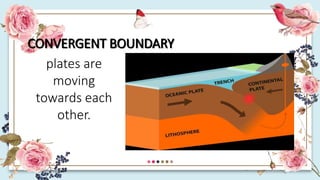
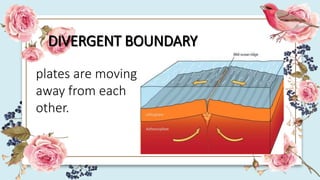
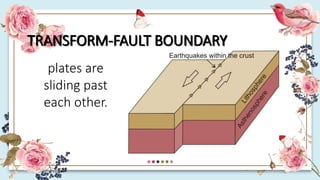
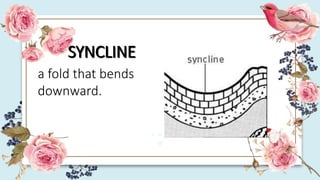
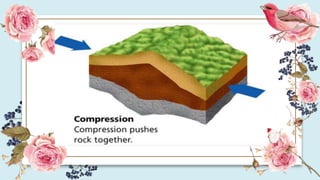
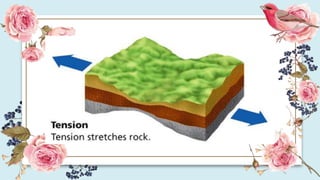
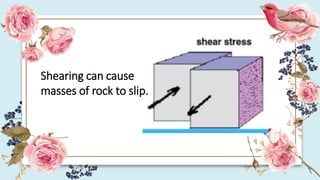
This document discusses how the movement of tectonic plates leads to the formation of folds and faults in rocks. It defines folds as bent rock layers due to compression, and faults as fractures between blocks of rock. There are three main types of folds - anticlines that arch up, synclines that arch down, and monoclines that bend rock layers. The three main types of faults are normal faults from tension, reverse faults from compression, and strike-slip faults from shear stresses. Stresses like compression, tension and shearing can cause rocks to fold, fracture or slip, resulting in plastic deformation or elastic deformation.