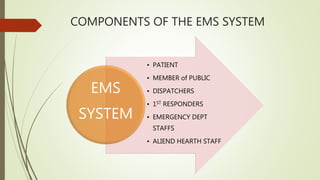
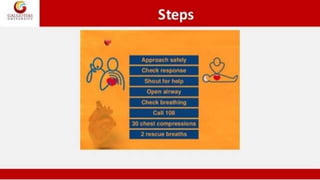
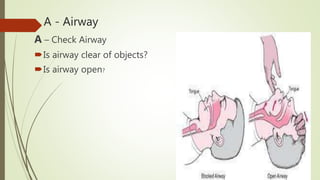
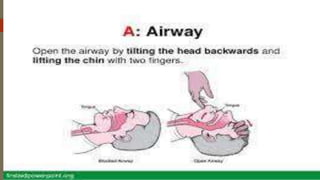
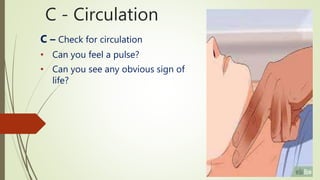
The document discusses the concepts and principles of first aid. It defines first aid as the immediate care given to prevent worsening of conditions until medical assistance is obtained. The principles of first aid include acting quickly but with a stable mind, understanding the cause of injury, and preventing worsening of the situation. It also outlines the components of an emergency medical services system and the contents of a basic first aid kit.