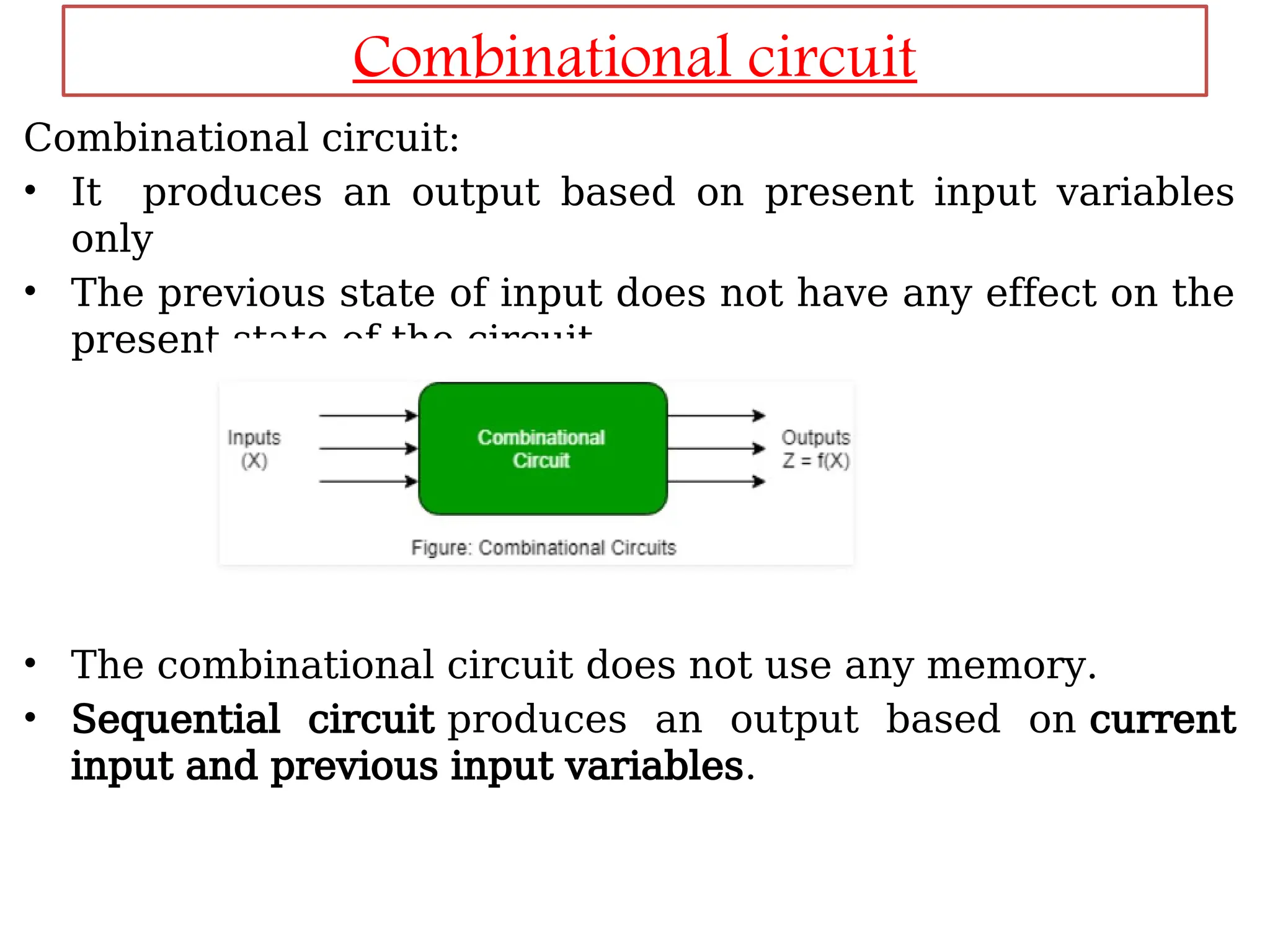
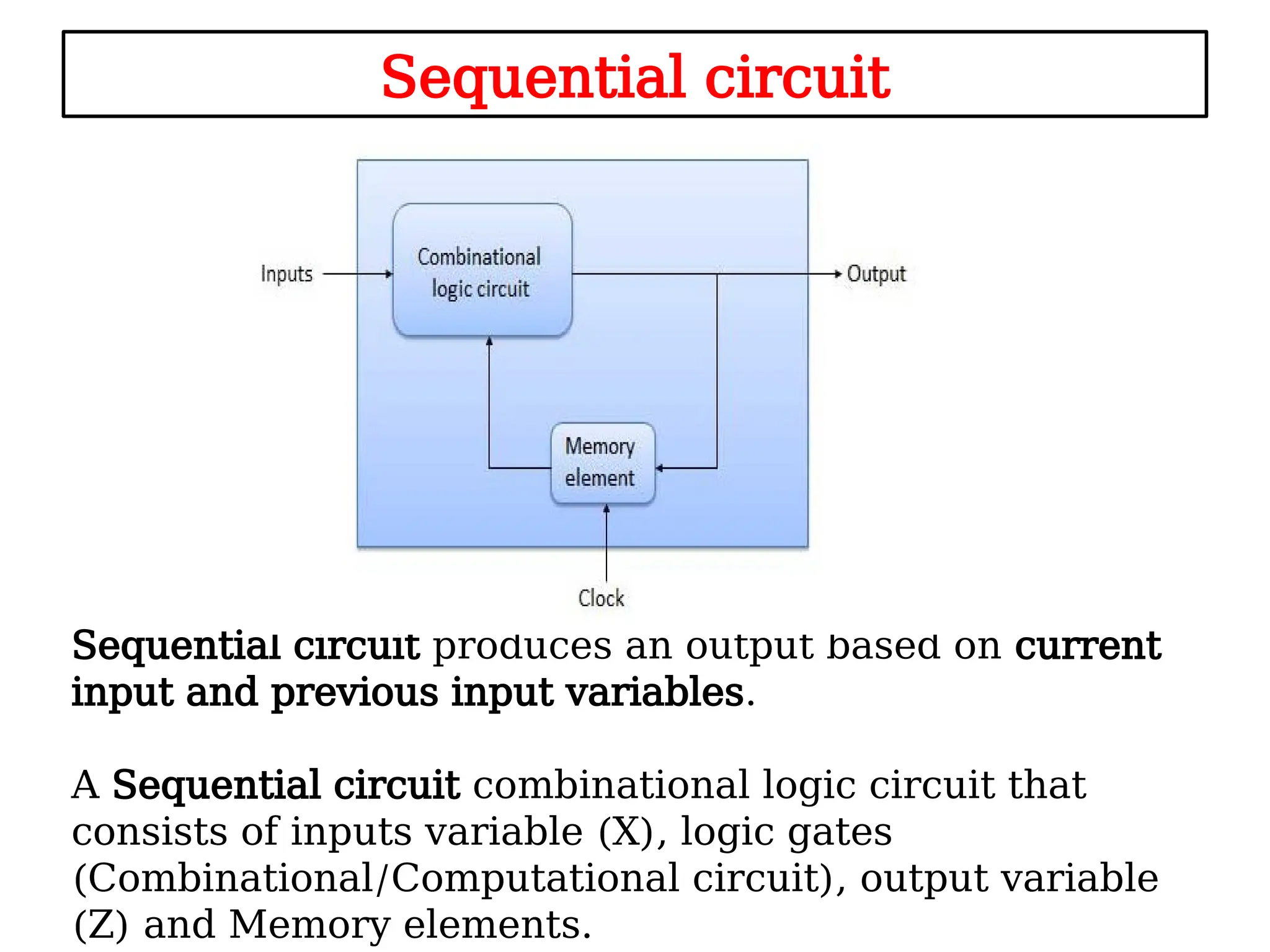
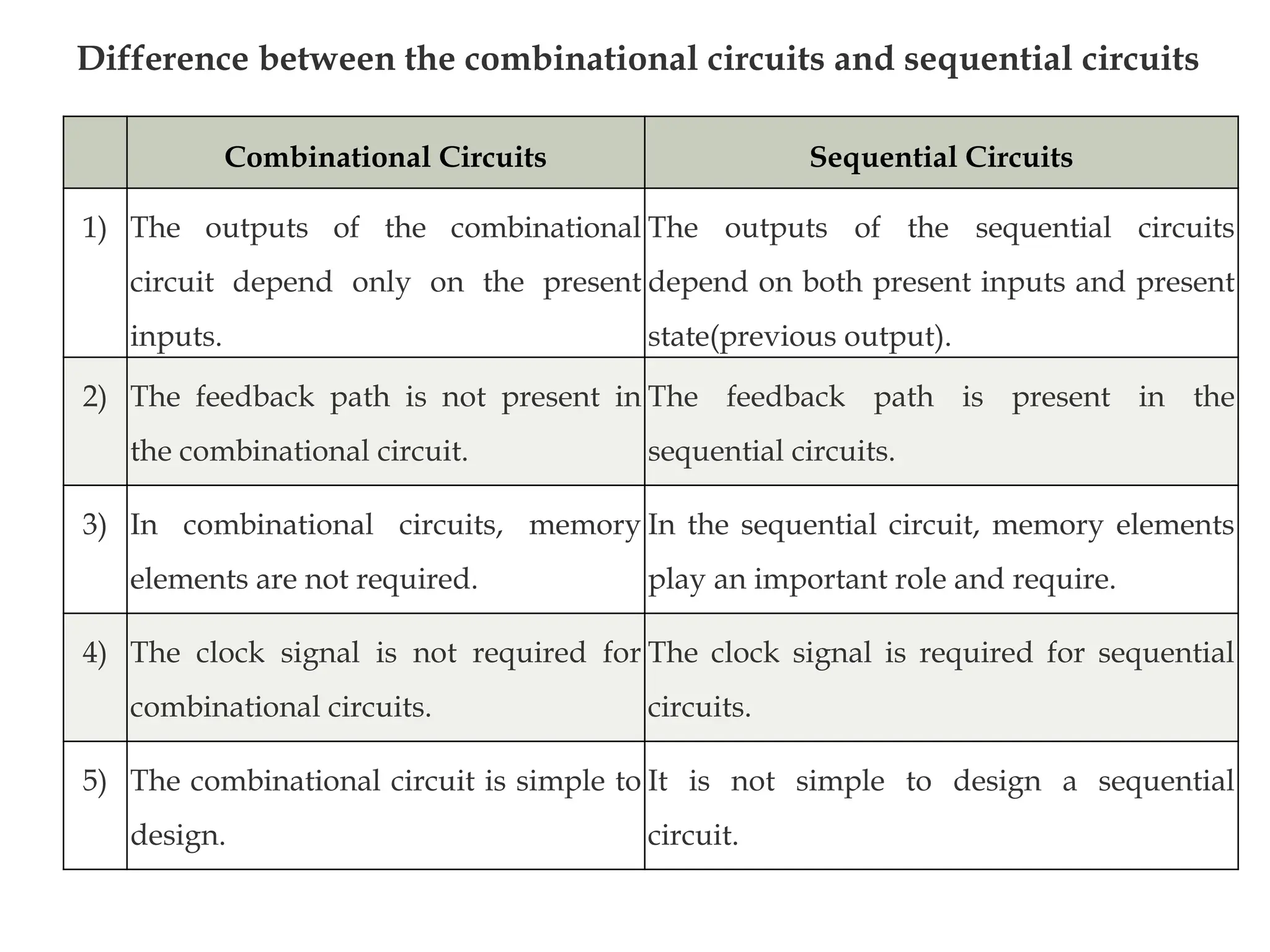
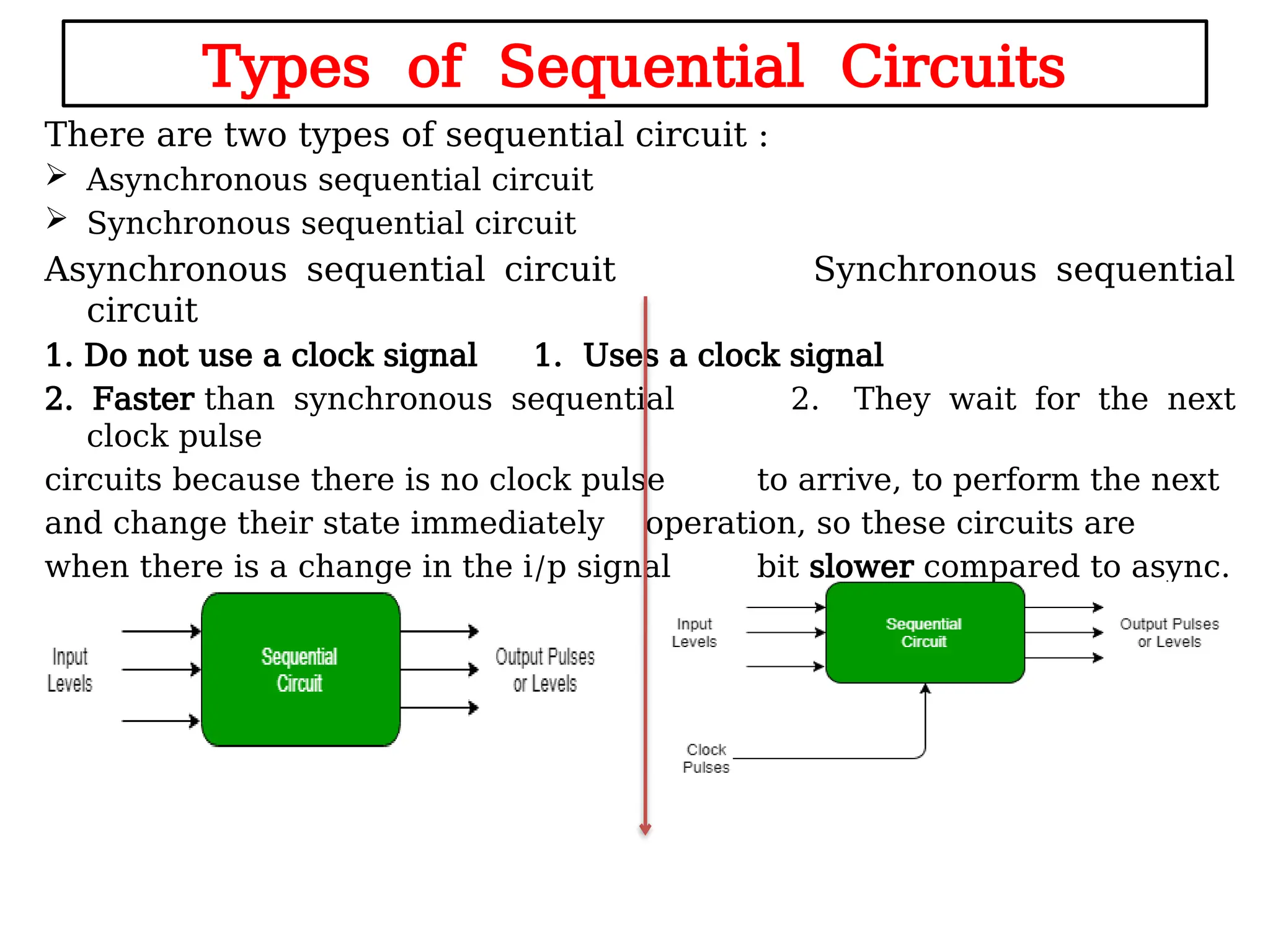
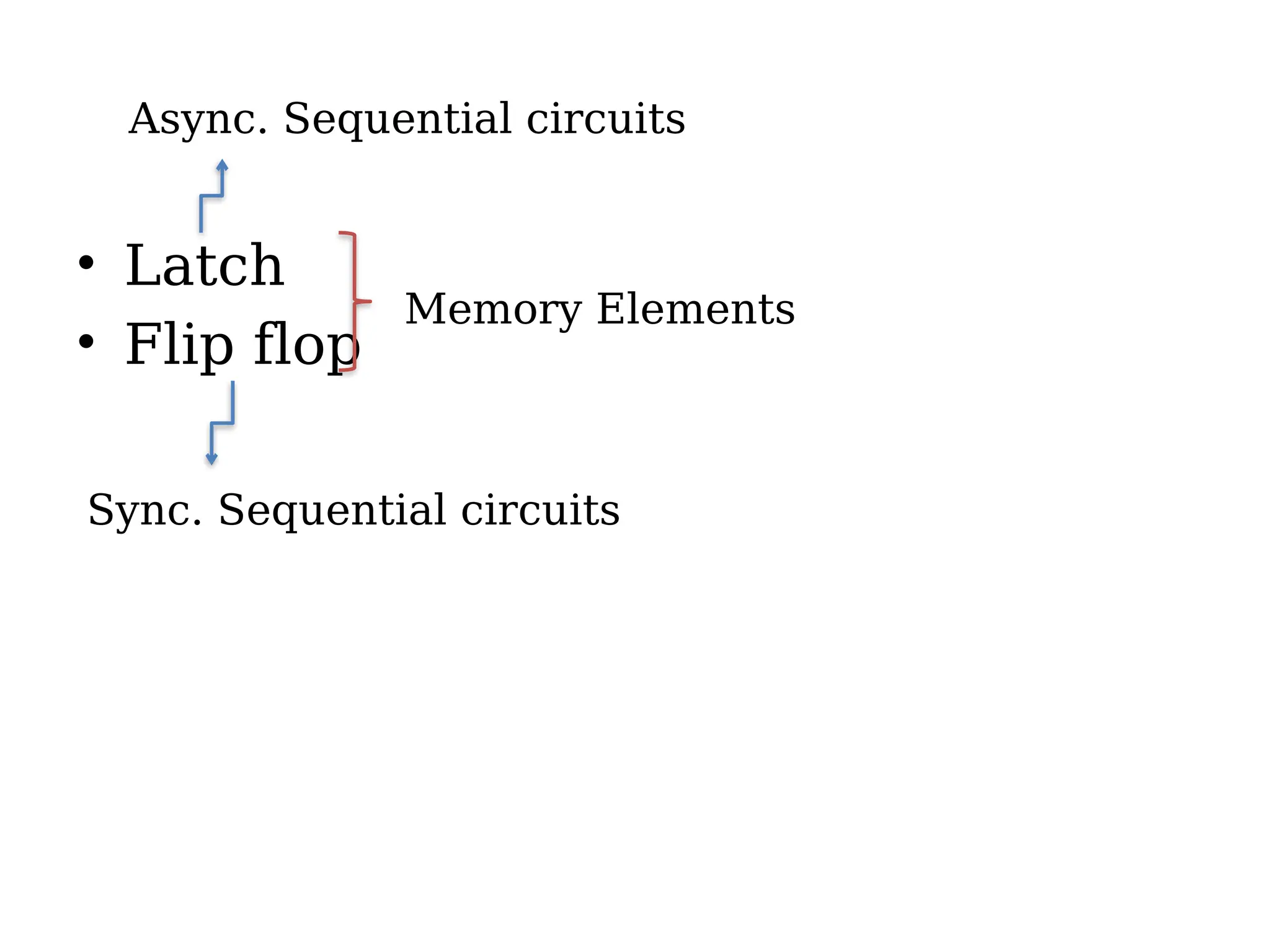
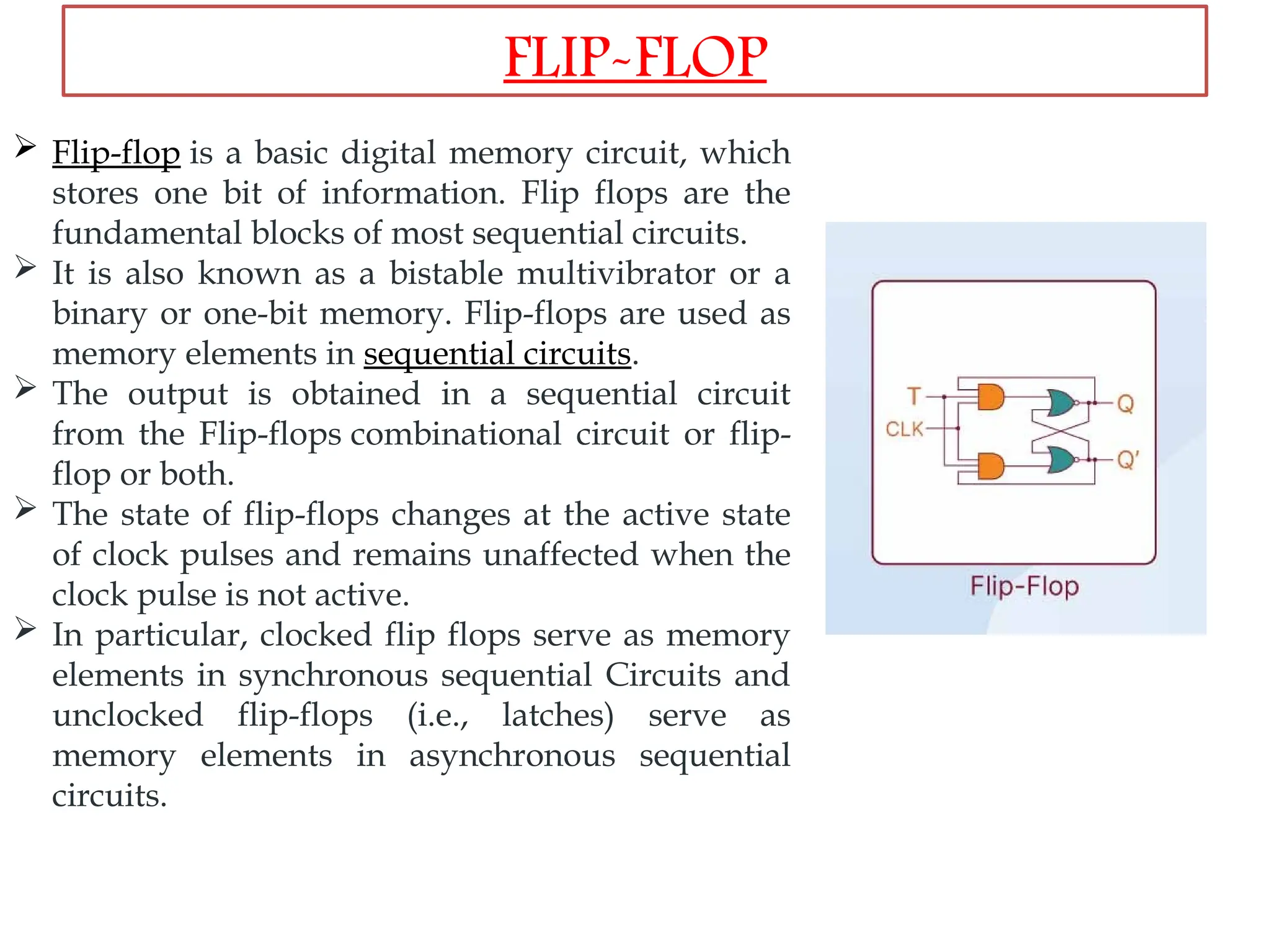
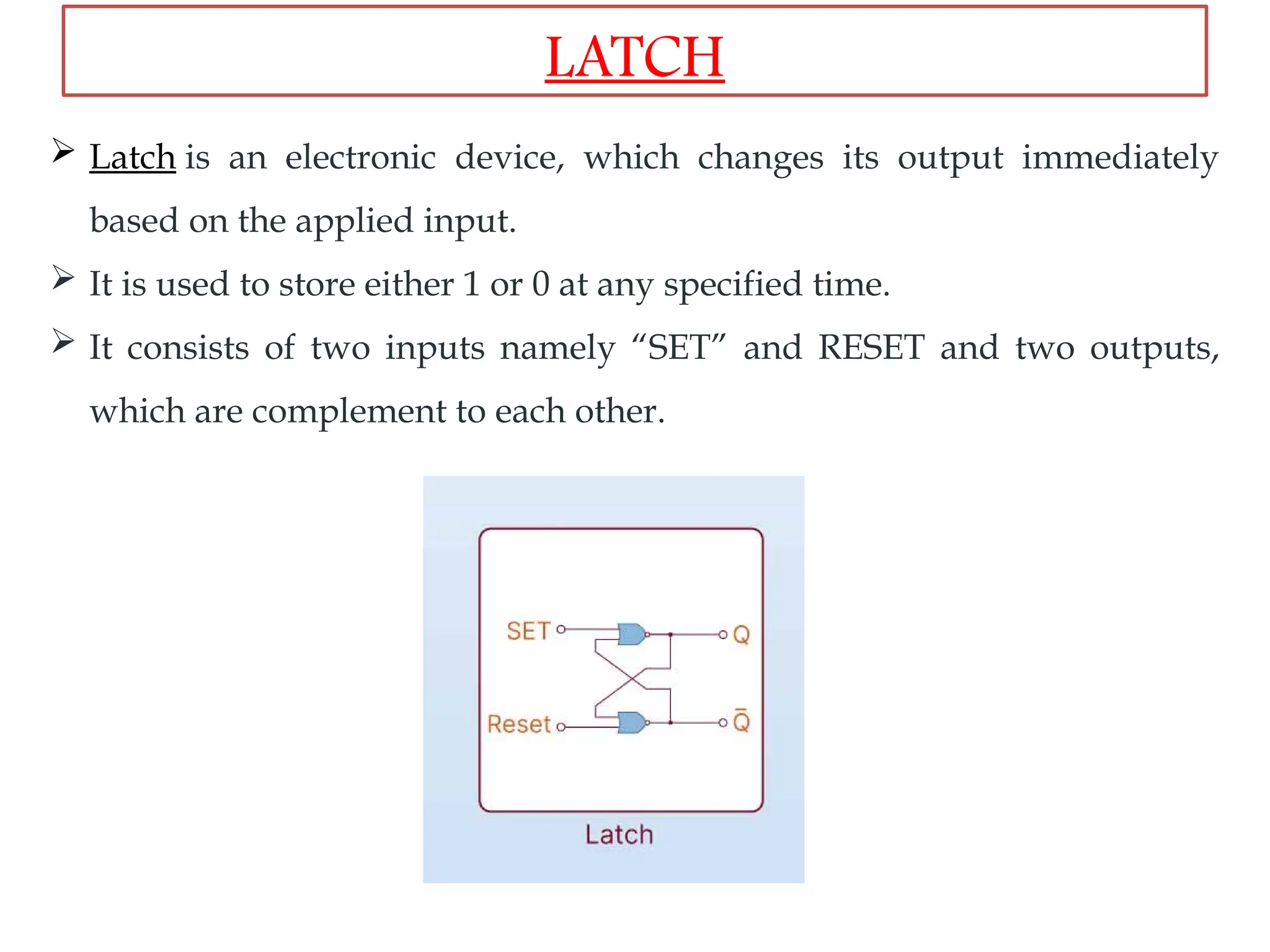
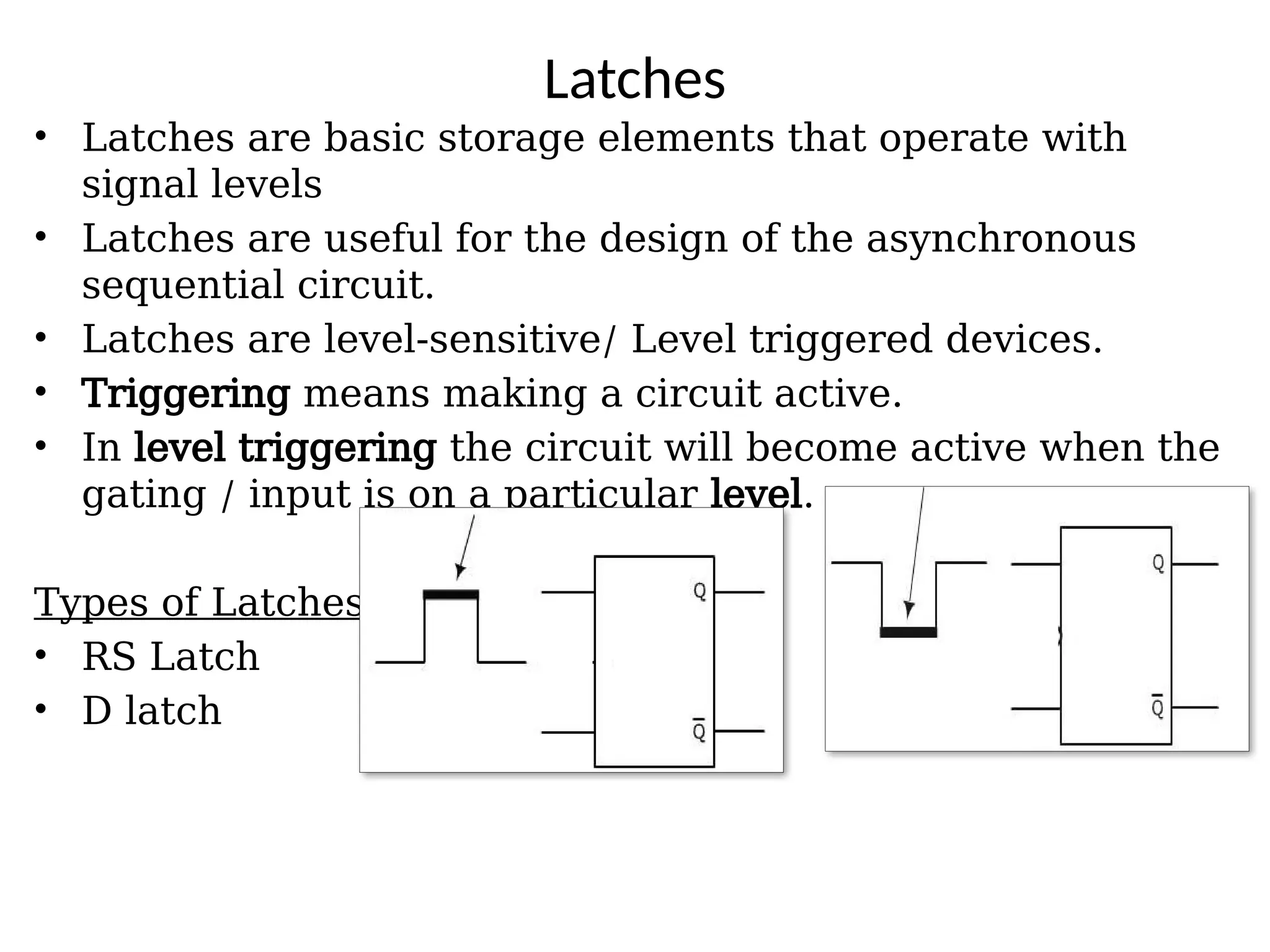
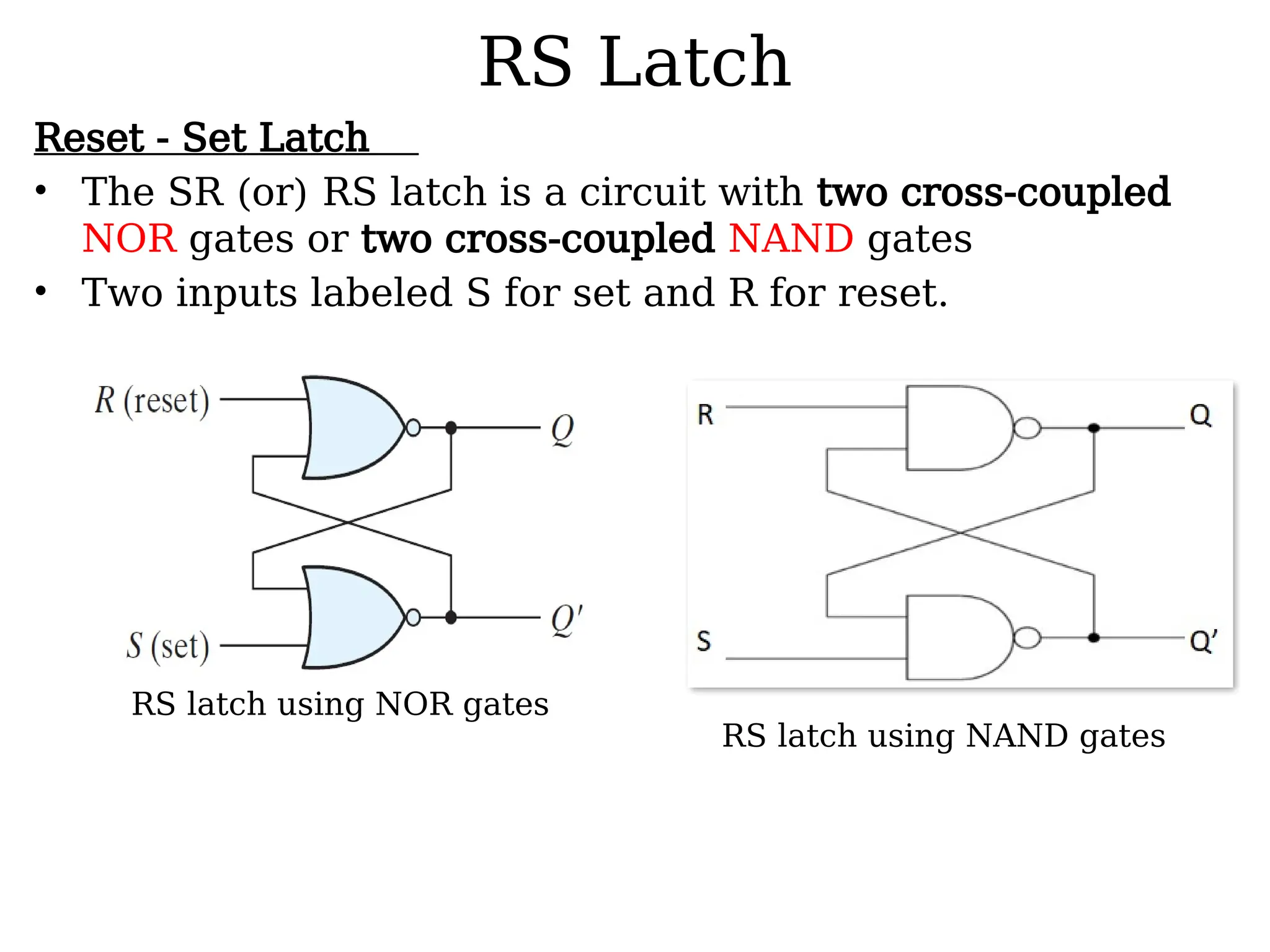
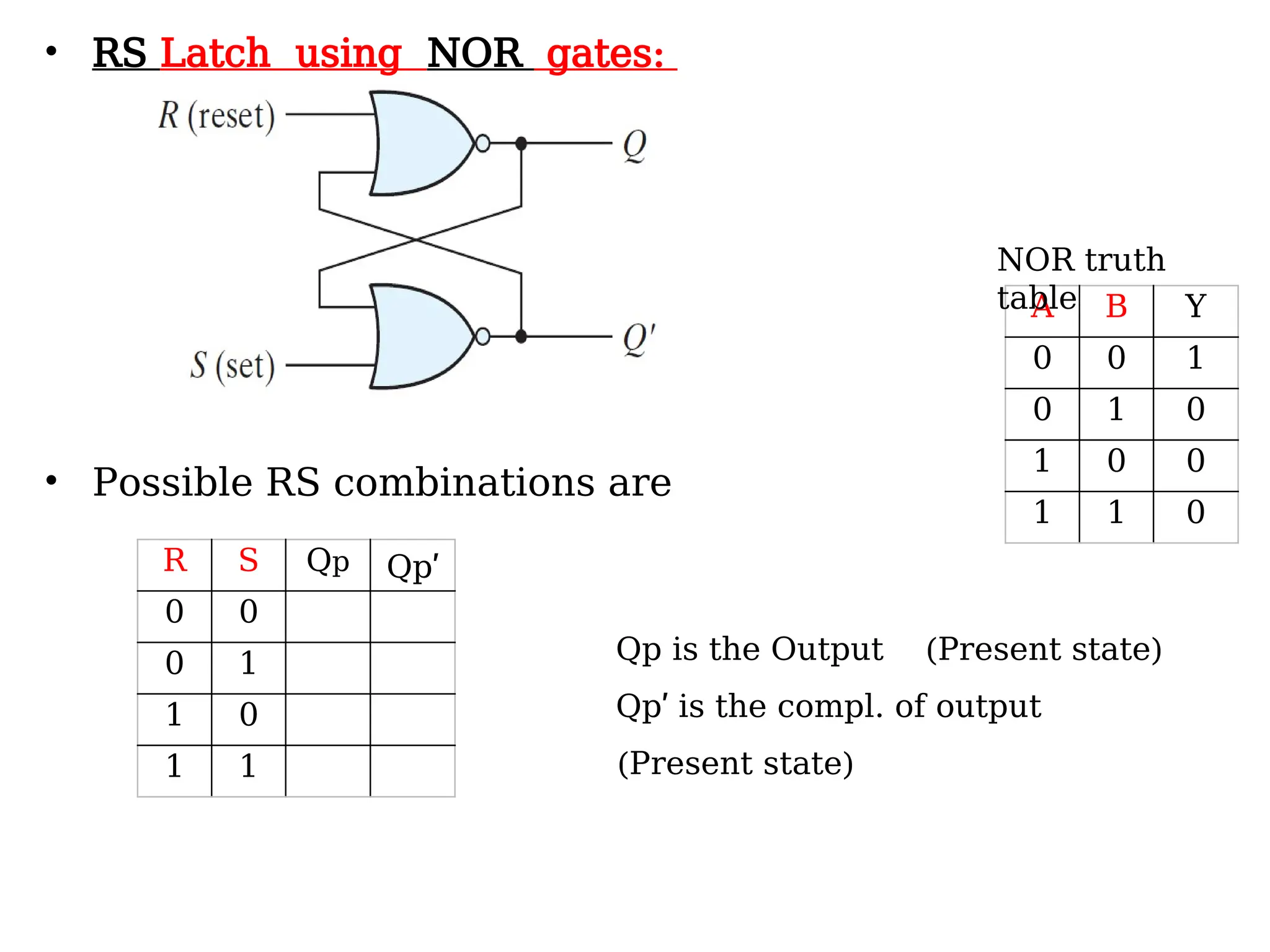
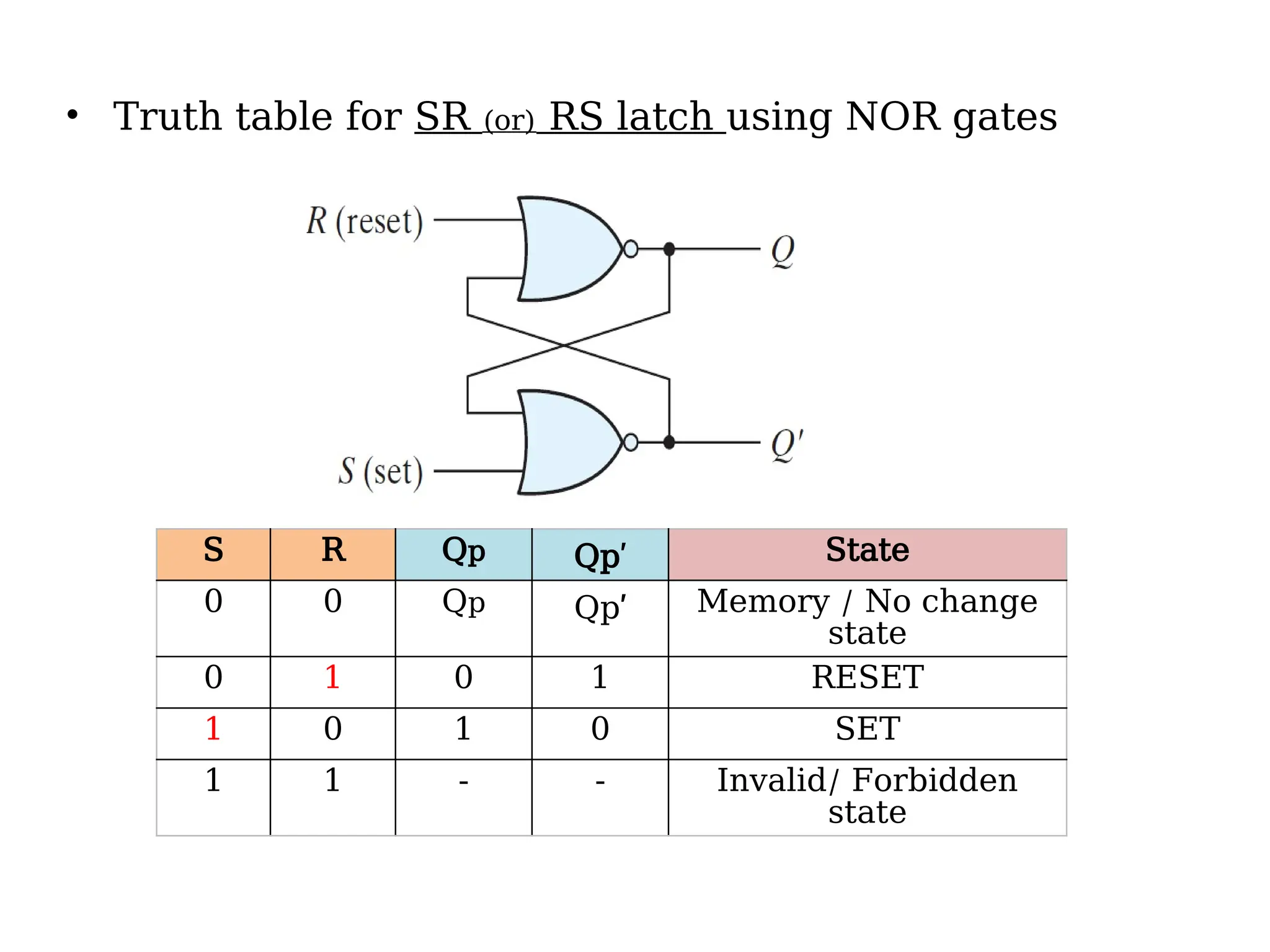
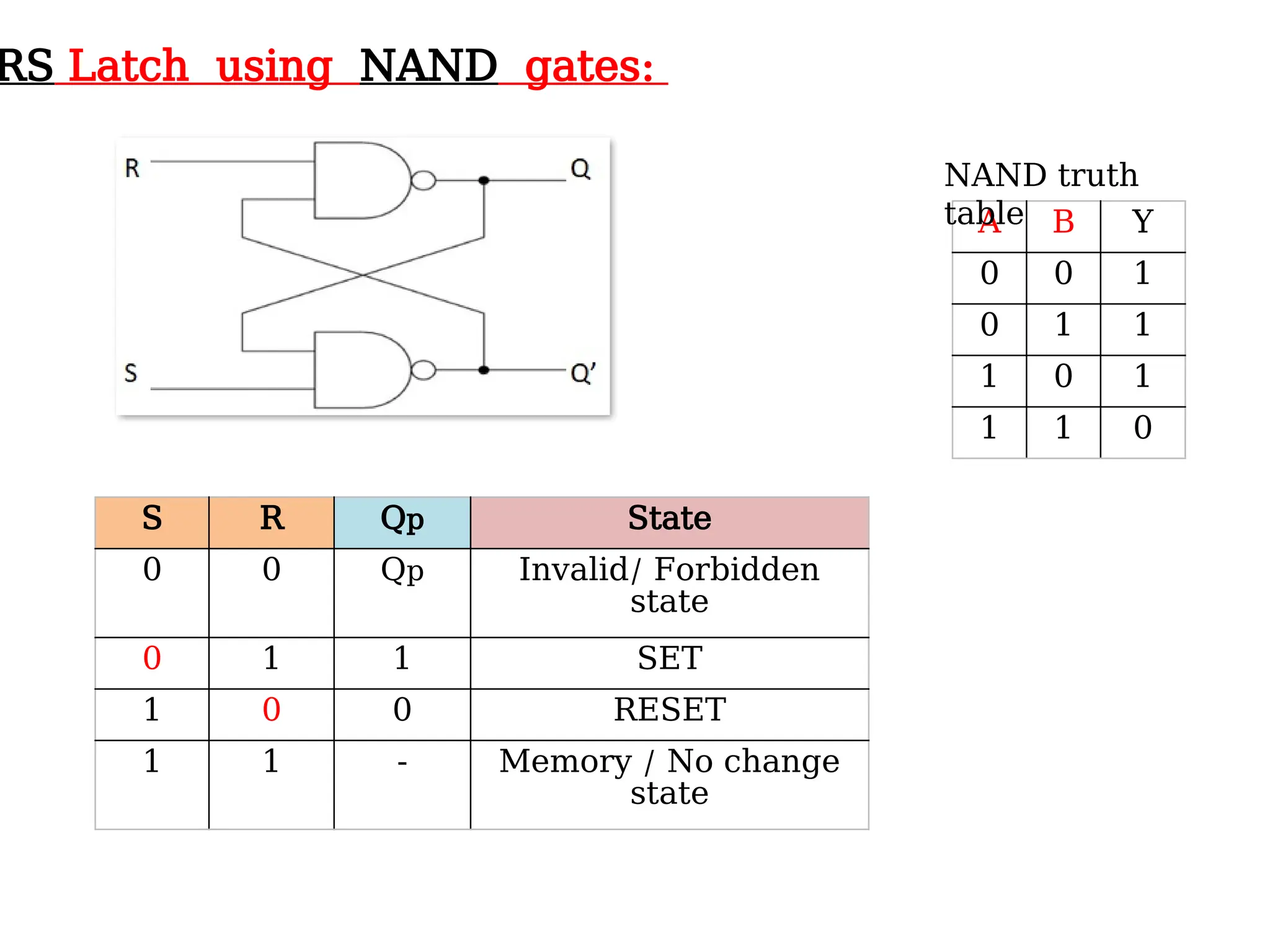
Sequential logic circuits are digital circuits that depend on both current inputs and historical states, distinguishing them from combinational circuits that rely only on present inputs. They incorporate memory elements, like flip-flops and latches, allowing them to maintain a state over time and requiring a clock signal for operation. Types of sequential circuits include asynchronous circuits, which do not use a clock, and synchronous circuits, which do, each having distinct applications in digital electronics.