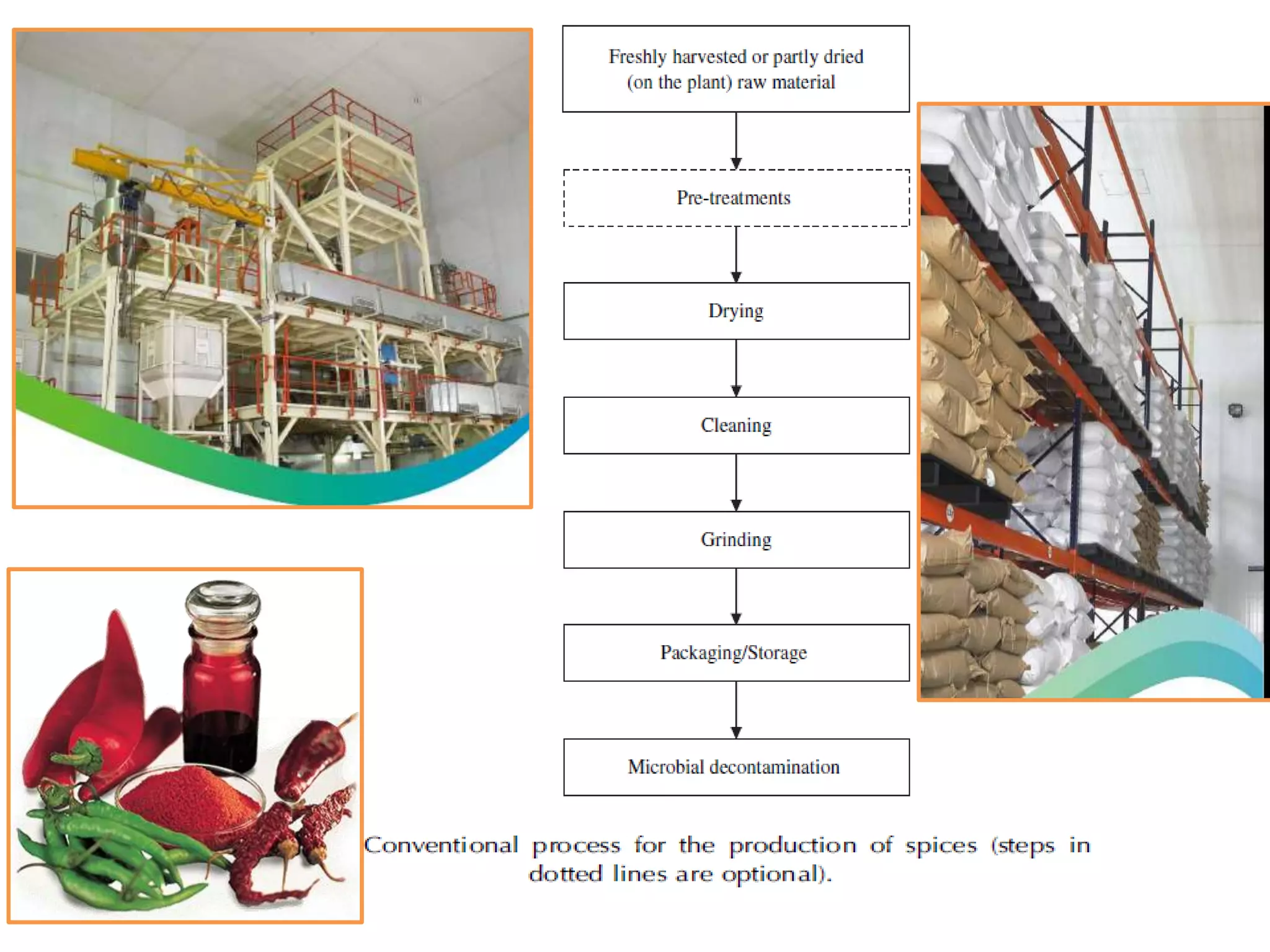
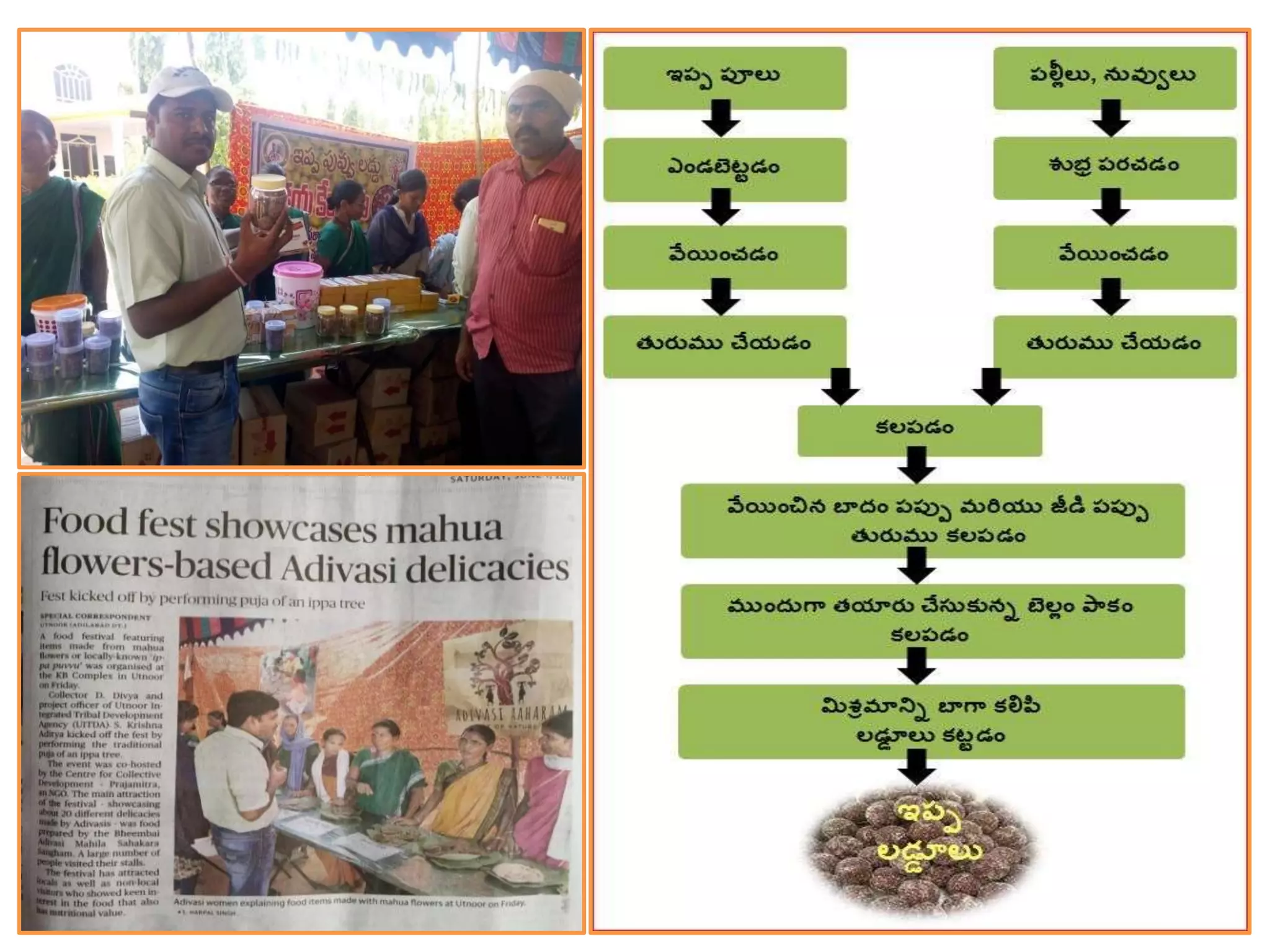
This document provides information on food processing plant layout and design. It discusses the objectives of plant layout which include minimizing material handling costs and maximizing space utilization. It also describes different types of layouts like product layout, process layout, and combination layout. Additional topics covered include principles of layout, location factors for industries, facility layout, and specific layouts for different food processing units like potato chips, soft drinks, and instant breakfasts. The document emphasizes hygienic design of facilities along with efficient material and information flow.