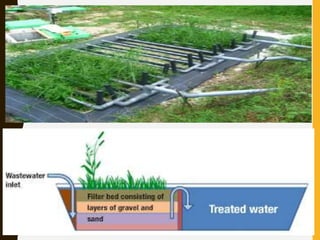
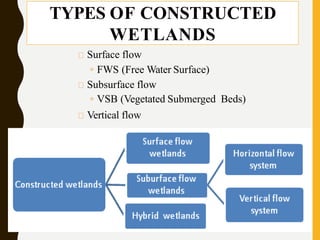
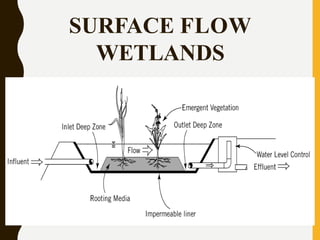
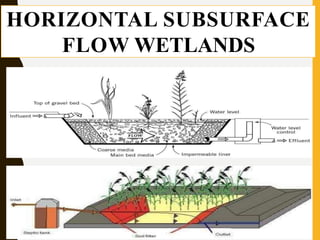
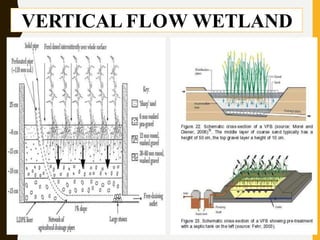
Constructed wetlands are cost-effective wastewater treatment systems utilizing shallow treatment cells with vegetation, requiring minimal maintenance and energy. They effectively remove solids, nutrients, and pathogens through natural processes and can provide aesthetic and ecological benefits. Different types of constructed wetlands, such as free water surface and subsurface systems, cater to varying climatic conditions and operational needs.