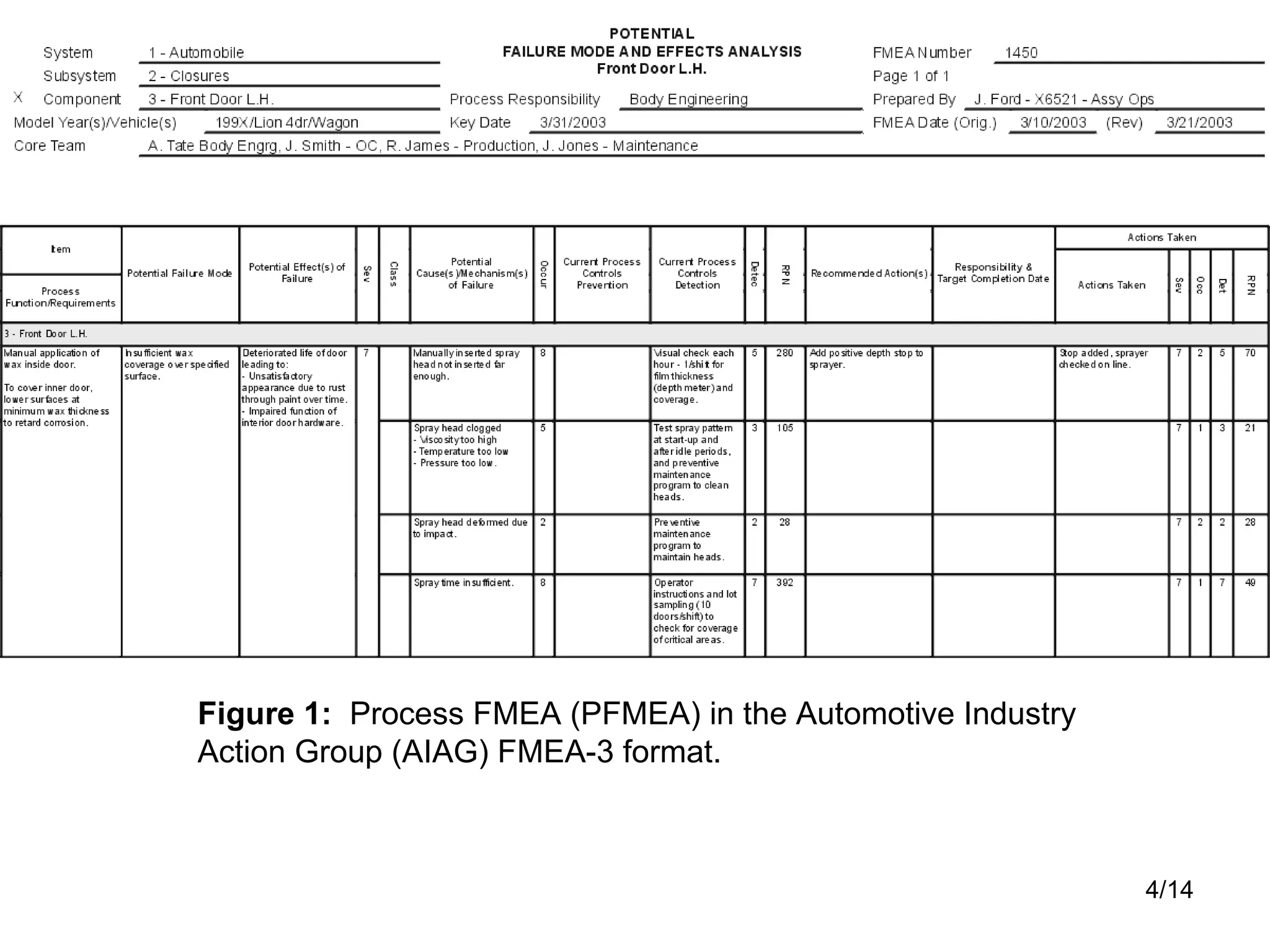
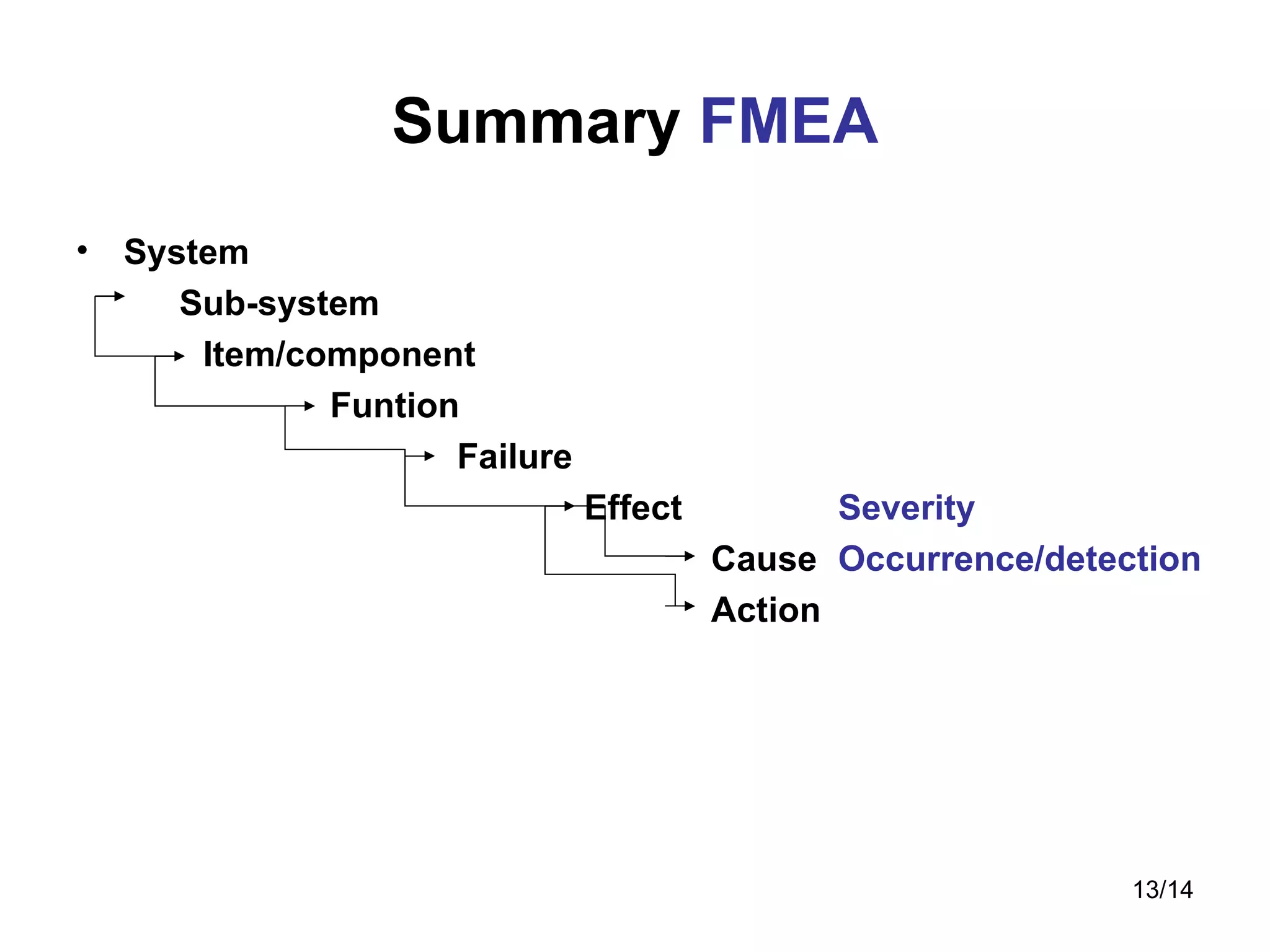
FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) and FMECA (Failure Modes, Effects and Criticality Analysis) are methodologies used to identify potential failures, assess risk, and prioritize corrective actions. They involve identifying items, functions, failures, effects, causes, controls, and recommended actions. Risk is evaluated using Risk Priority Numbers for FMEA or a Criticality Analysis for FMECA. The results are used to improve design, increase reliability, and reduce costs.