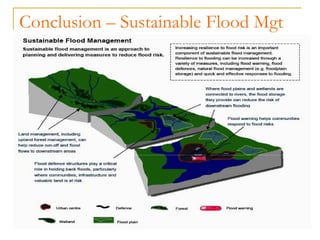
The document outlines a two phase process for flood management: 1) non-structural and 2) structural approaches. Non-structural approaches involve flood risk assessment and planning. Structural approaches involve both large-scale flood defense systems and small-scale, sustainable urban drainage systems to control stormwater runoff. These systems include attenuation tanks, filter strips, permeable surfaces, basins, ponds, and self-closing flood barriers. The goal is to implement both non-structural planning and structural defenses to holistically manage flood risk.