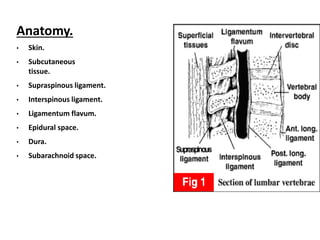
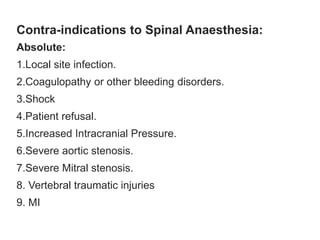
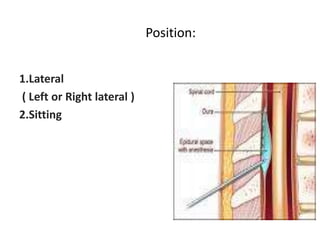
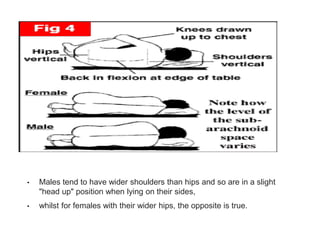
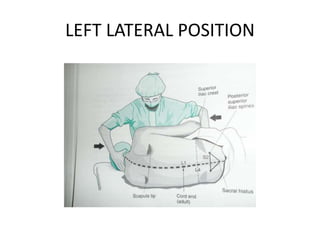
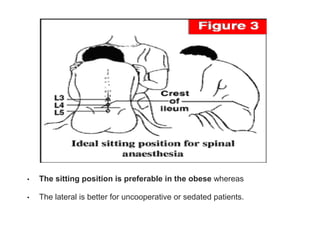
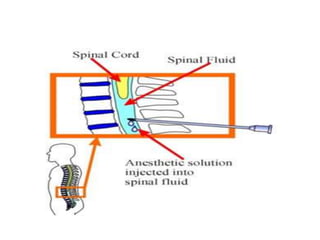
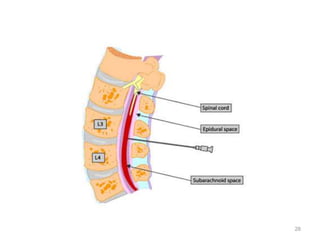
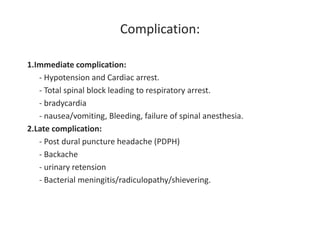
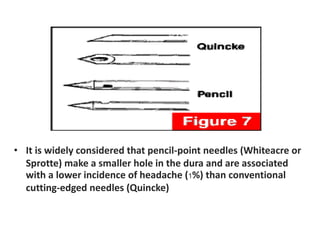
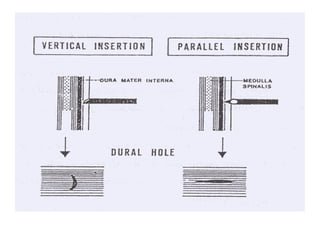
Spinal anesthesia involves injecting local anesthetic into the fluid-filled space surrounding the spinal cord. This blocks pain and other sensations below the injection site. The document discusses the anatomy of spinal anesthesia, commonly used local anesthetics, indications, contraindications, proper administration technique, and potential complications and their treatments. It provides a comprehensive overview of spinal anesthesia.