Embed presentation
Downloaded 93 times


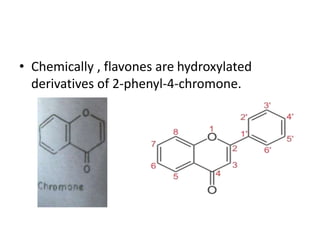


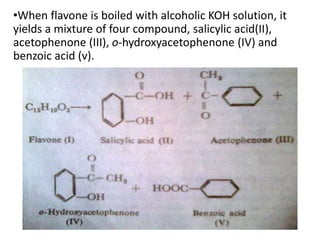
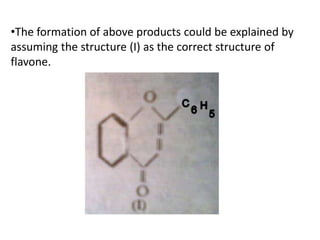
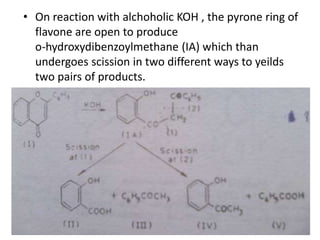
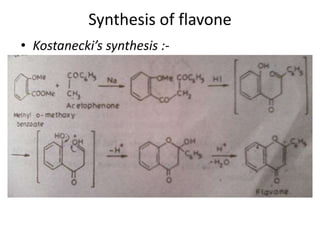
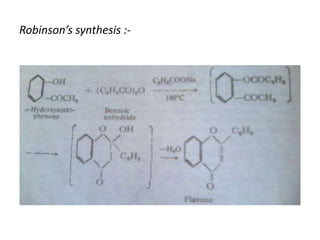
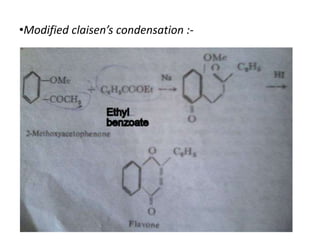
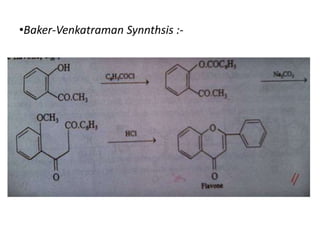
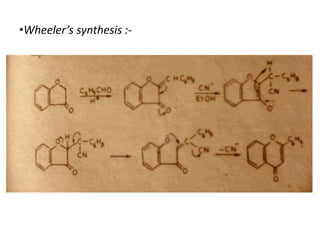

Flavones are yellow plant pigments that occur either freely or as glycosides. They are hydroxylated derivatives of 2-phenyl-4-chromone. Flavones are yellow solids that are soluble in water and ethanol. Their structure was determined to be C15H10O2 based on analytical data and molecular weight determination. When boiled with alcoholic KOH, flavones produce a mixture of four compounds: salicylic acid, acetophenone, o-hydroxyacetophenone, and benzoic acid, explaining their core structure. Several methods can be used to synthesize flavones, including Kostanecki's, Robinson's, modified Claisen's condensation, Baker-Ven












