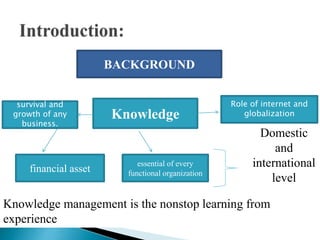
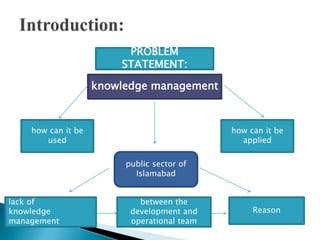
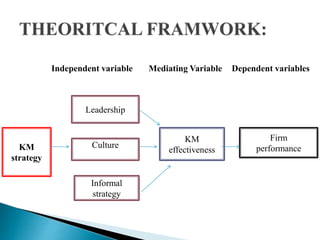
The document discusses knowledge management (KM) effectiveness in the public sector of Islamabad. It aims to determine the relationship between leadership, culture, KM strategy, information technology, and firm performance on KM effectiveness. It presents hypotheses about the positive impacts of leadership, culture, KM strategy, and information technology on KM effectiveness. The study found a lack of KM strategy and leadership negatively impacted projects. It suggests KM effectiveness acts as a mediator to improve organizational performance. Future research should validate findings in other organizations and sectors.