Embed presentation
Downloaded 151 times
![Network Security Henric Johnson Blekinge Institute of Technology, Sweden www.its.bth.se/staff/hjo/ [email_address] +46 708 250375](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-ns1-13479/75/Intoduction-to-Network-Security-NS1-1-2048.jpg)


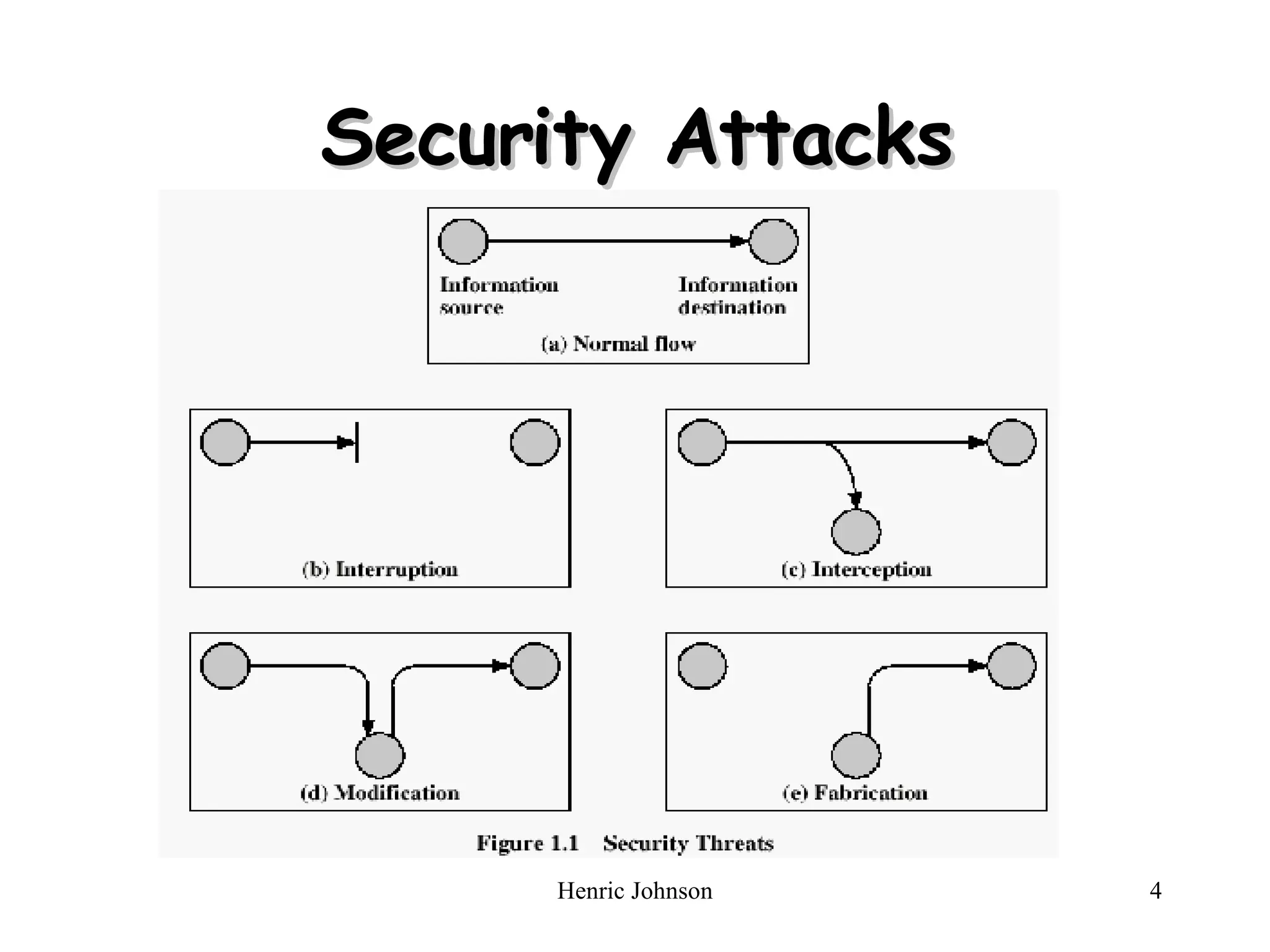

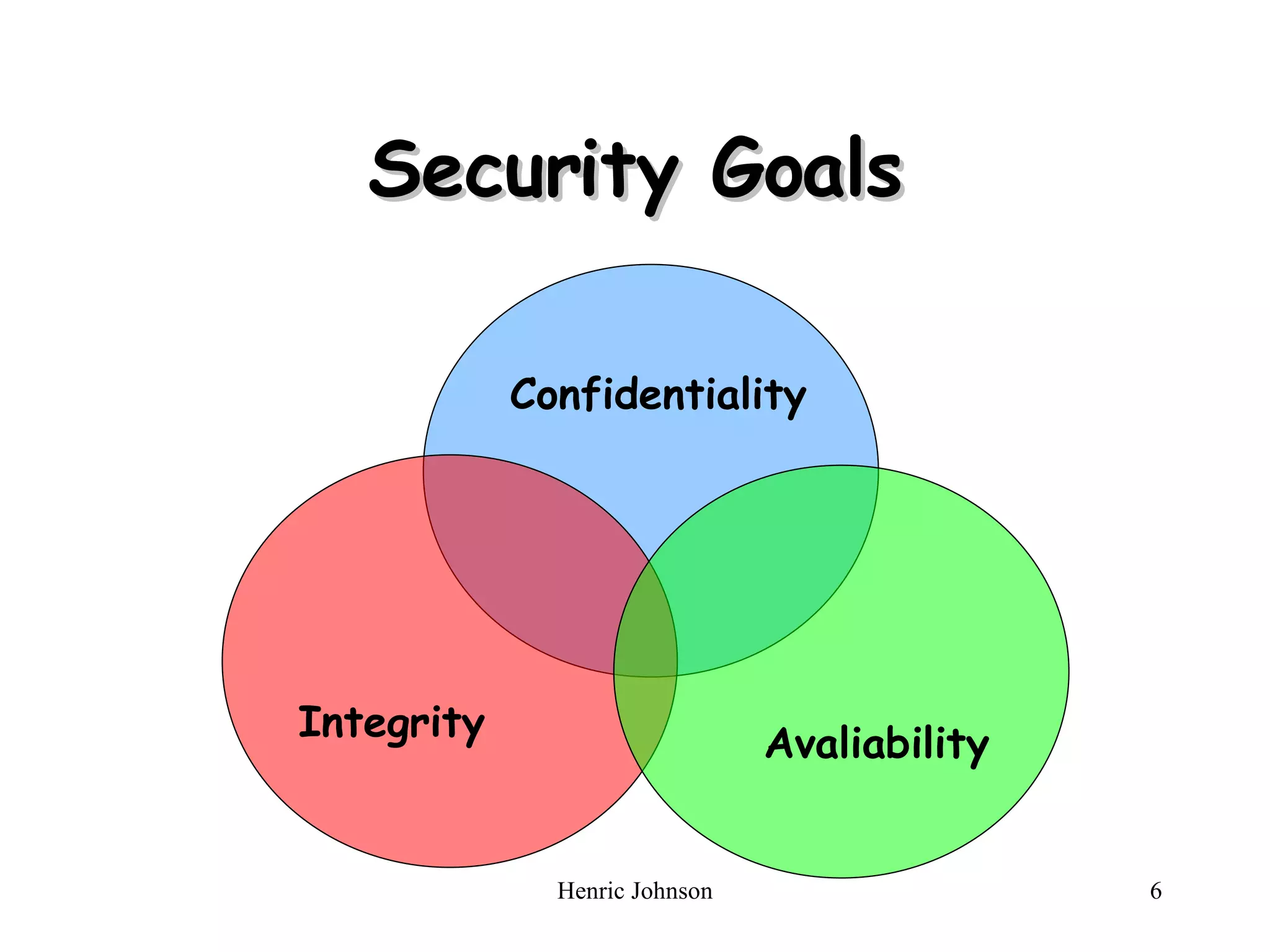
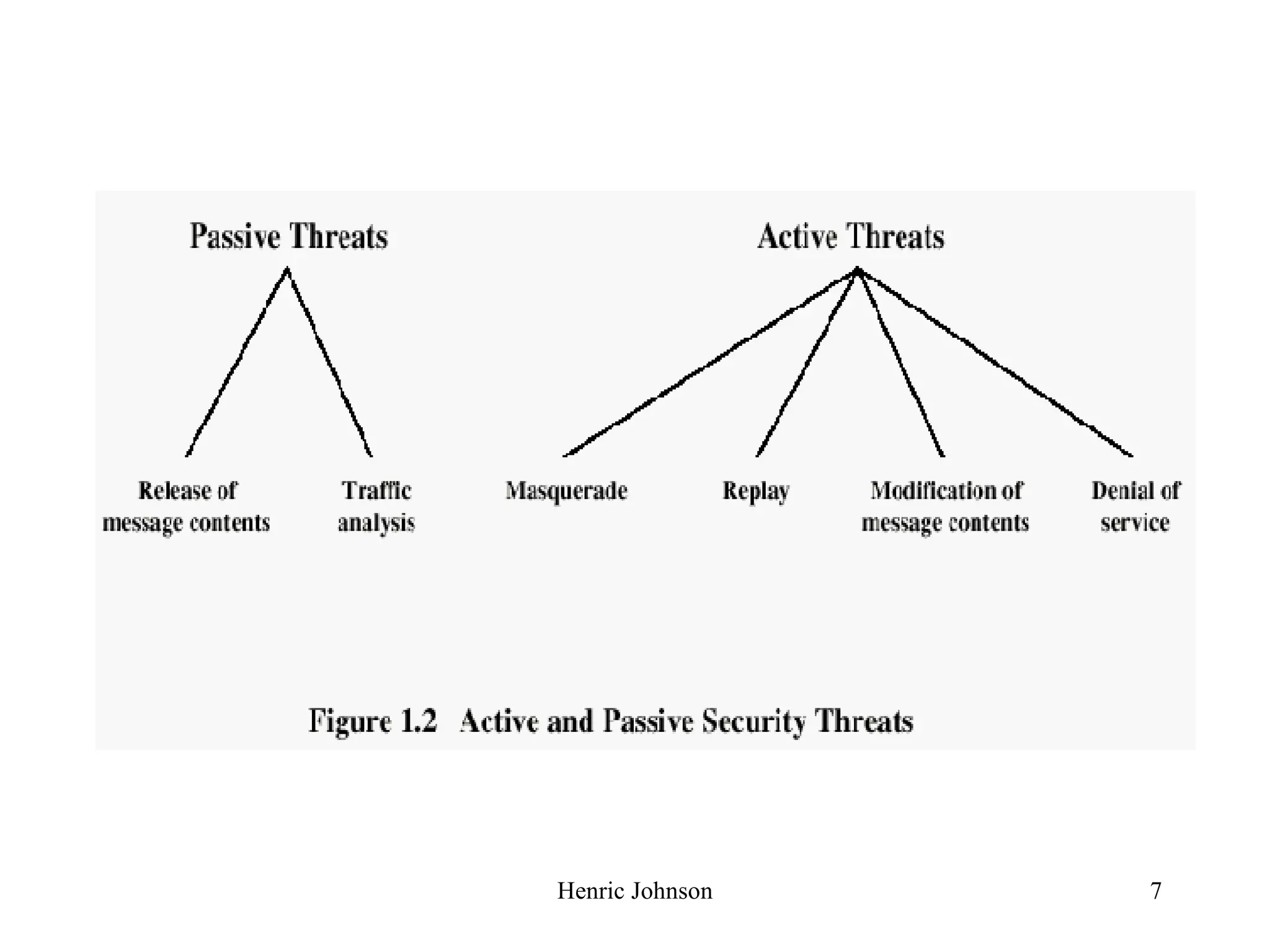

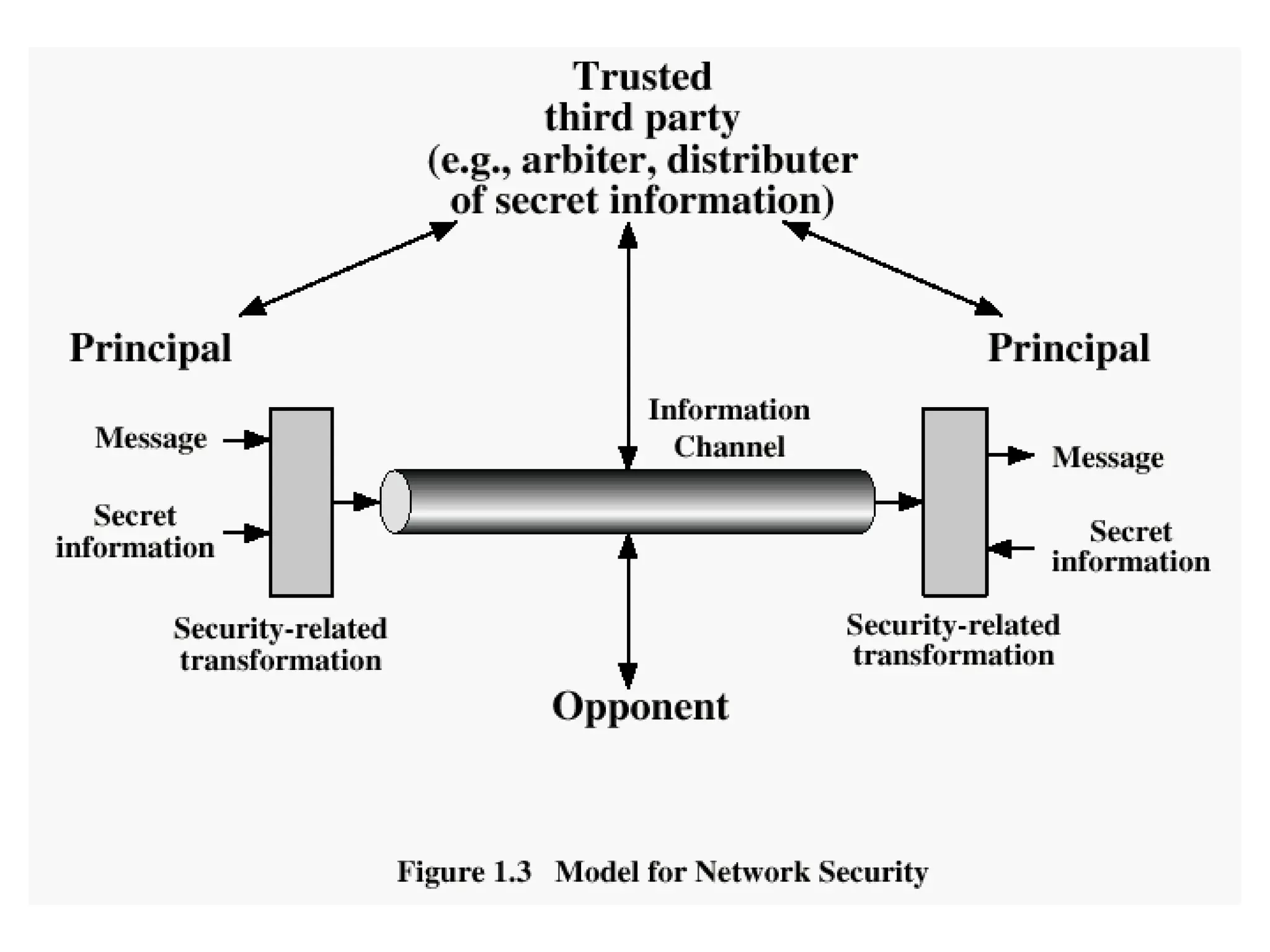
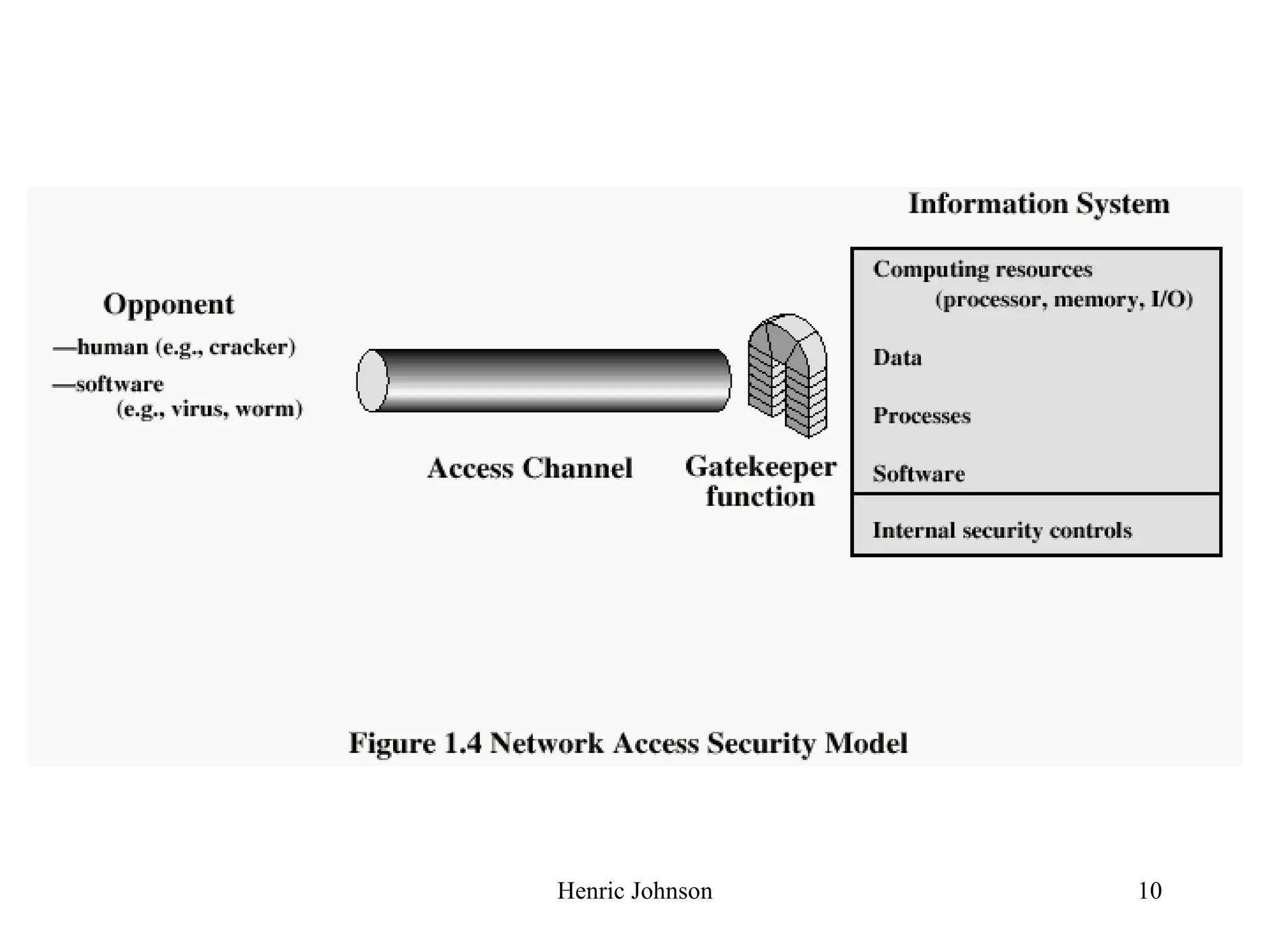



The document outlines various security concepts including attacks, services, mechanisms, and methods of defense for network security. It discusses security attacks like interruption, interception, modification, and fabrication. It also covers security services like confidentiality, authentication, integrity, non-repudiation, and availability. Finally, it mentions methods of defense such as encryption, software and hardware controls, policies, and physical controls.
![Network Security Henric Johnson Blekinge Institute of Technology, Sweden www.its.bth.se/staff/hjo/ [email_address] +46 708 250375](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter-ns1-13479/75/Intoduction-to-Network-Security-NS1-1-2048.jpg)












