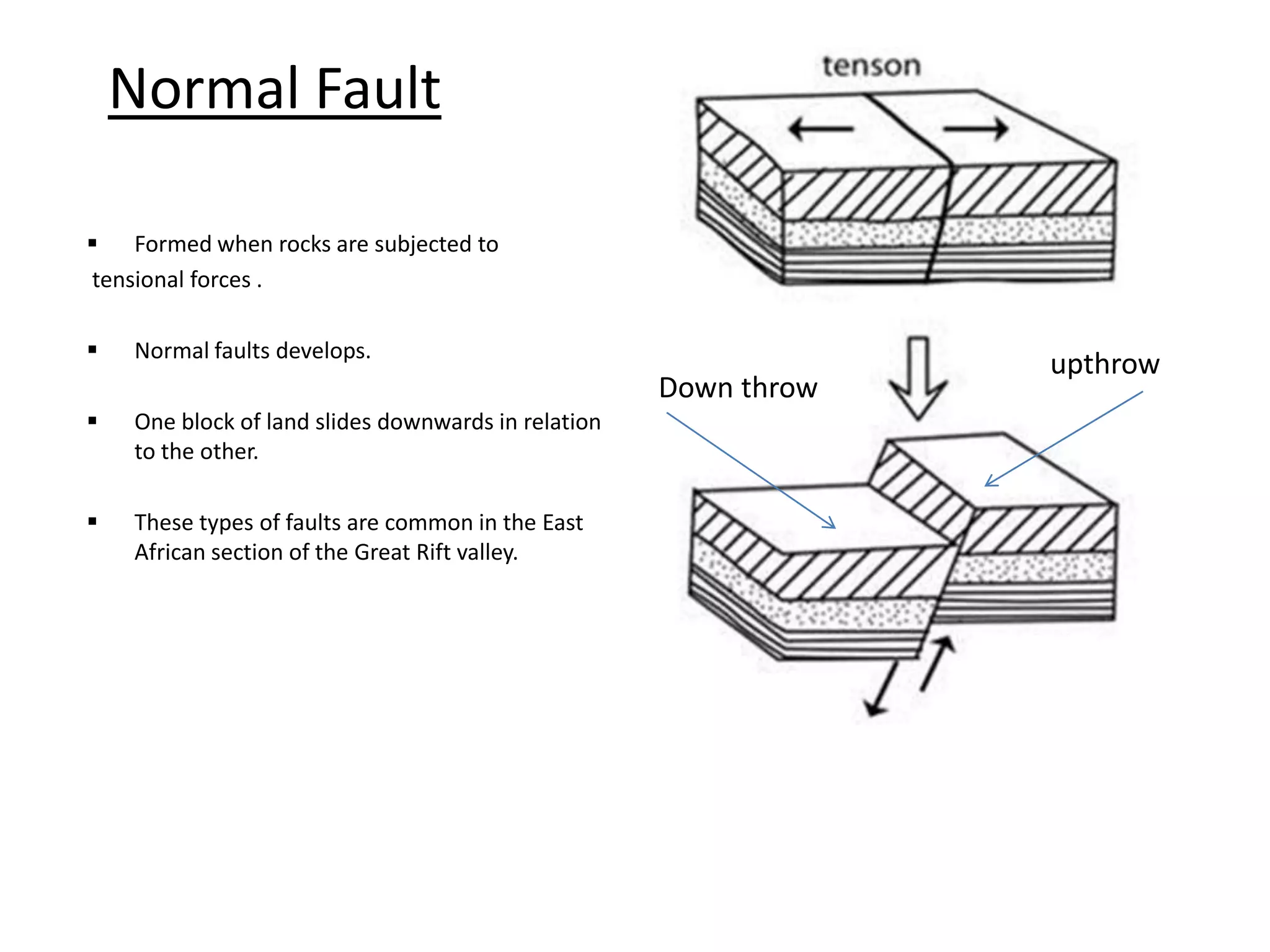
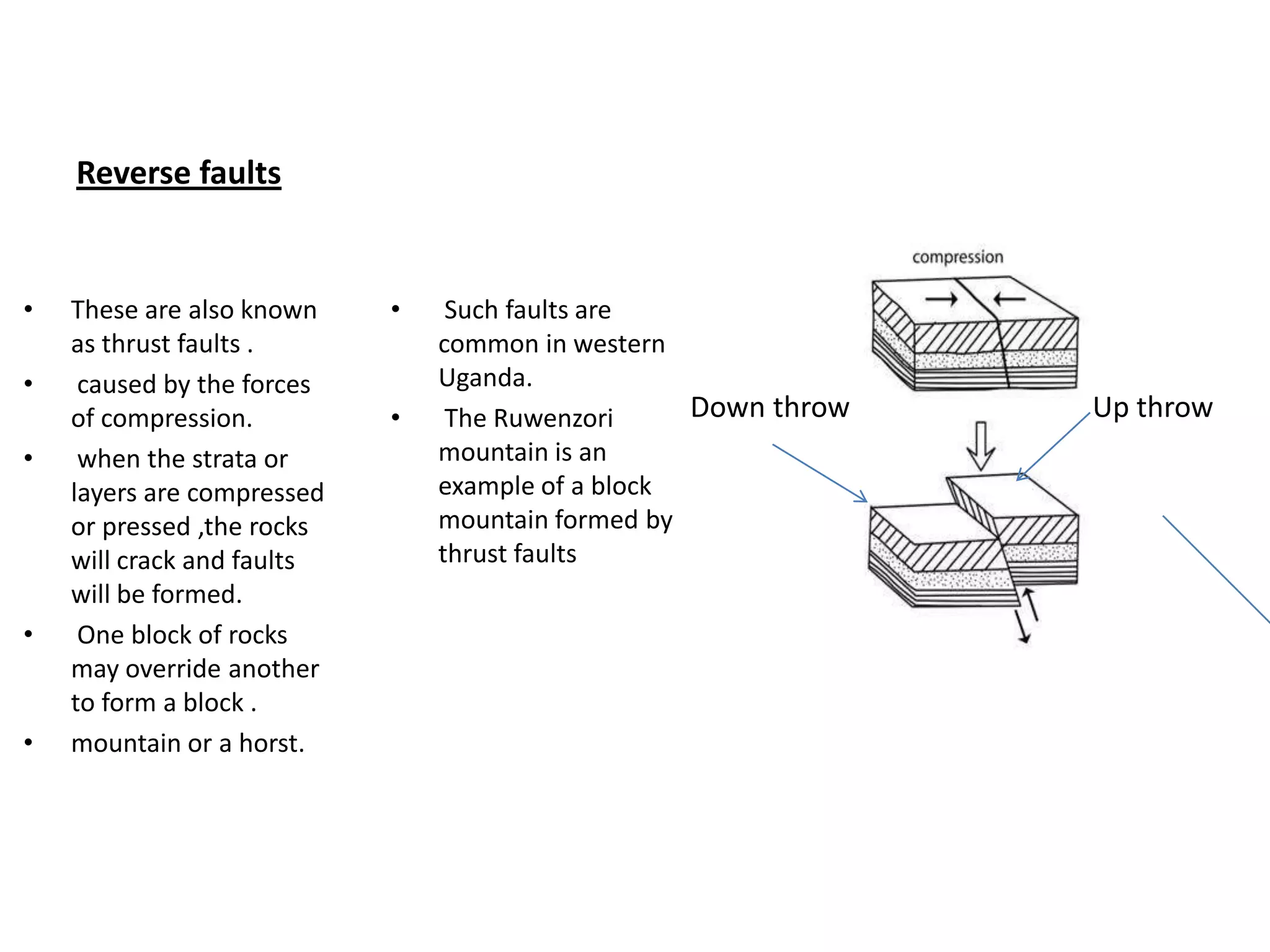
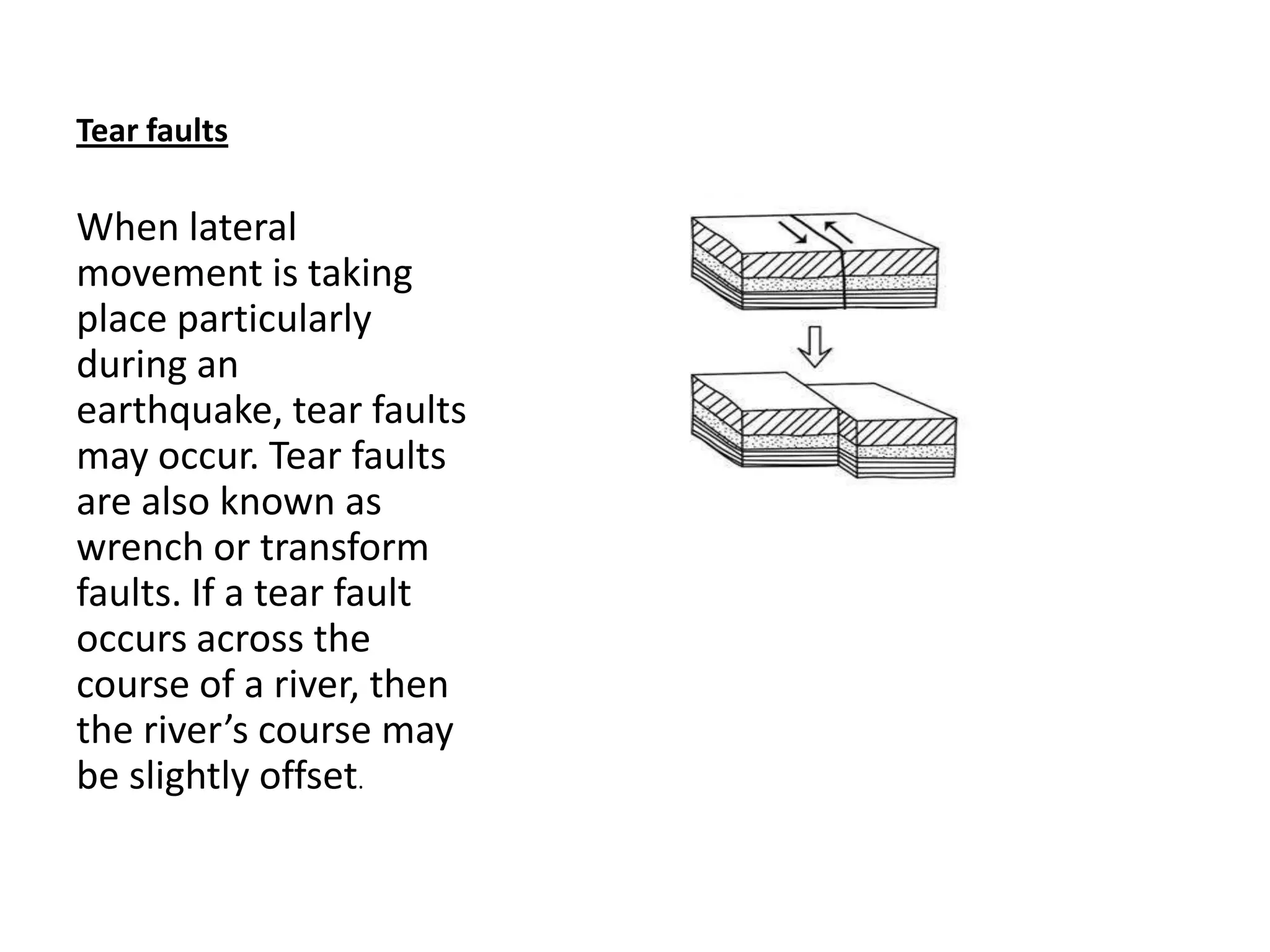
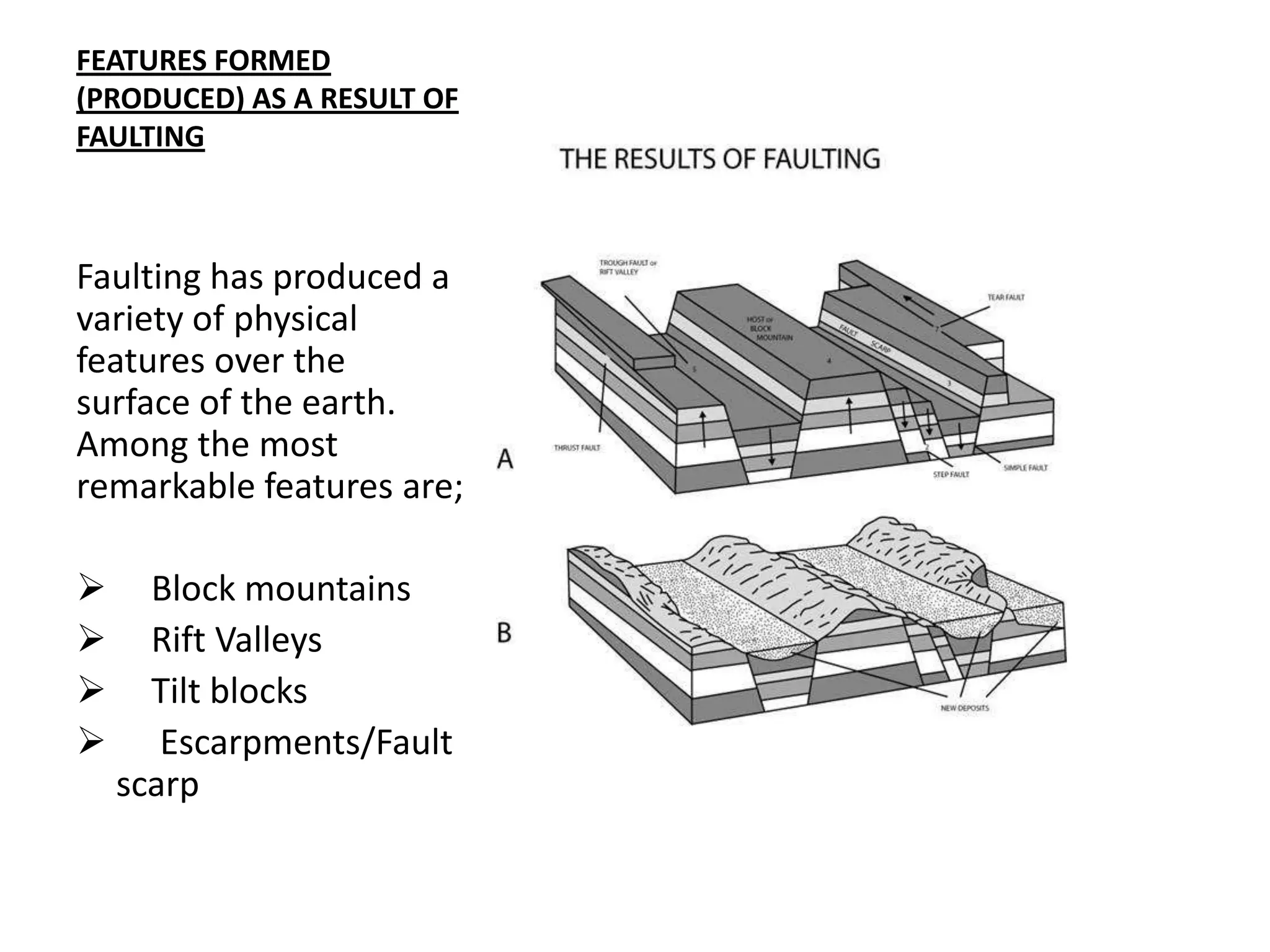
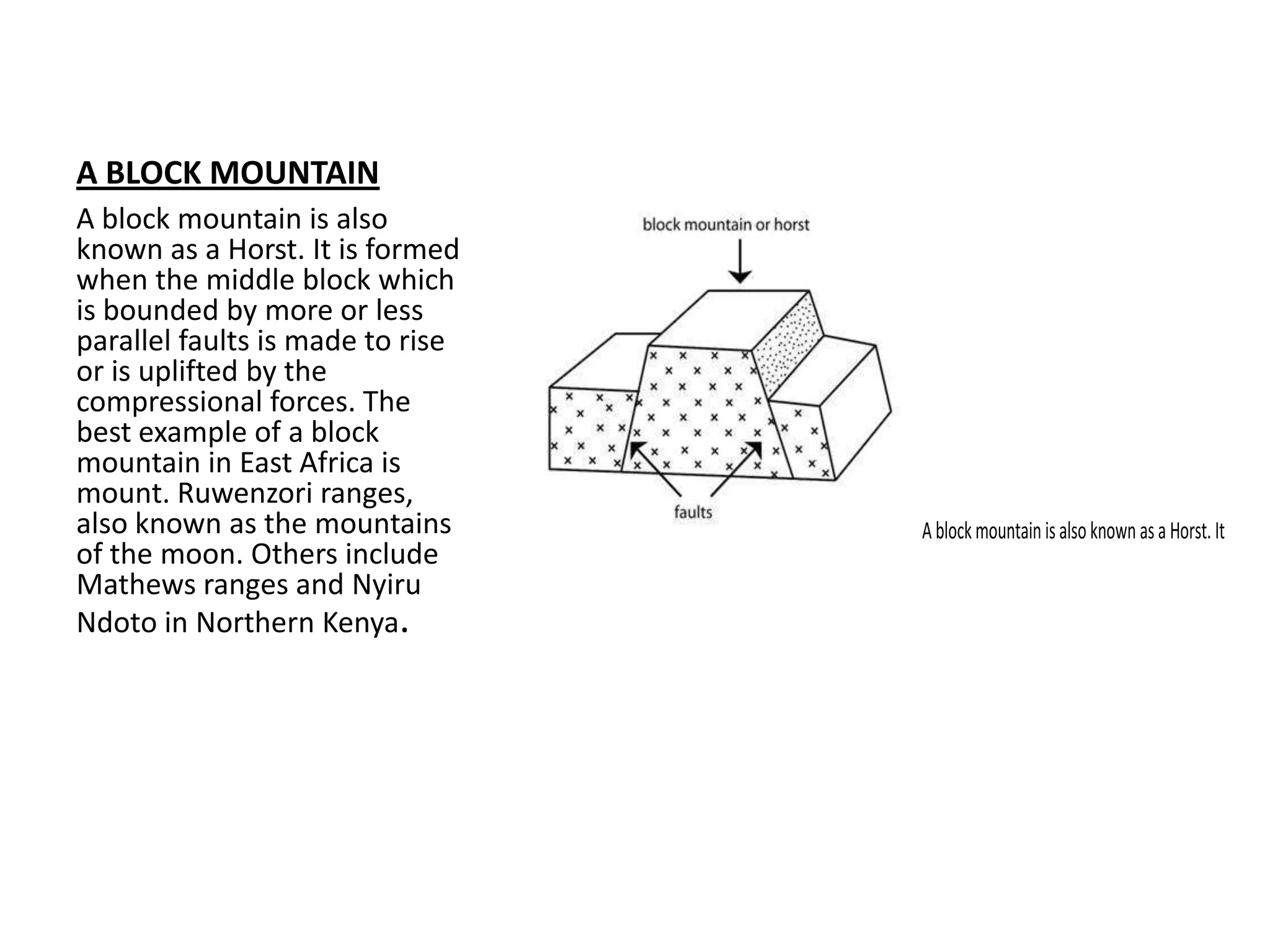
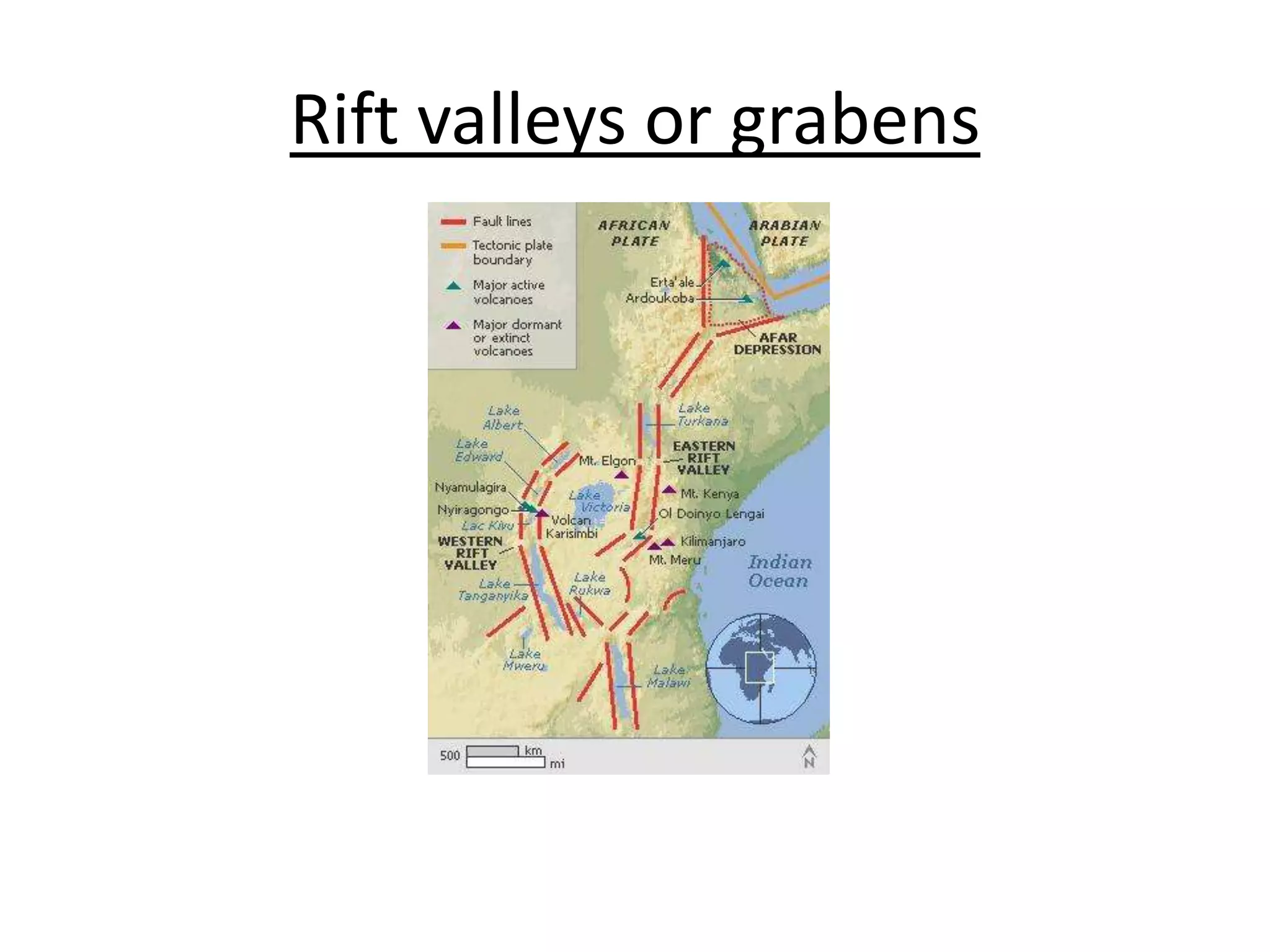
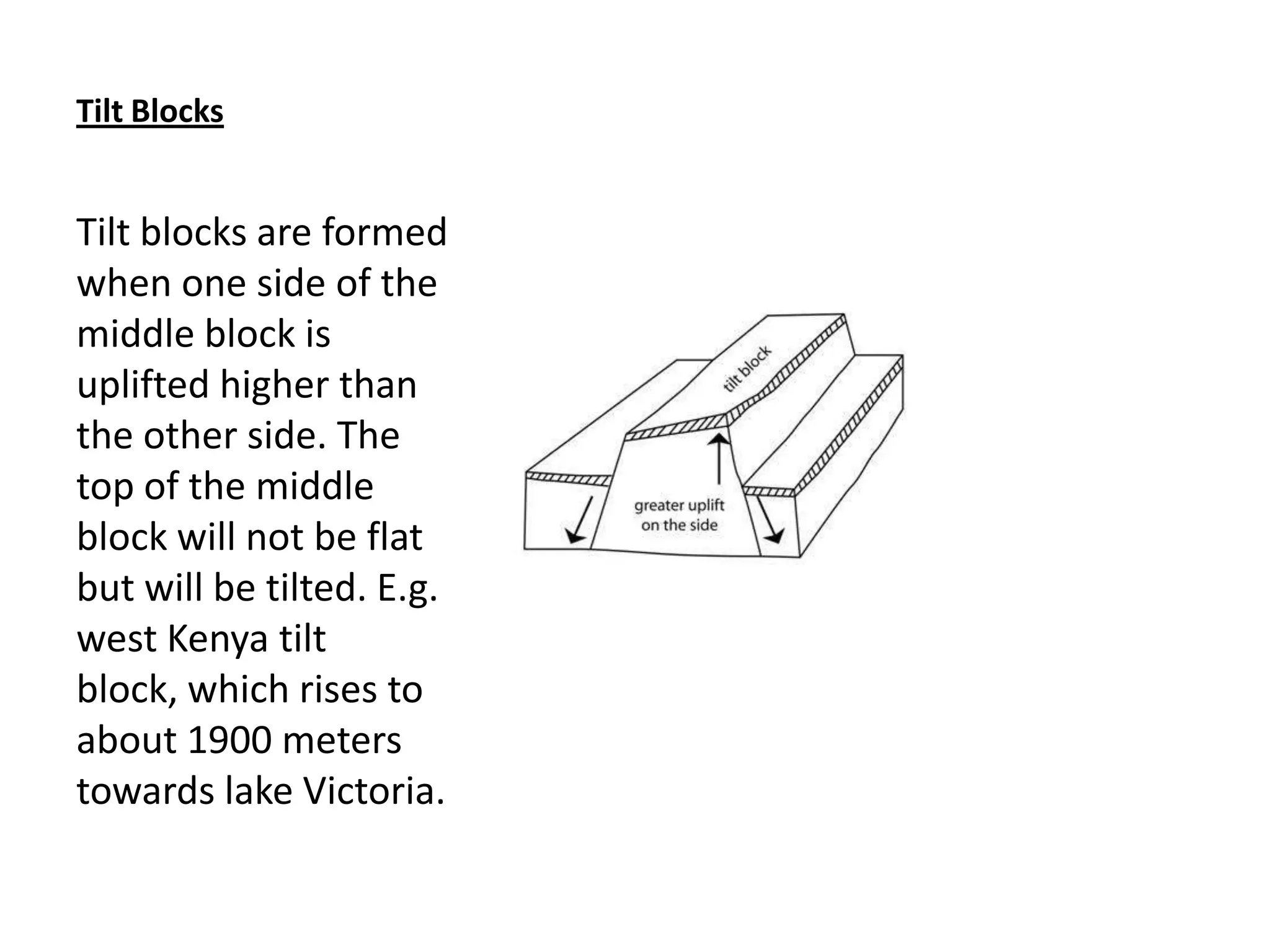
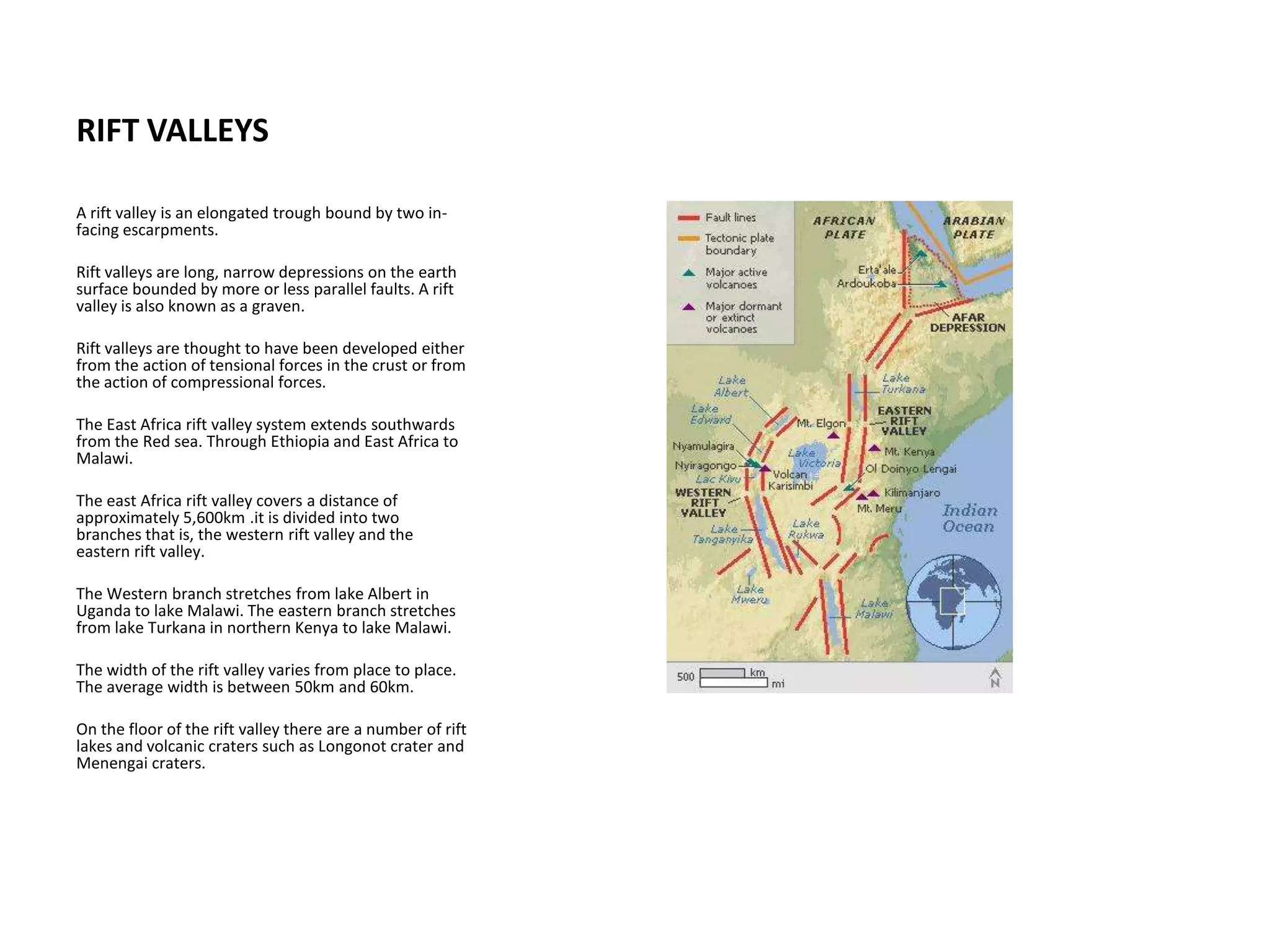
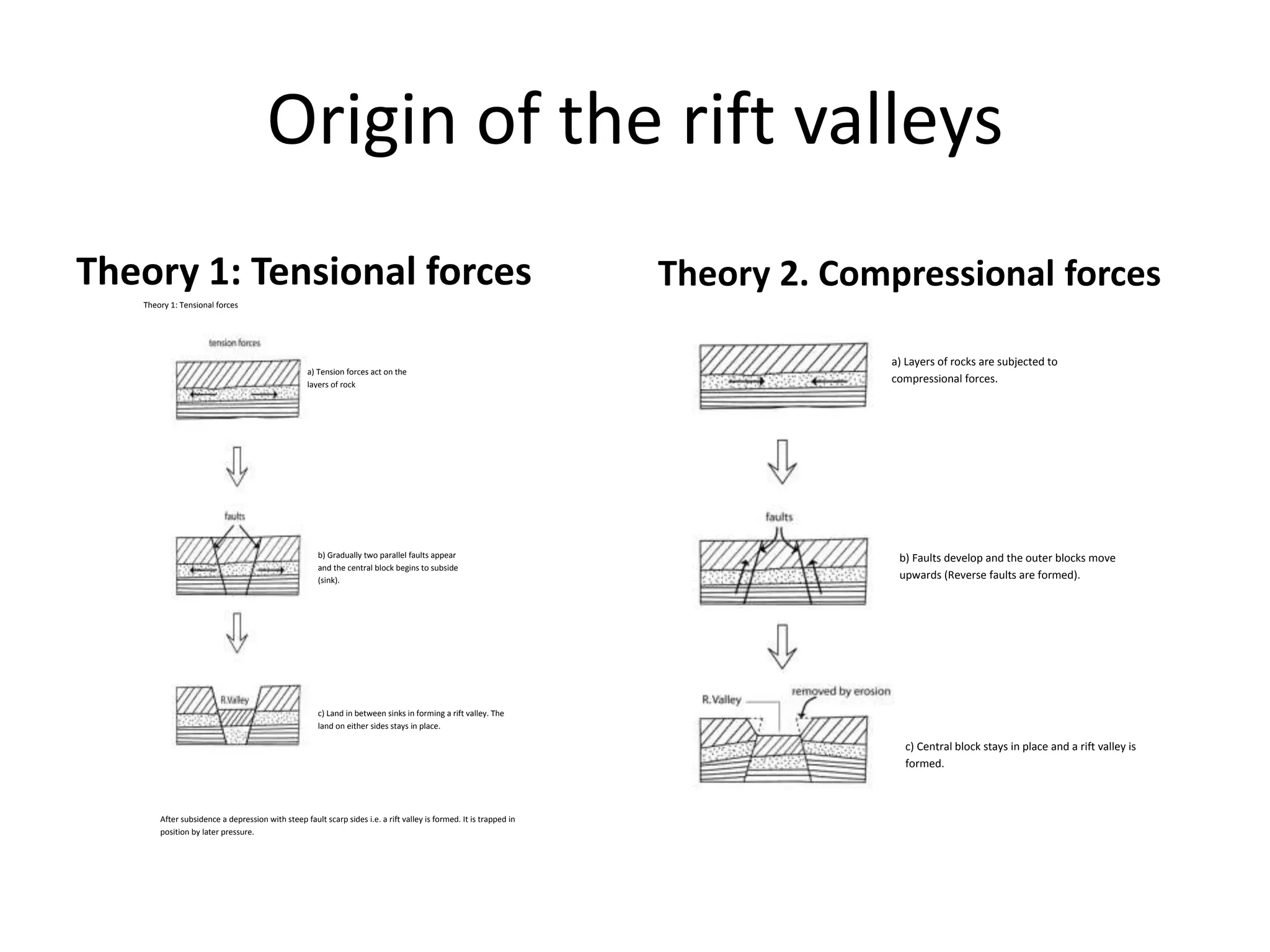
Faulting occurs when rocks crack or fracture due to tensional or compressional forces within the Earth's crust. This can form different types of faults such as normal faults, reverse faults, and tear faults. Faulting produces landforms like block mountains, rift valleys, tilt blocks, and escarpments. Rift valleys are long depressions bounded by parallel faults, such as those found in East Africa. They form through tension or compression and contain lakes like Lake Turkana and Lake Tanganyika. Faulting benefits the region by providing resources, attractive landscapes, and opportunities for agriculture, fishing, mining, and tourism.