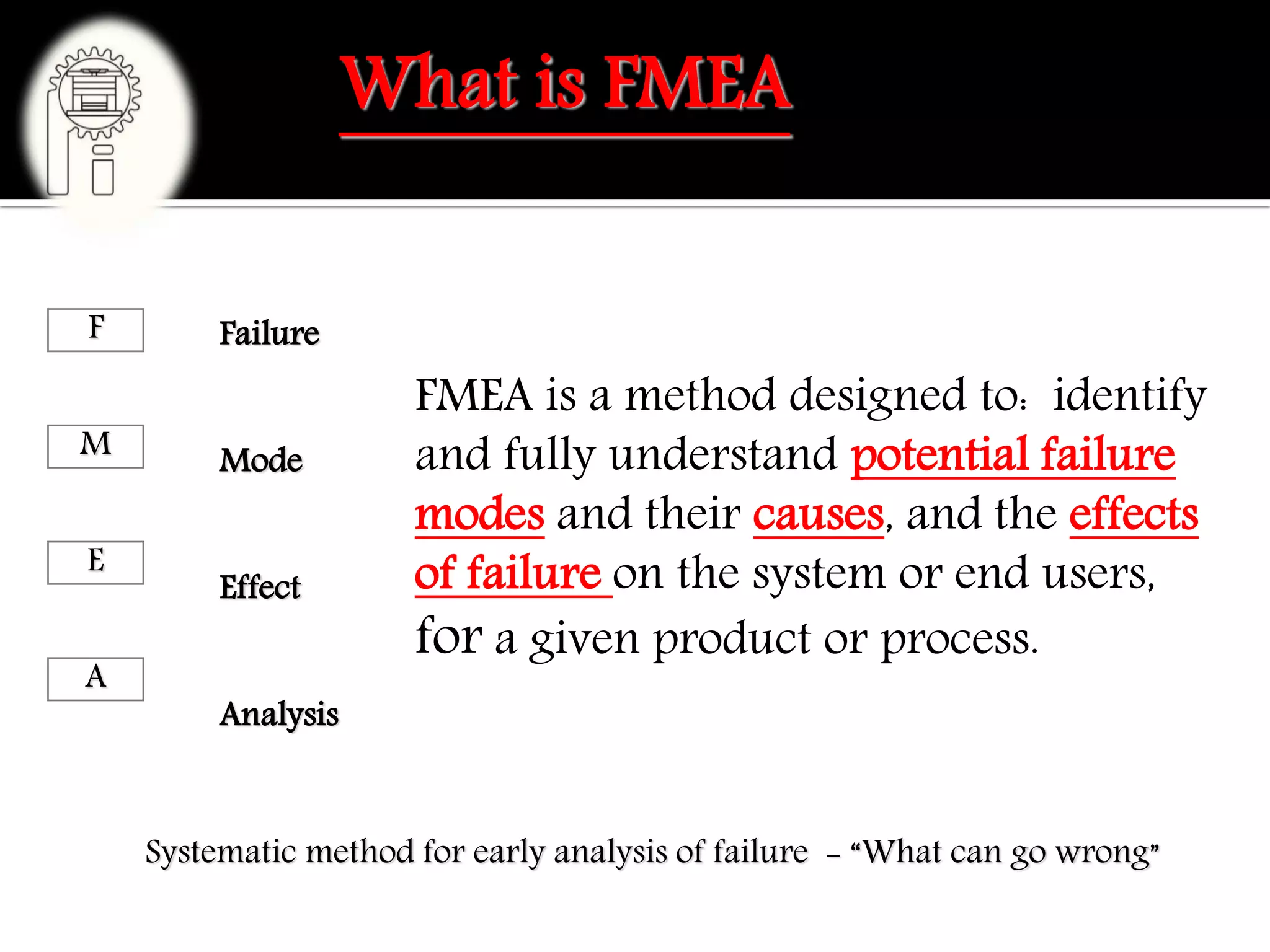
This document provides an overview of failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA). It defines FMEA as a method to identify potential failure modes, causes, and effects. The document outlines the history of FMEA, from its origins in 1955 to its widespread use today. It also describes the different types of FMEA (system, design, process) and when each is applied. Key aspects of performing a process FMEA like potential causes, controls, severity, occurrence, detection, and risk priority number are defined.