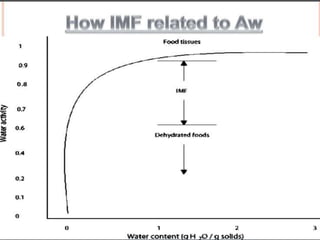
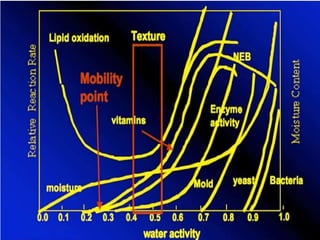
This document discusses intermediate moisture foods (IMF), which are foods with a water activity between 0.6-0.9 that prevents microbial growth. Examples include jams, jellies, candies, baked goods, honey, and dried meats. IMF have 10-50% moisture. Water activity measures the availability of water for microbial growth. IMF provide food preservation by controlling water activity and may include additional preservatives. While IMF don't require refrigeration, they can contain high sugar or salt and their texture may deteriorate if not properly handled.