Embed presentation
Download to read offline




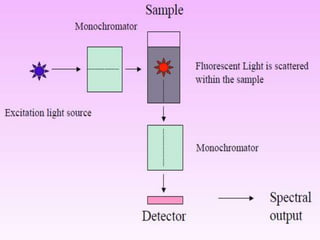






Two main types of instruments for fluorescence analysis are filter fluorimeters and spectrofluorometers. Filter fluorimeters use filters and monochromators to select excitation and emission wavelengths, while spectrofluorometers use a light source, filters or monochromators to select excitation wavelengths, and detectors to measure emission intensities of multiple wavelengths simultaneously. Lasers provide high intensity light at narrow wavelengths but have limited tunability, while other sources like mercury and xenon lamps have adjustable wavelengths but lower intensity. Monochromators are used to precisely select wavelengths but cannot block all stray light.










