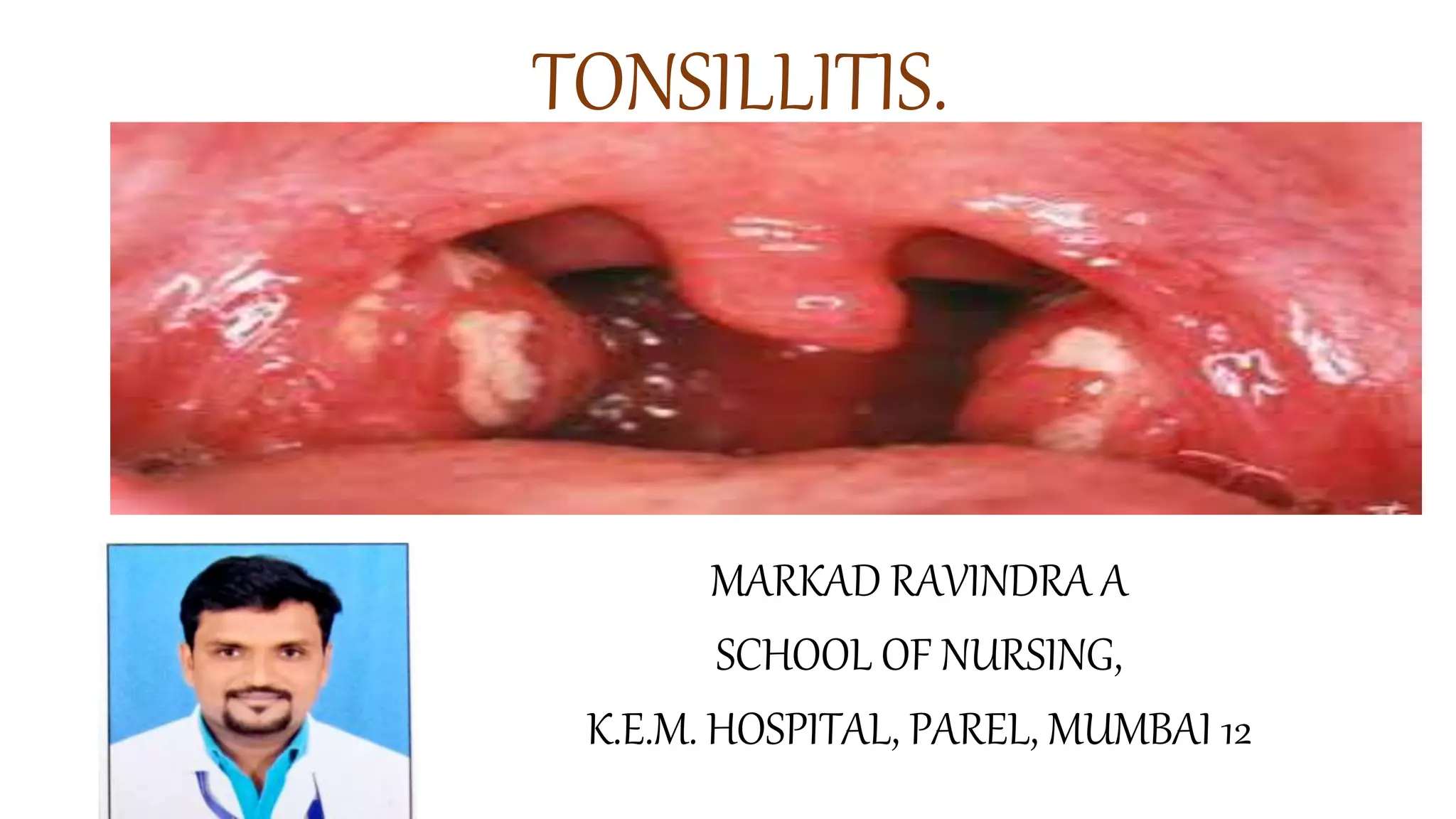
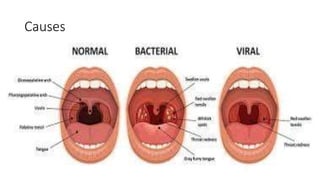
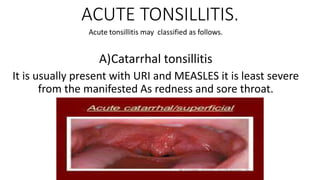
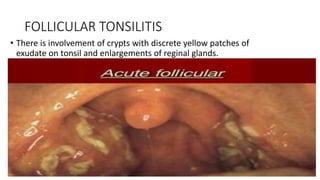
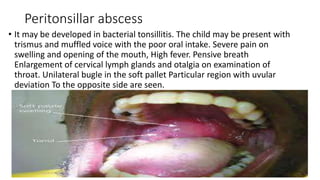
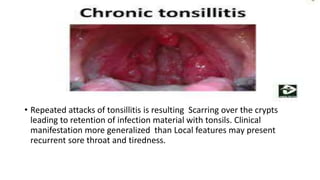
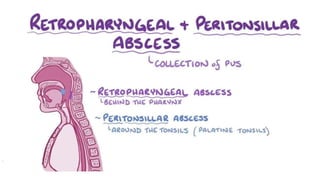
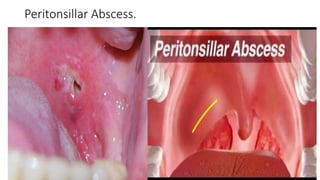
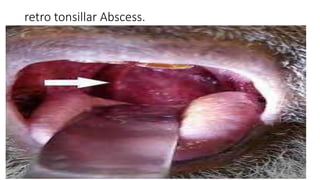
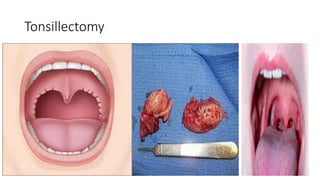
Tonsillitis is an inflammation of the tonsils, which are glands located on either side of the throat. It is commonly caused by a bacterial or viral infection. The main types of tonsillitis are acute tonsillitis and chronic tonsillitis. Acute tonsillitis causes symptoms like a sudden onset of throat pain, fever, chills, and swollen tonsils. Chronic tonsillitis can result from repeated attacks of acute tonsillitis and causes long-term issues like poor appetite, bad breath, and difficulty breathing. Complications of tonsillitis include peritonsillar and retrotonsillar abscesses. Treatment involves rest, analgesics, antibiotics, and tonsillectomy in severe or recurrent cases.