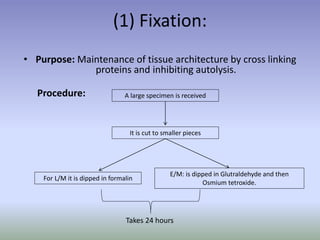
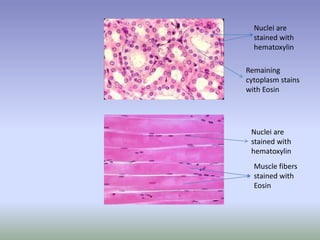
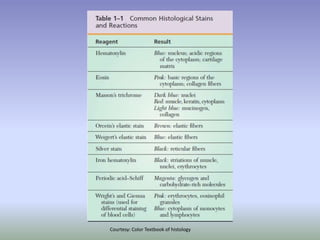
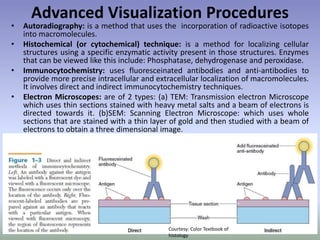
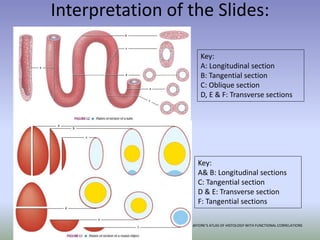
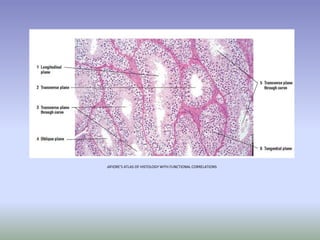
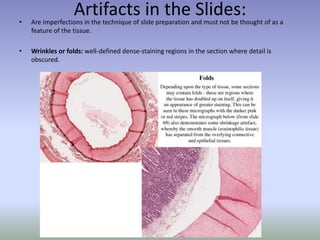
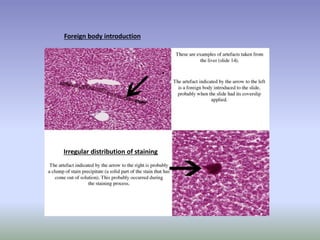
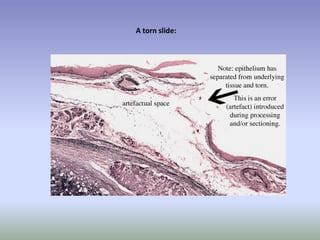
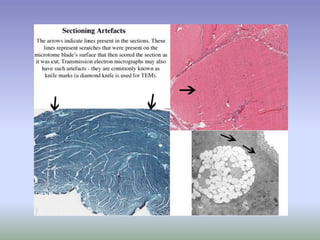
This document is a comprehensive guide on histology, detailing its objectives, the importance of microscopy, and the processes involved in preparing histological slides, such as fixation, dehydration, embedding, sectioning, mounting, and staining. It also covers various microscopy techniques, including bright-field, phase contrast, and electron microscopy, and discusses advanced visualization methods like immunocytochemistry. Additionally, it emphasizes the interpretation of slides and common artifacts encountered in histological samples.