Pranav Vashistha presented on cloud computing. He discussed basic concepts like traditional on-premise computing versus cloud computing. He covered first movers in cloud like Amazon, Google, and Microsoft. Pranav defined cloud computing and explained its components including clients, data centers, distributed servers. He described the three main cloud service models - Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Pranav also covered types of cloud, benefits like scalability and cost savings, and applications like storage and databases.





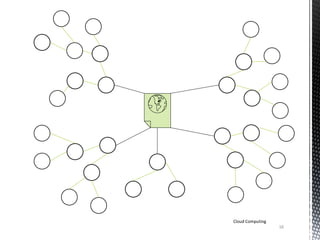
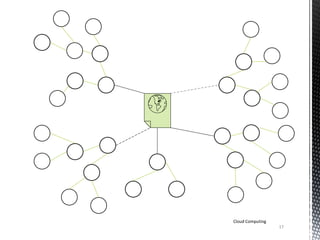
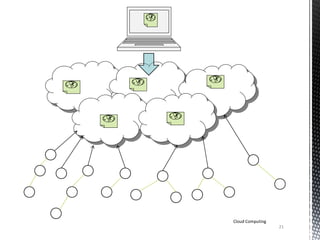
![Components of Cloud [3]
Internet
Clients
Computers
Distributed
Servers
Datacenter
Cloud Computing
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloud1-140519000512-phpapp01/85/Basics-of-Cloud-Computing-8-320.jpg)

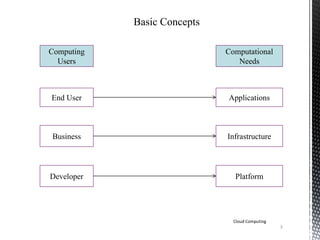
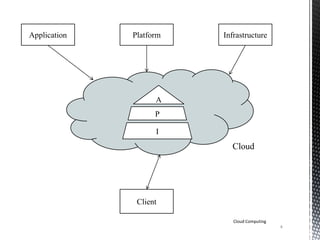
![Cloud’s Service Models [1]
The services of a cloud includes the following traits:-
• Multitenancy
• Device Independency
• Large Scalability
• Low barriers to entry.
It includes the following three models of services:-
1. Software as a Service (SaaS)
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Cloud Computing
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloud1-140519000512-phpapp01/85/Basics-of-Cloud-Computing-10-320.jpg)
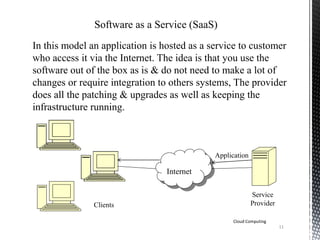



![15
Cloud Computing
Why Cloud Computing [2]
Traditional approach of hosting..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloud1-140519000512-phpapp01/85/Basics-of-Cloud-Computing-15-320.jpg)