Embed presentation
Downloaded 627 times

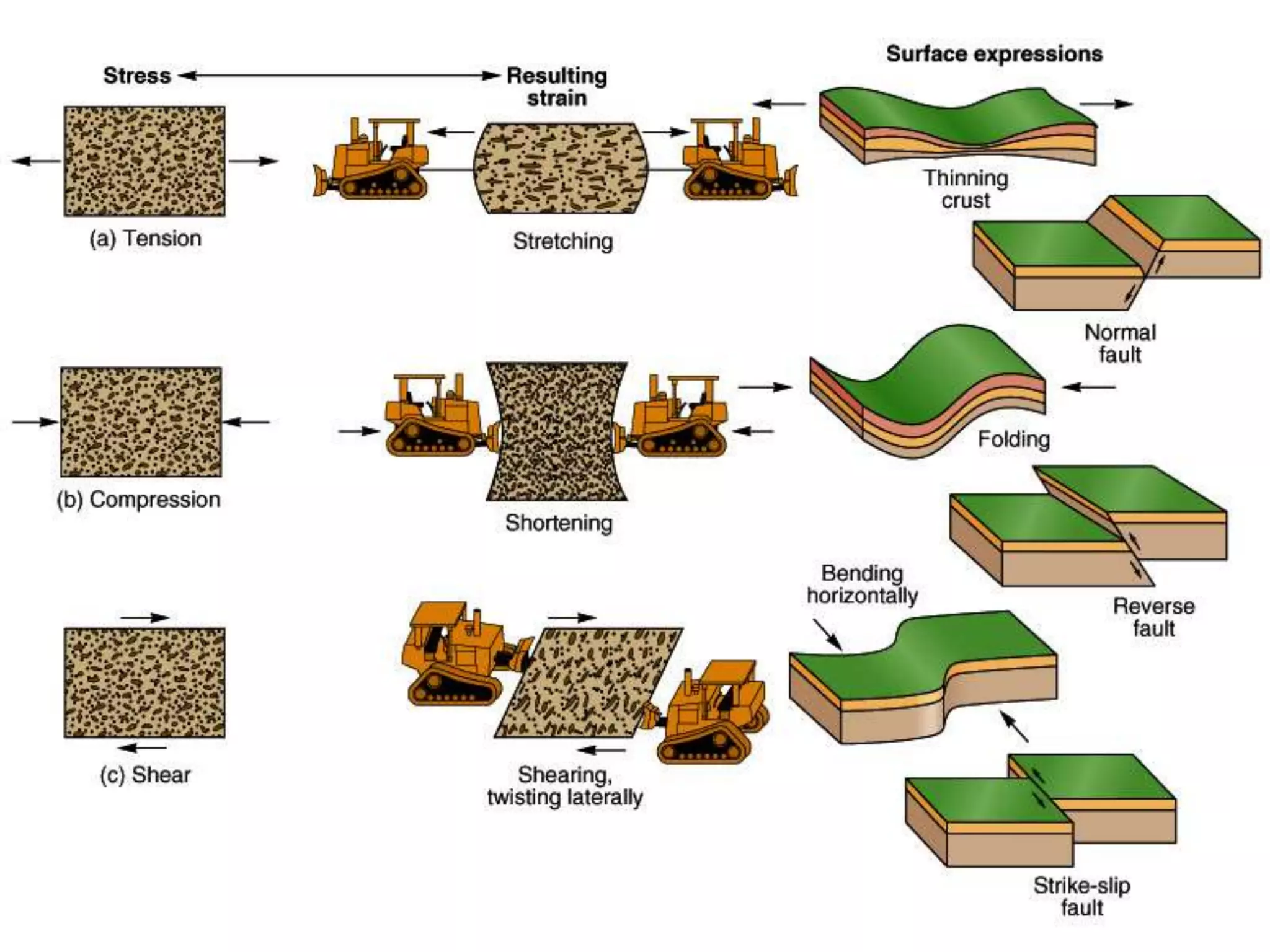


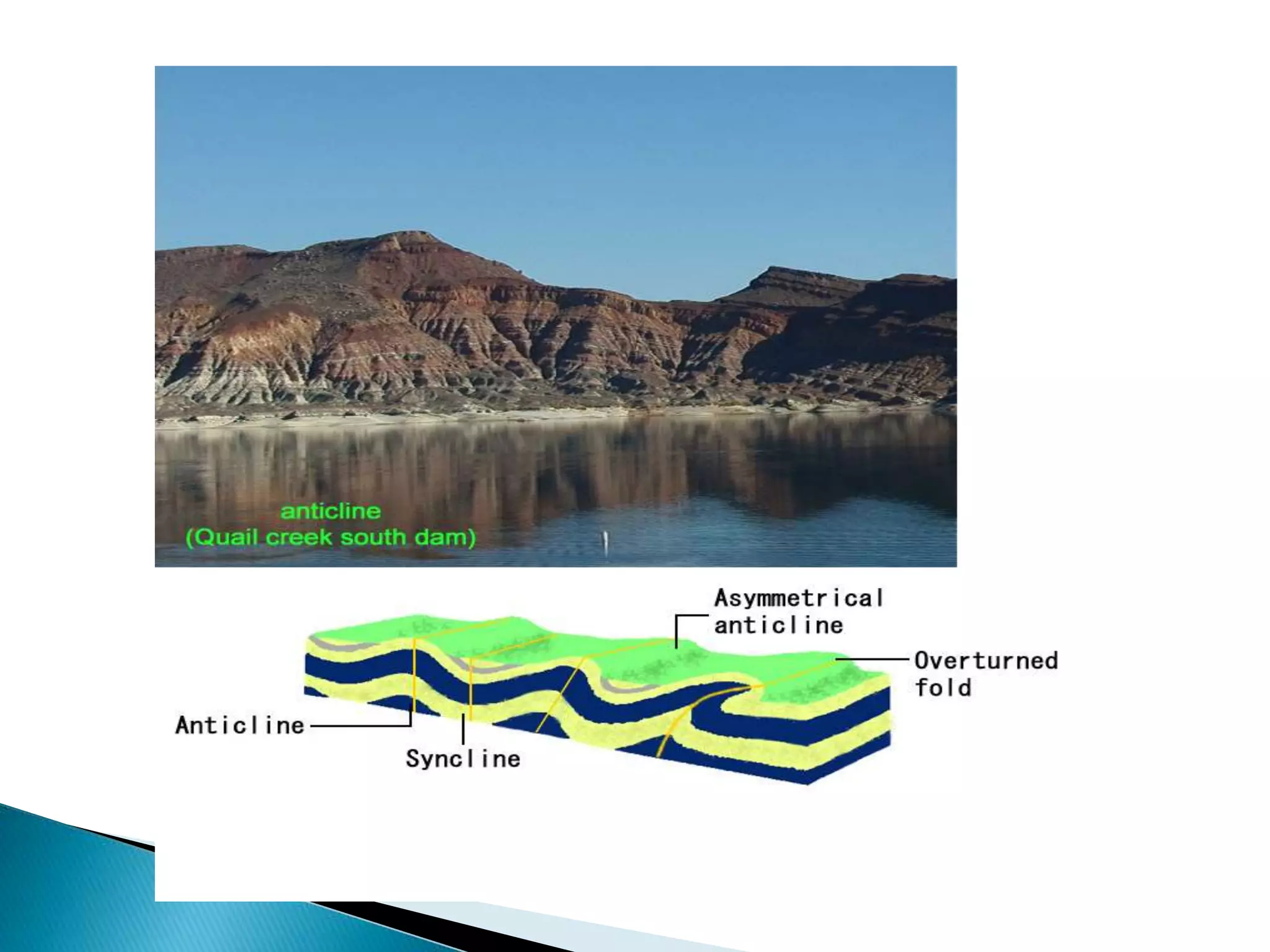

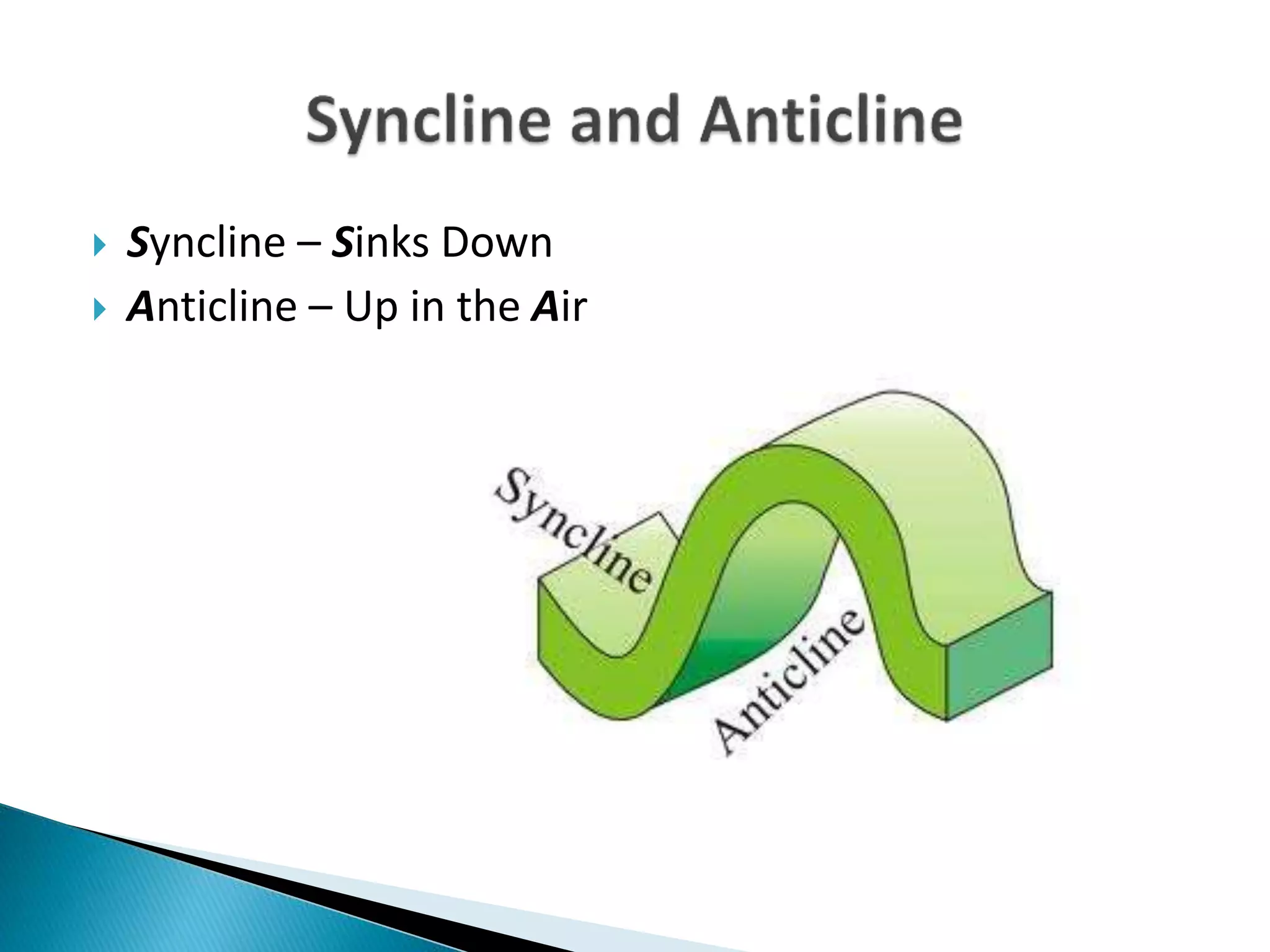


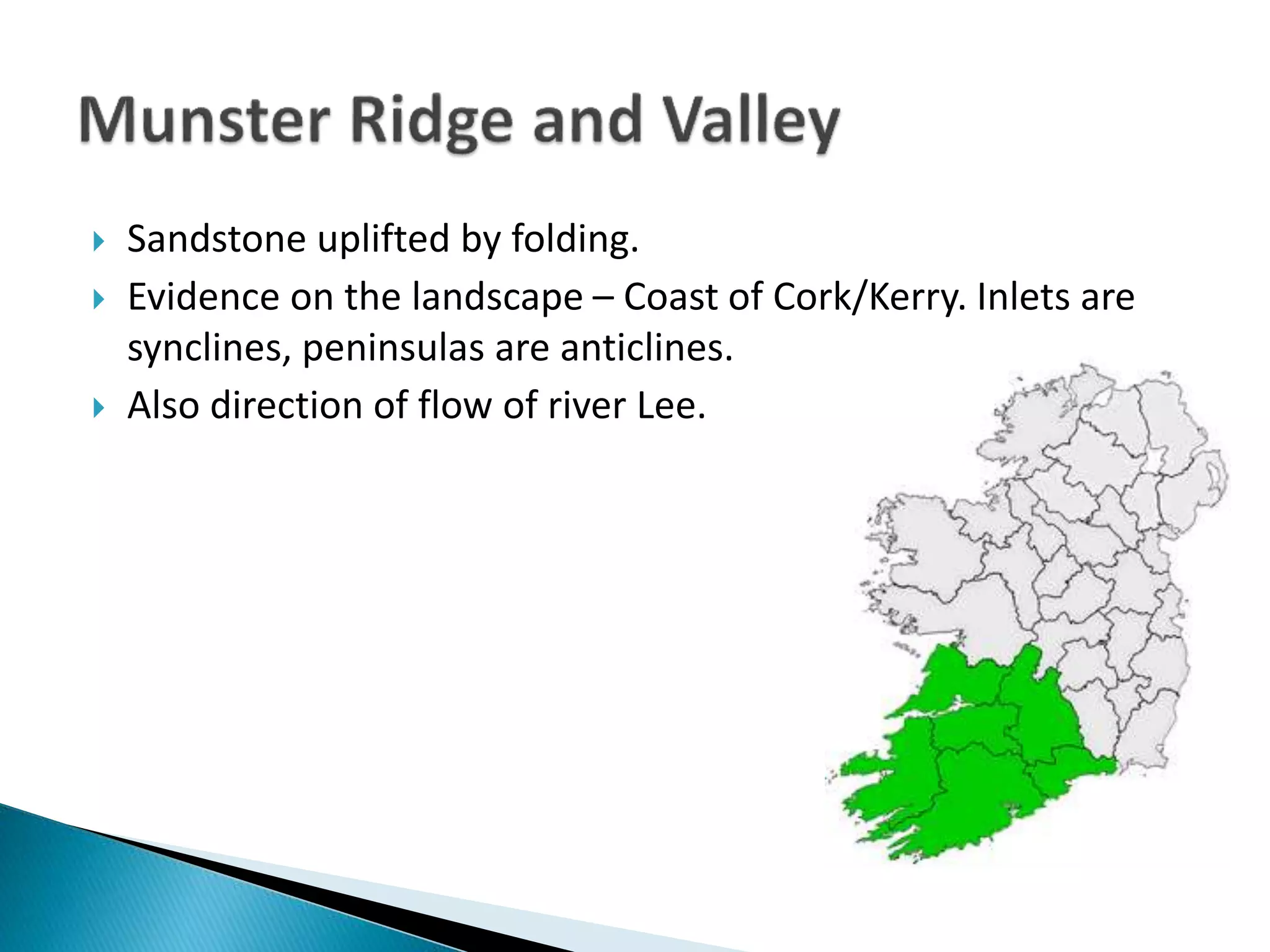
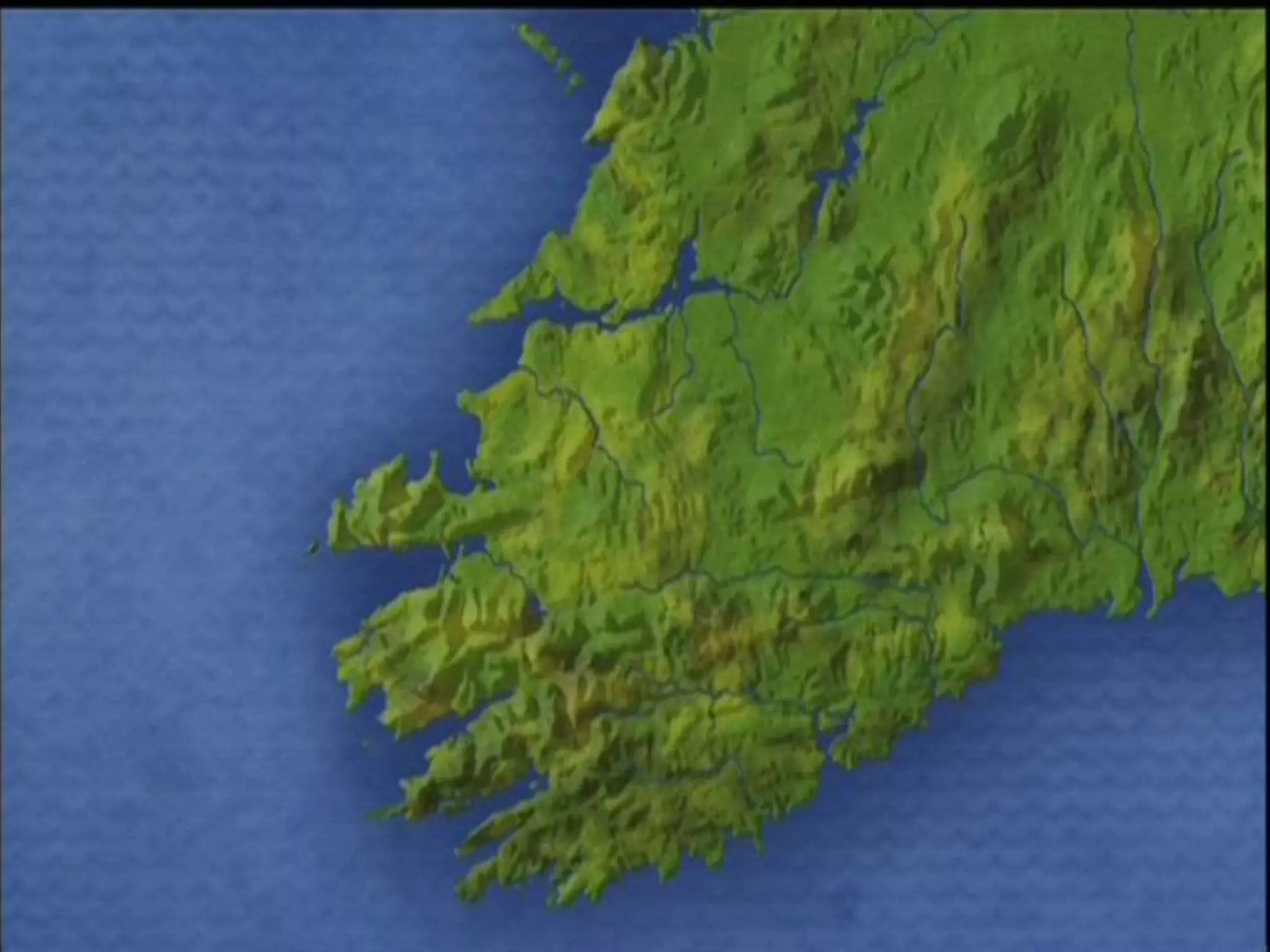
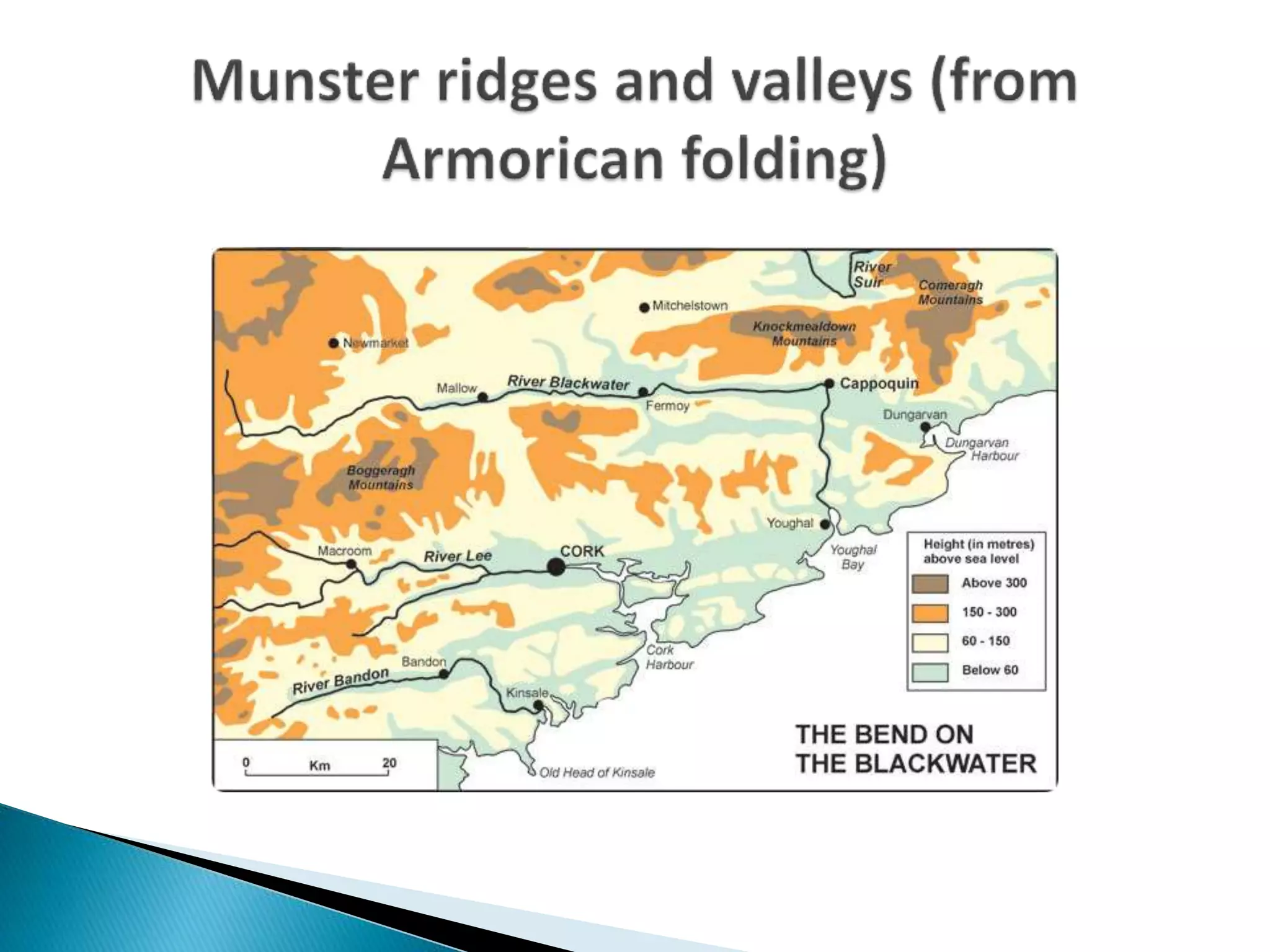

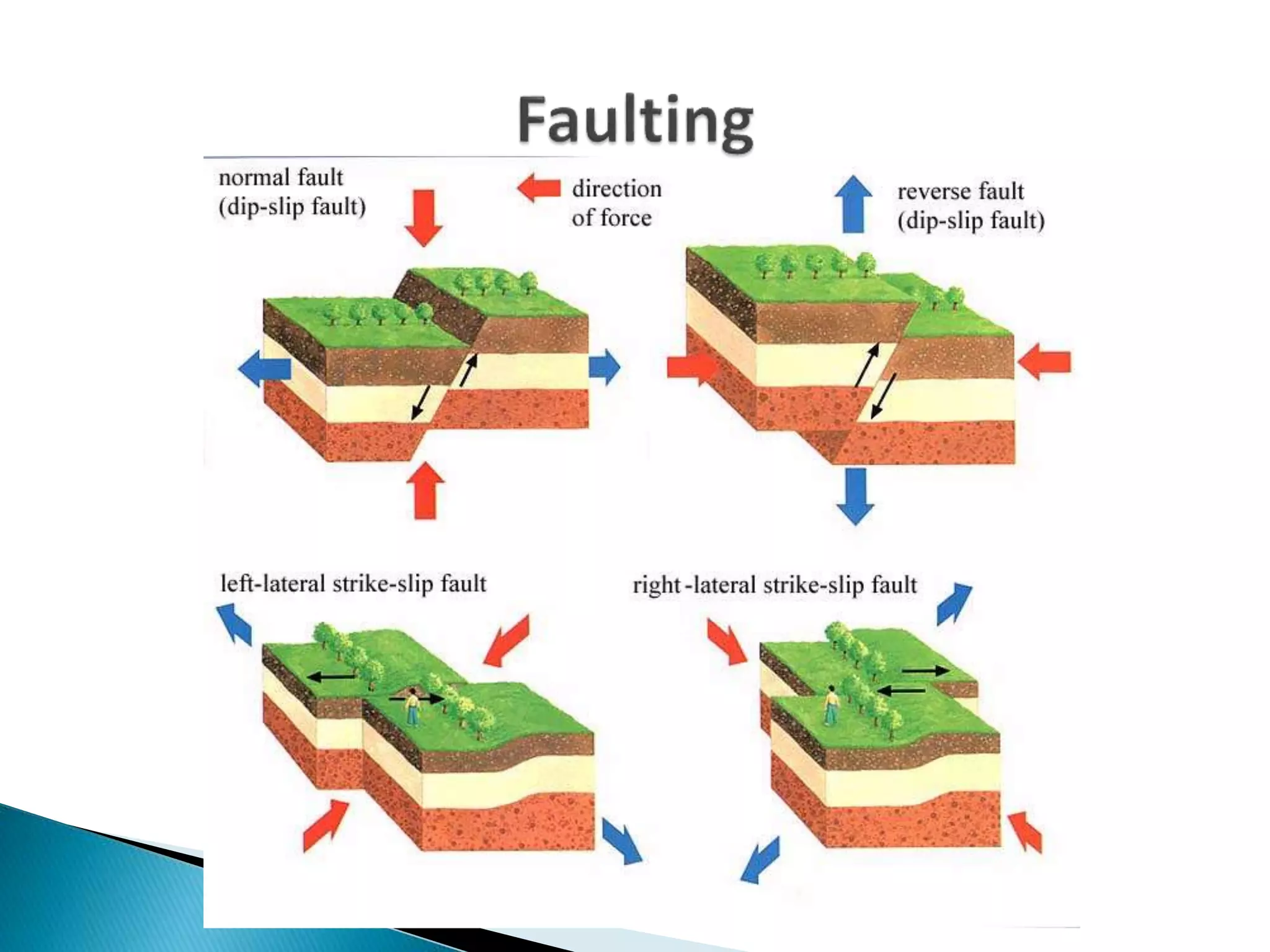
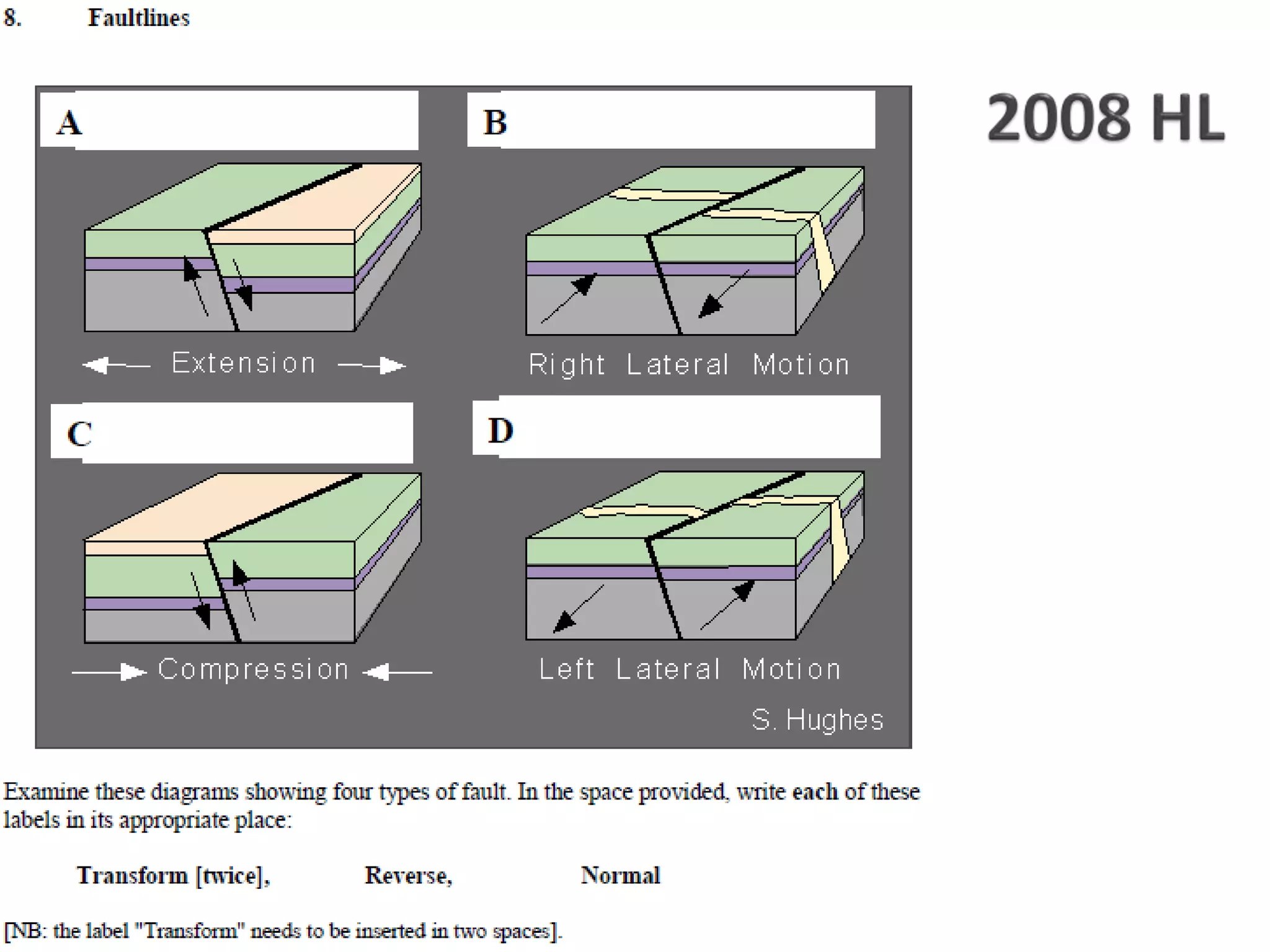
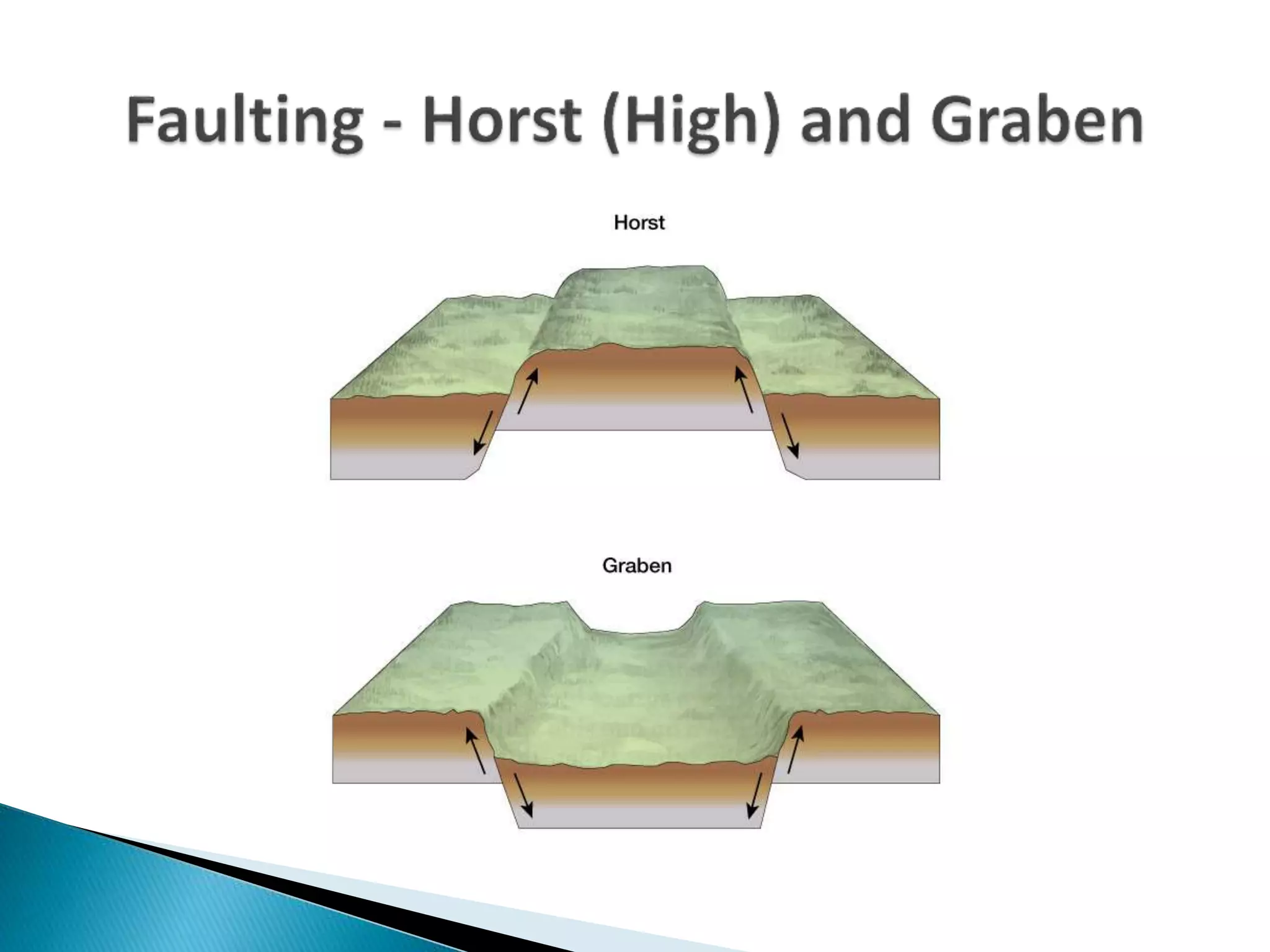
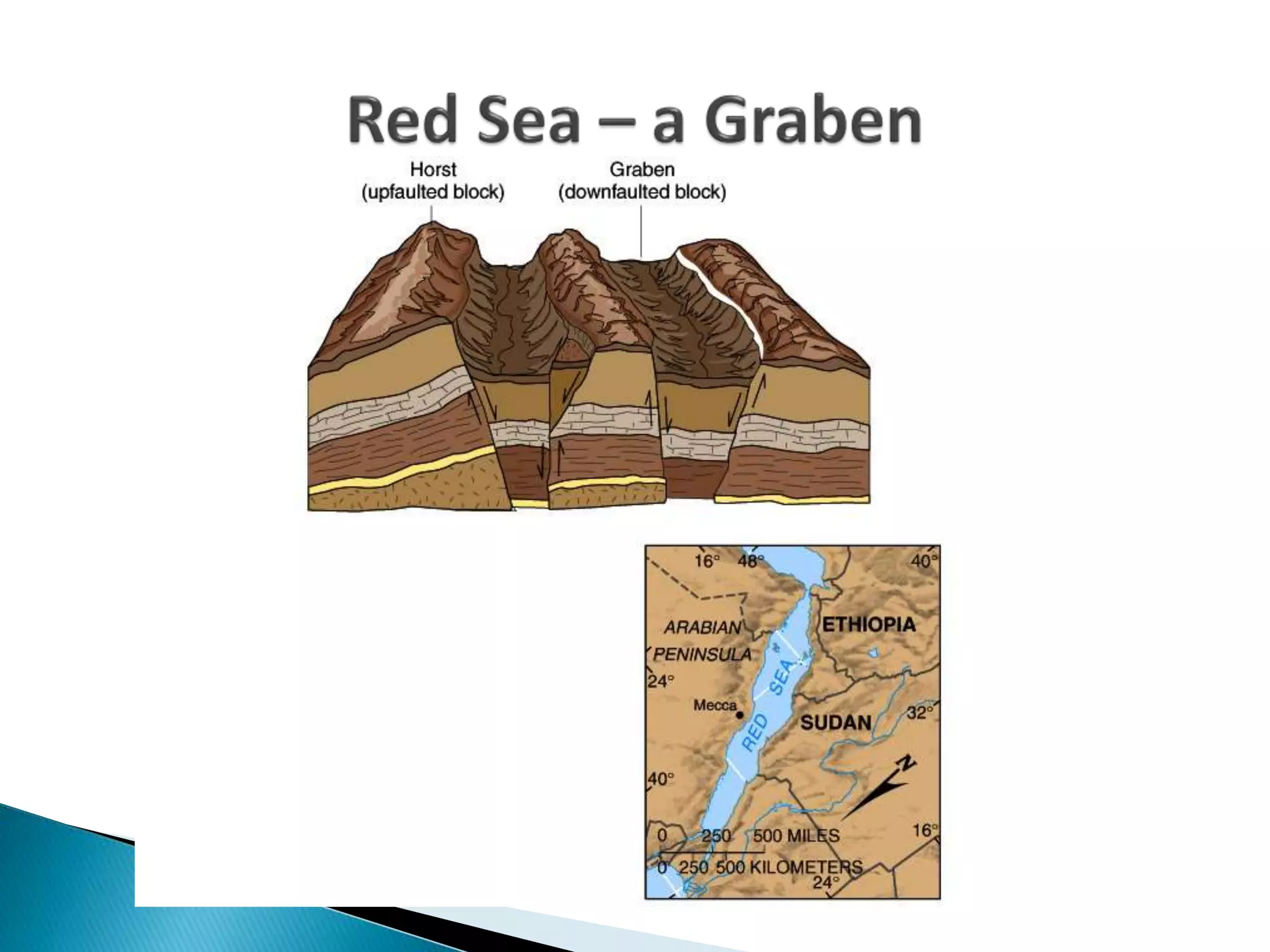



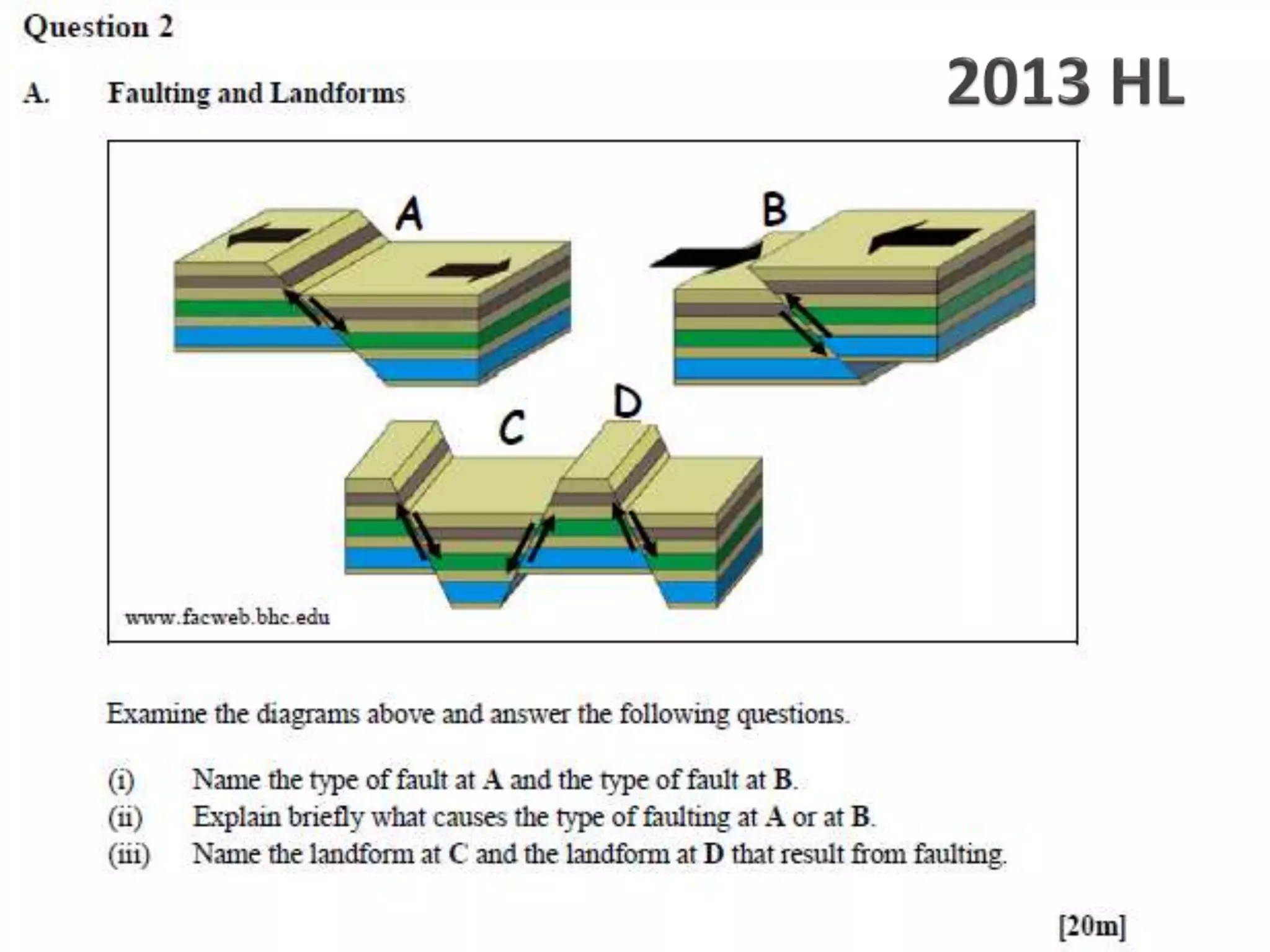

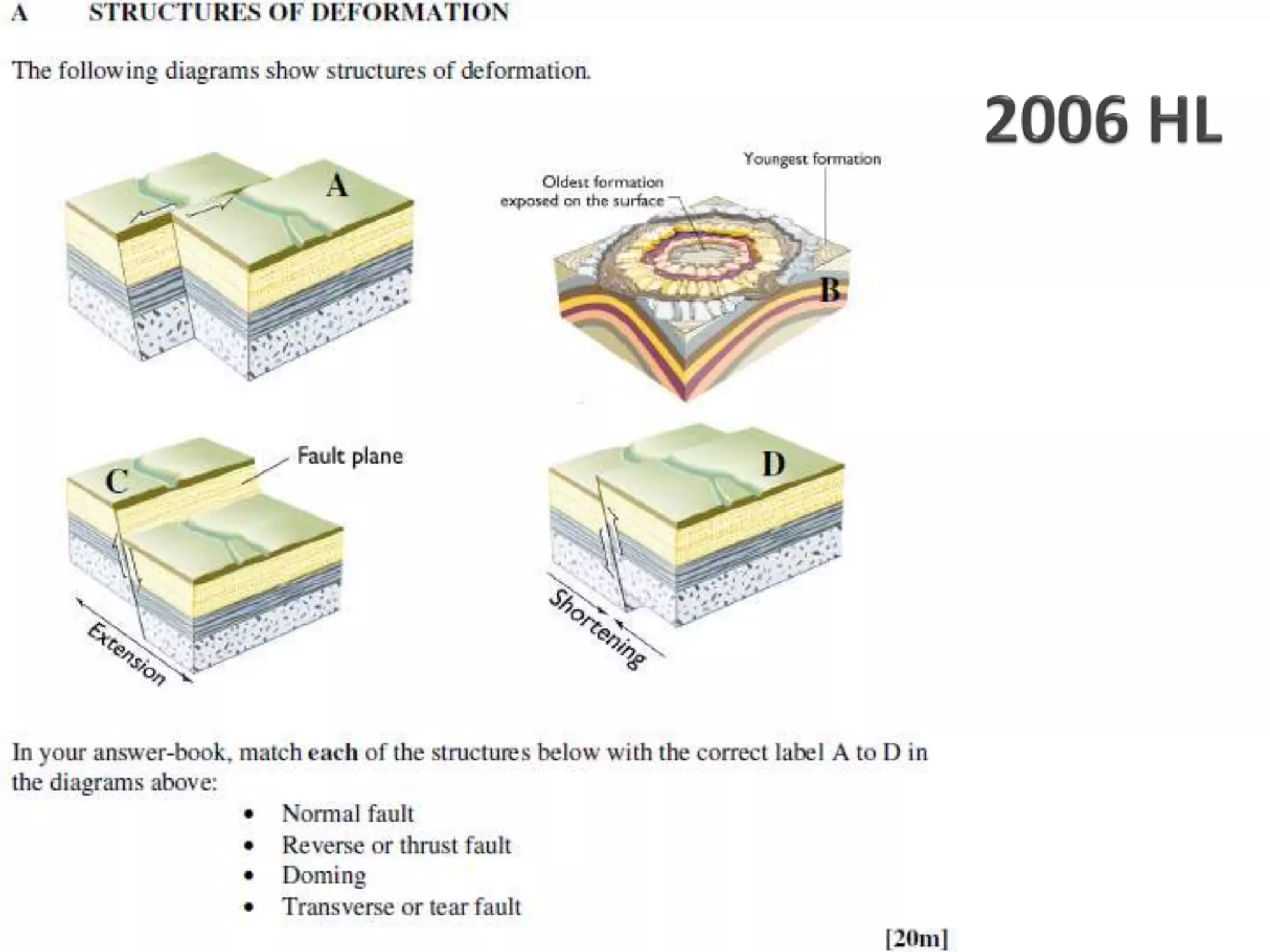

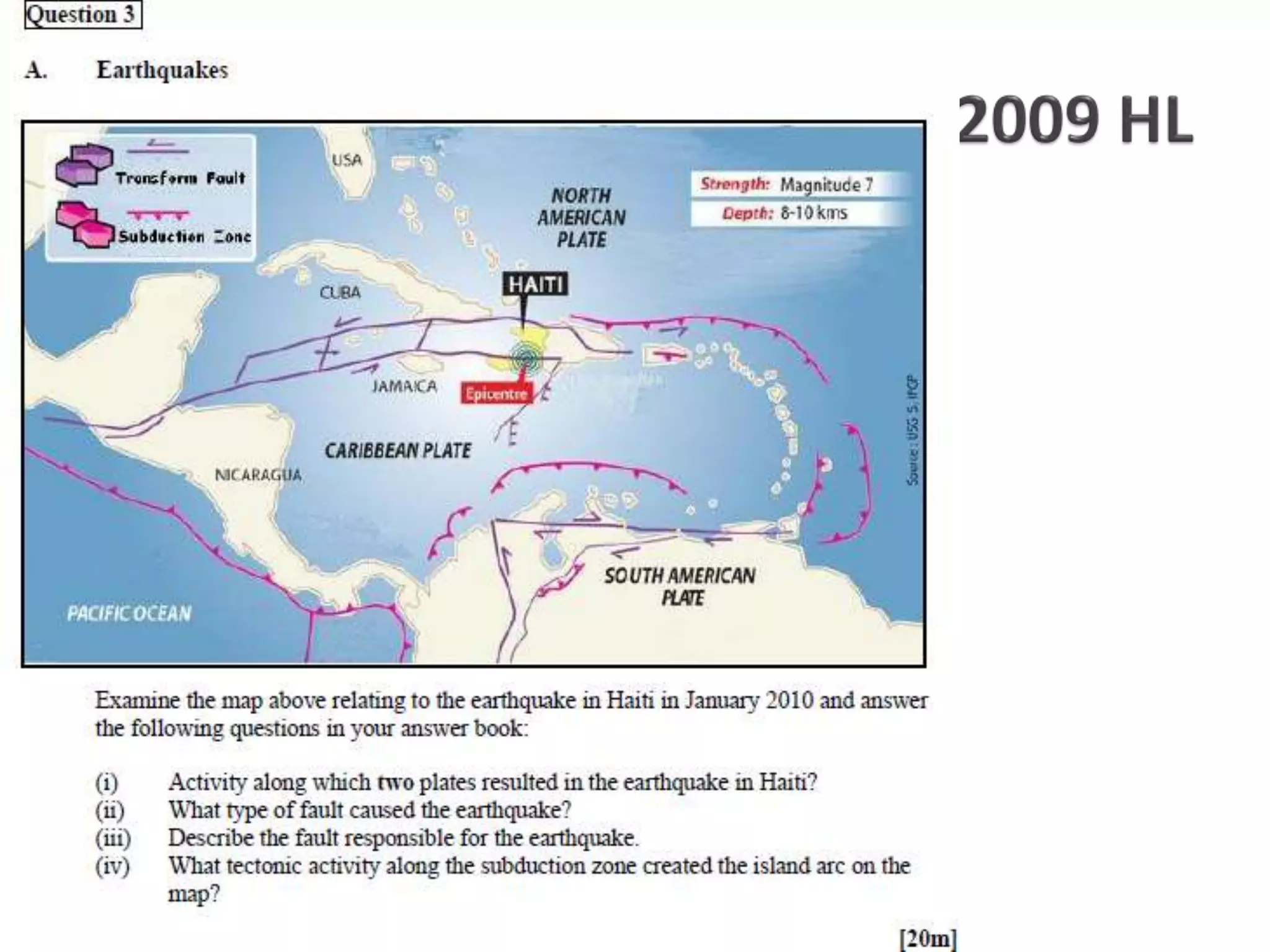



The document discusses geological processes of folding and faulting, describing how folding is a result of compression while faulting can occur due to compression, tension, or shearing. It highlights specific landforms such as synclines and anticlines, with examples from the landscape of Cork/Kerry, while also explaining types of faults: normal, reverse, thrust, and tear faults. The content emphasizes the importance of landscape impact and includes a marking scheme for assessing discussion on these processes.


























