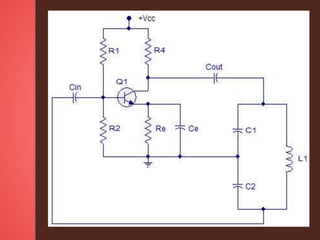
An electronic oscillator is a circuit that produces periodic signals like sine or square waves, classified mainly as voltage-controlled oscillators. The Colpitts oscillator, invented by Edwin H. Colpitts in 1916, generates high-frequency sinusoidal oscillations and consists of an RC-coupled amplifier and feedback network. It finds applications in generating high-frequency signals for mobile and radio communications and requires specific configurations for sustained oscillation frequencies.