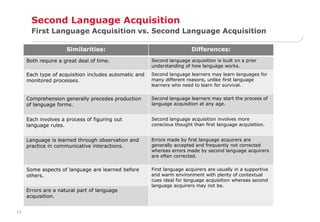
This document summarizes several theories of first and second language acquisition:
- Behaviorist theory proposed by Skinner viewed language as learned through reinforcement of behaviors. Piaget's cognitive theory saw language emerging from cognitive development and representation of knowledge. Vygotsky's socio-cultural theory emphasized the role of social interaction and the zone of proximal development.
- Theories of second language acquisition draw from first language acquisition research. Krashen's theory included five hypotheses, particularly the importance of a low affective filter. Lenneberg proposed a critical period for language acquisition. Chomsky viewed an innate universal grammar.
- Differences between first and second language acquisition include second language learners having prior language knowledge and more conscious learning,