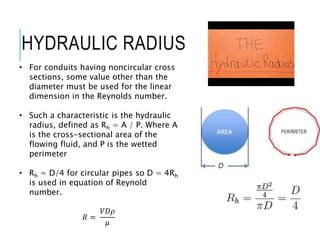
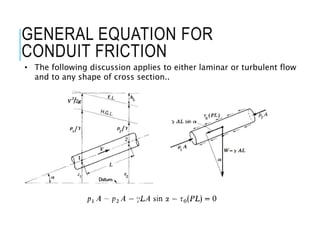
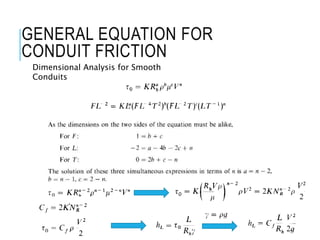
This document discusses laminar flow in pipes. It introduces that piping systems are commonly studied in engineering. For laminar flow, velocity alone does not determine if flow is laminar or turbulent, there are three flow regimes based on Reynolds number: laminar, transition, and turbulent flow. The critical Reynolds number that defines the transition between laminar and turbulent flow is around 2,000. For non-circular pipes, hydraulic radius replaces diameter in Reynolds number calculations. The document then discusses equations for conduit friction loss and laminar flow in pipes specifically.