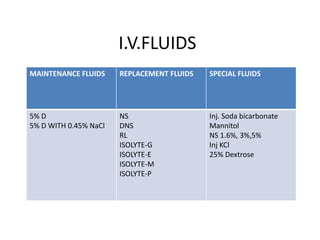
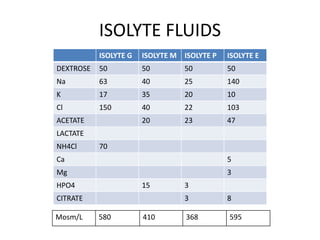
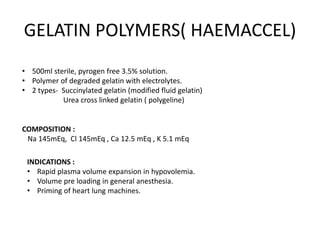
This document summarizes a presentation on fluids and electrolytes given by Dr. Ankit Kaura. It discusses various intravenous fluids including crystalloids like normal saline, Ringer's lactate, and dextrose saline as well as colloids like albumin, dextran, gelatin, and hydroxyethyl starch. For each fluid, the document outlines their composition, pharmacological properties, indications, contraindications, and administration details. The effects of large volume crystalloid infusion and differences between colloids are also summarized.