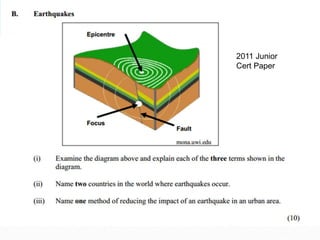
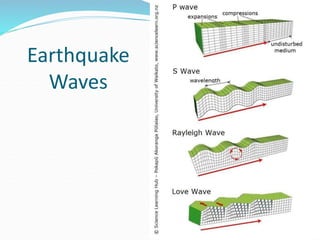
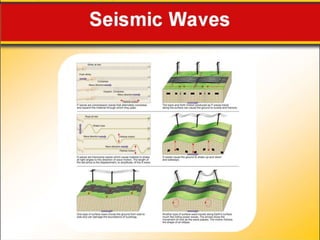
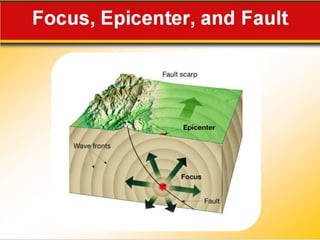
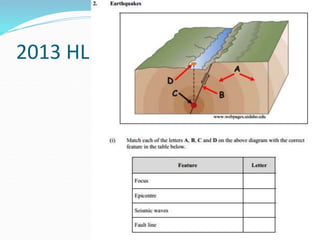
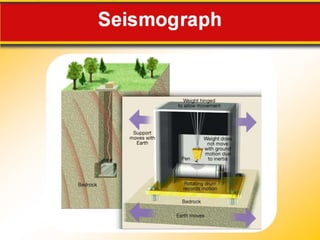
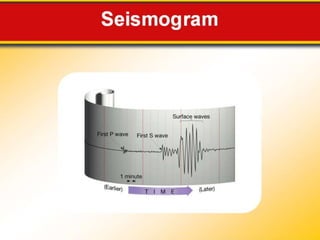
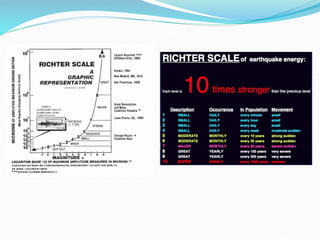
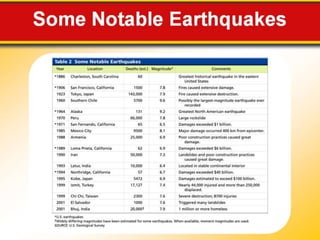
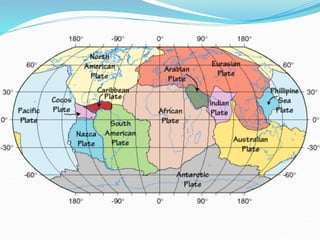
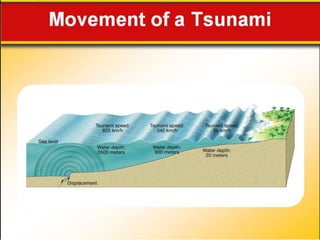
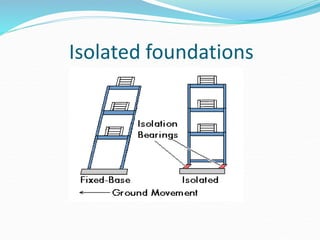
The document discusses earthquake waves, their depths, and the mechanisms used to predict earthquakes, such as seismograph activity and measurements of crustal stress. It also covers the impact of the 2010 Haiti earthquake and ideas for making buildings earthquake-proof. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of understanding plate tectonics in explaining the distribution of earthquakes worldwide.