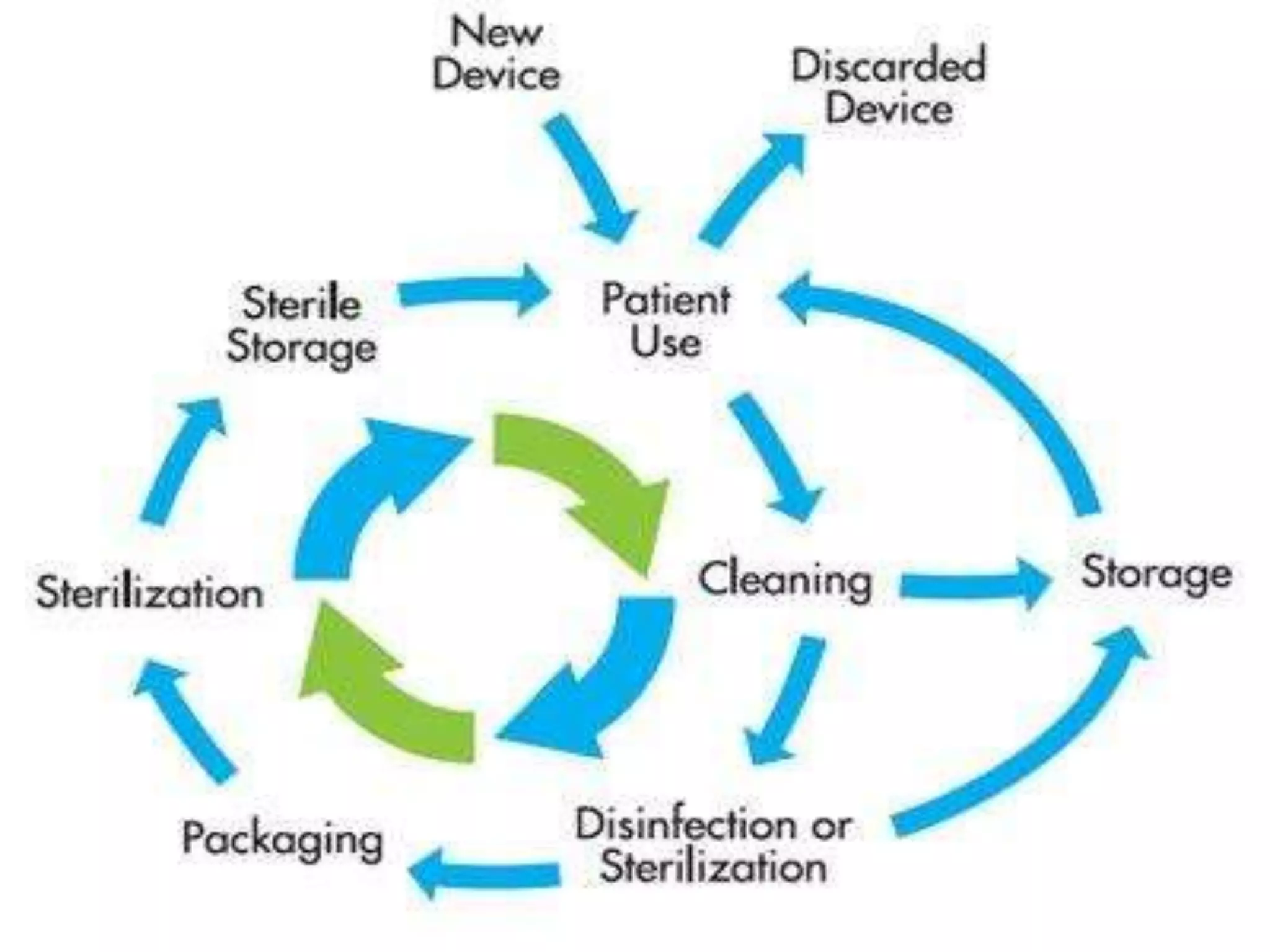
The document discusses various types of materials, equipment, and linen used in hospitals and their care and maintenance. It covers the different categories of equipment including reusable and disposable items. It provides details on the proper cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization techniques for different materials like linen, rubber goods, steel instruments, glass, and plastic items. The document also discusses the care and maintenance of other items like furniture and machinery equipment. It emphasizes the importance of maintaining proper inventory and indent records for materials and ensuring their optimal availability.