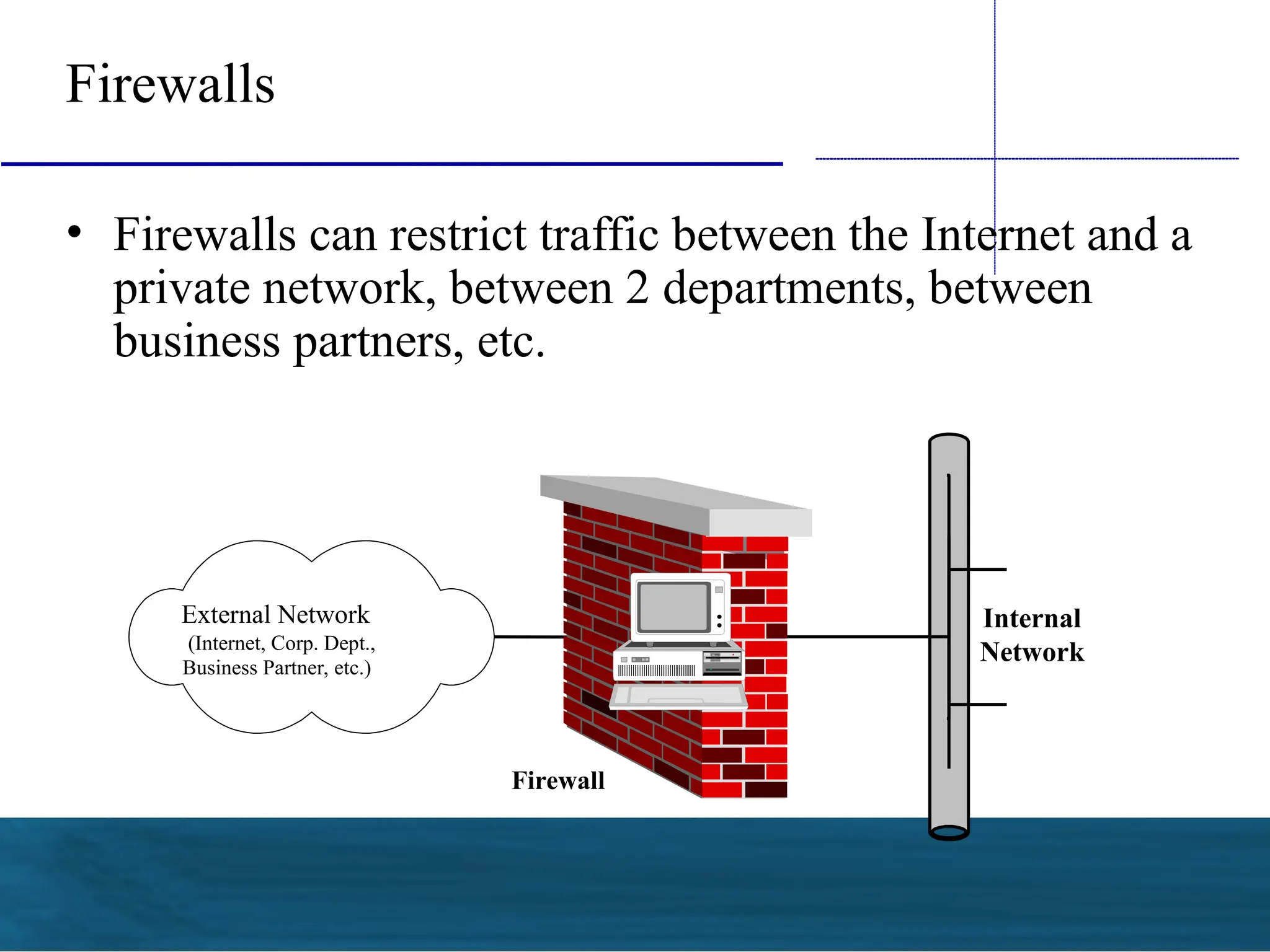
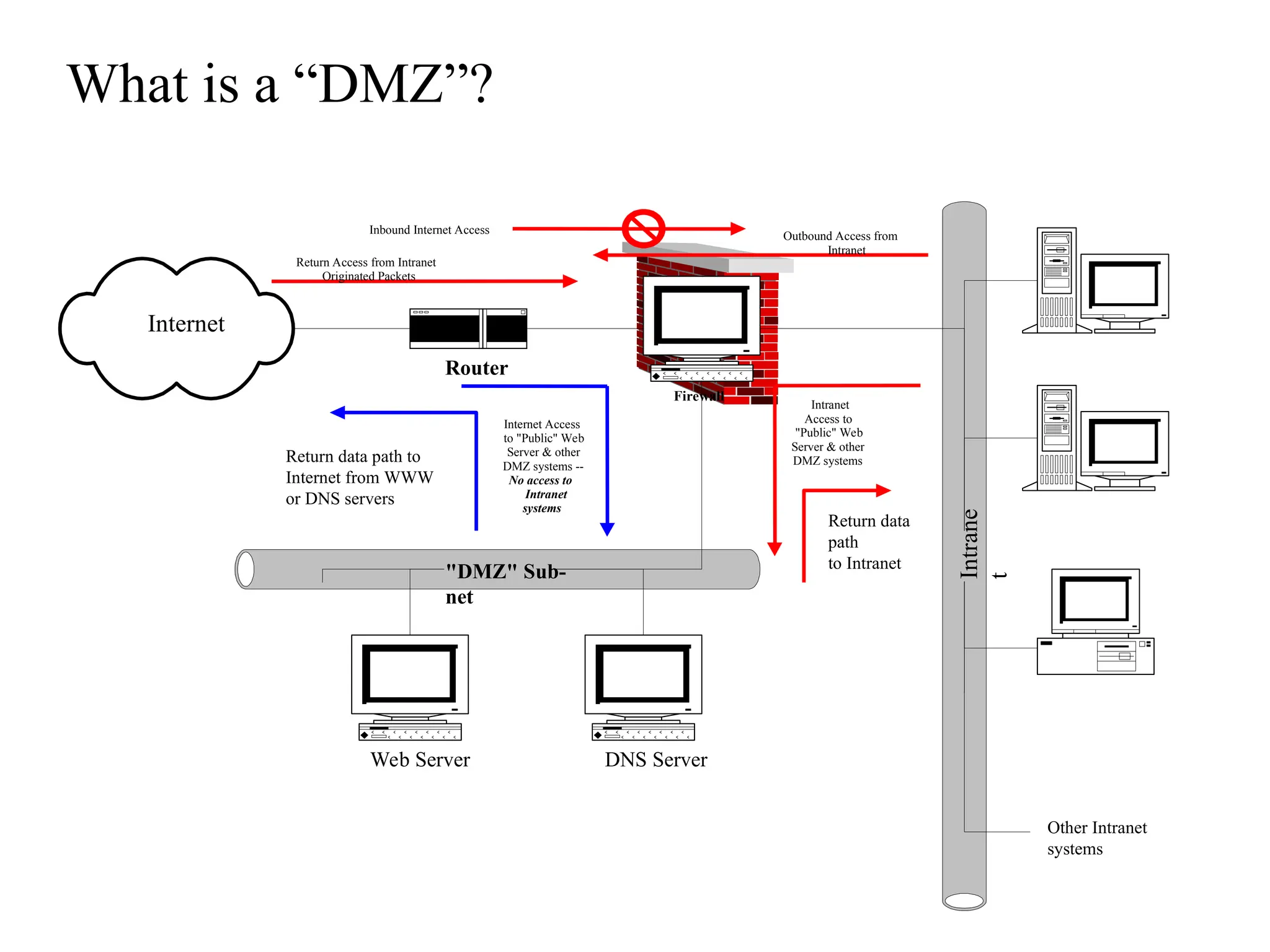
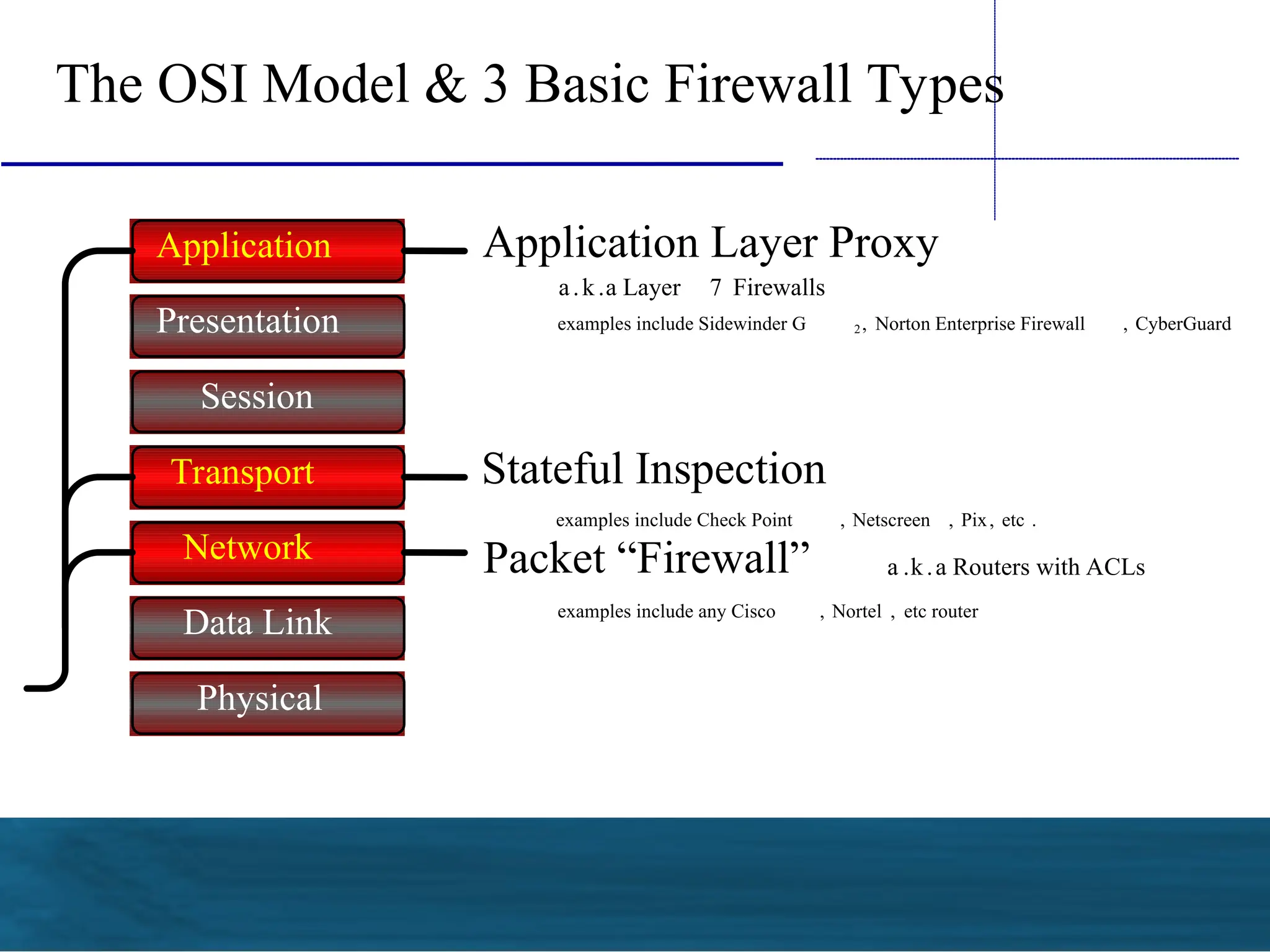
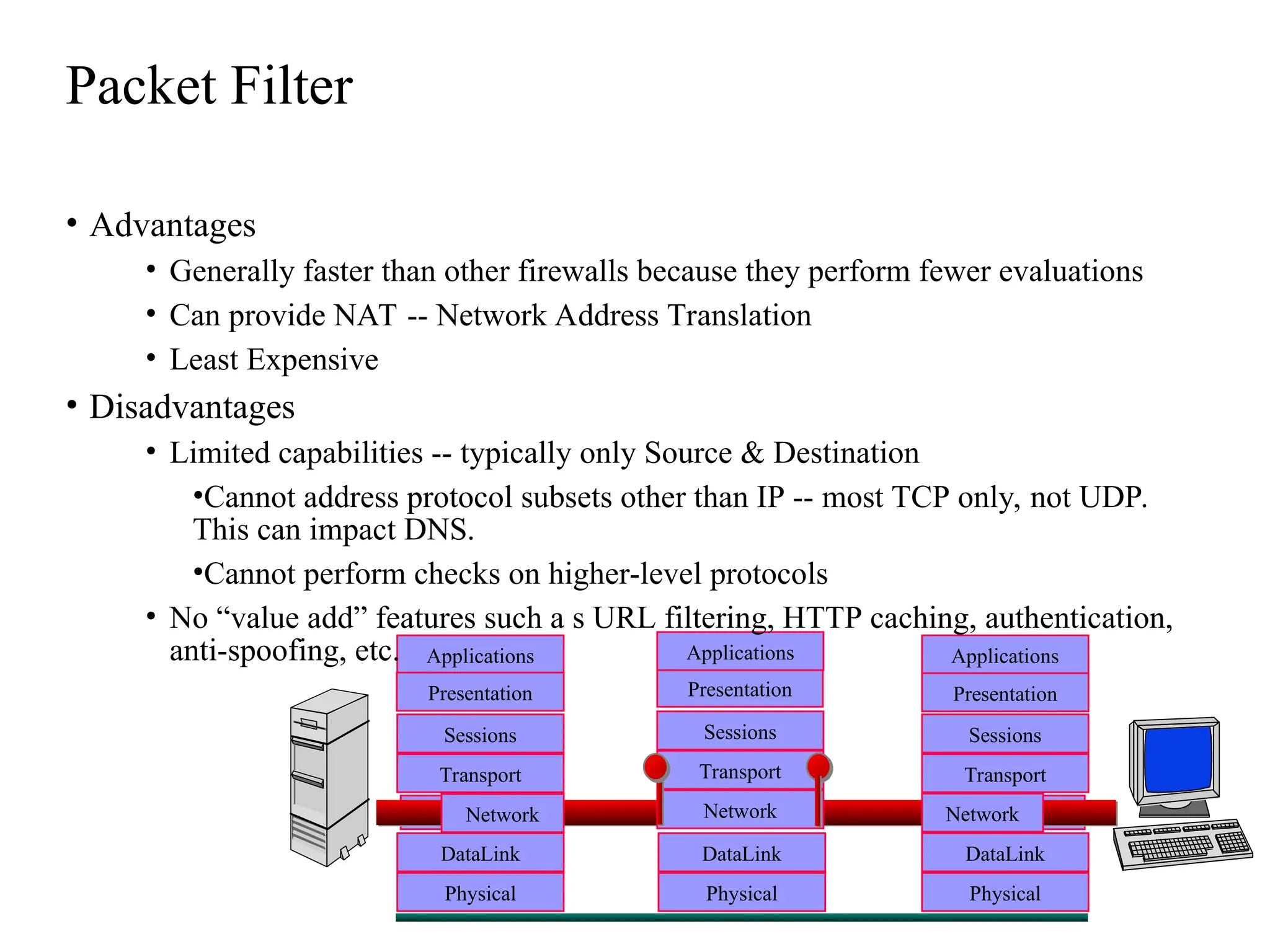
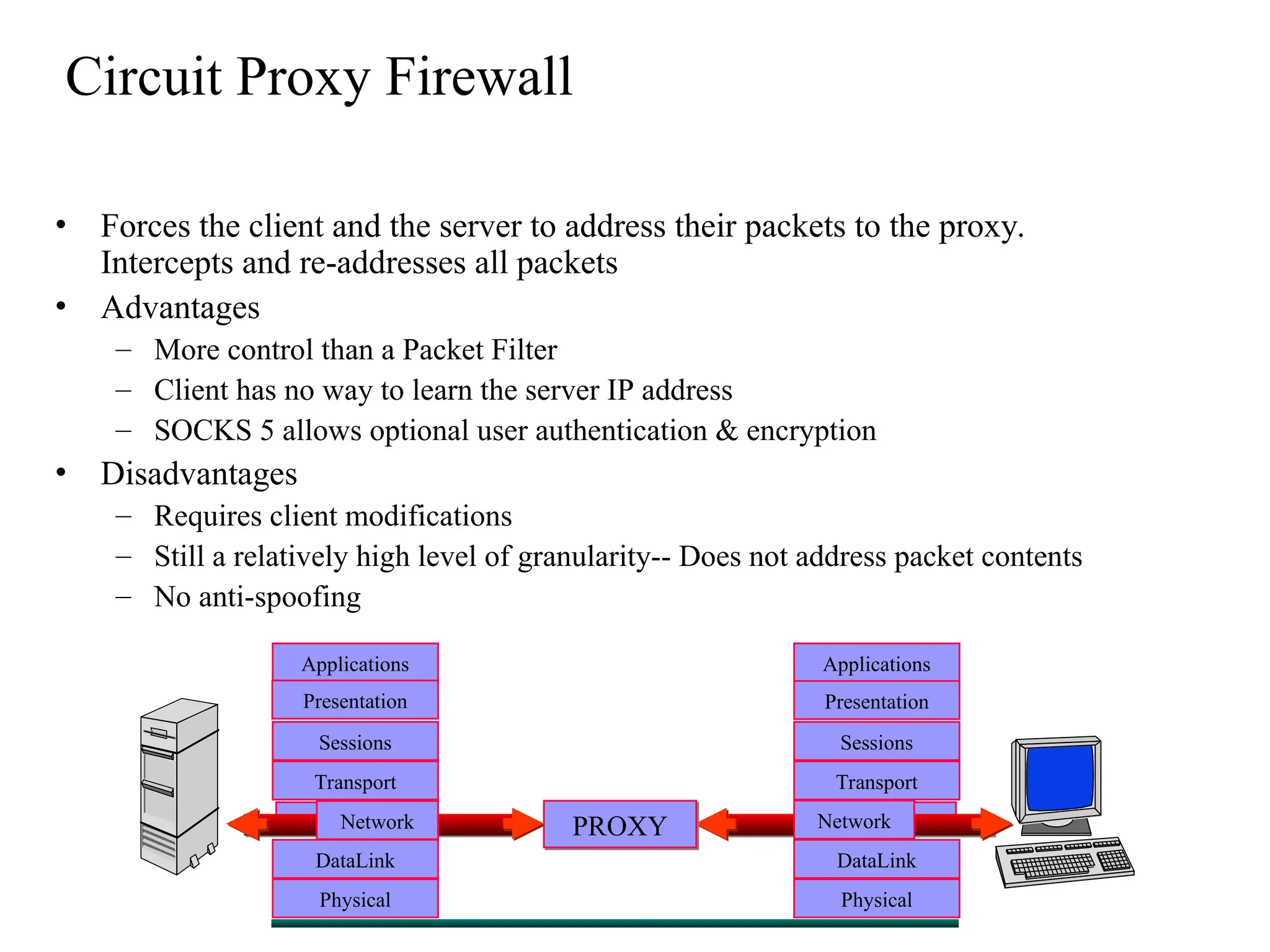
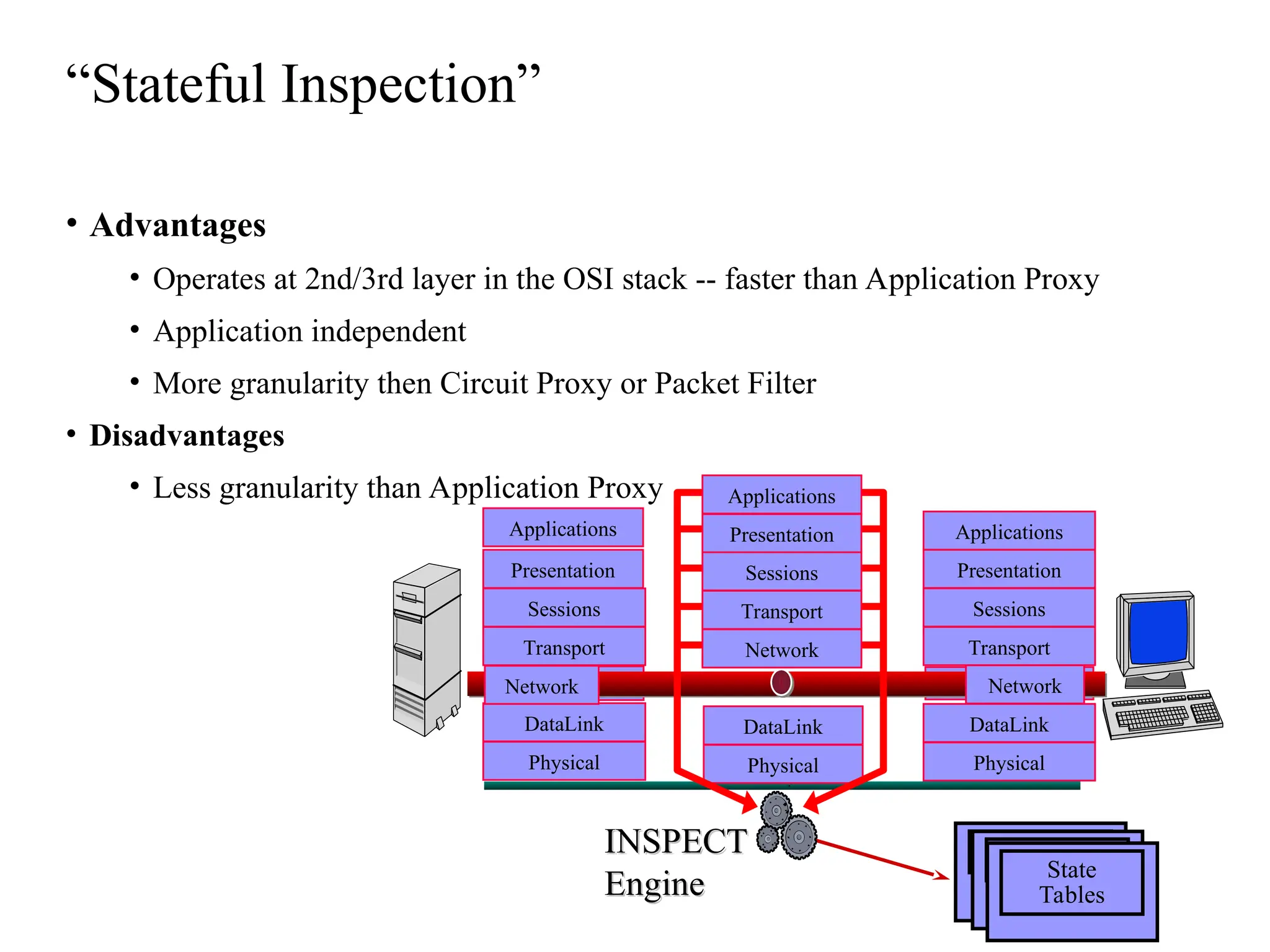
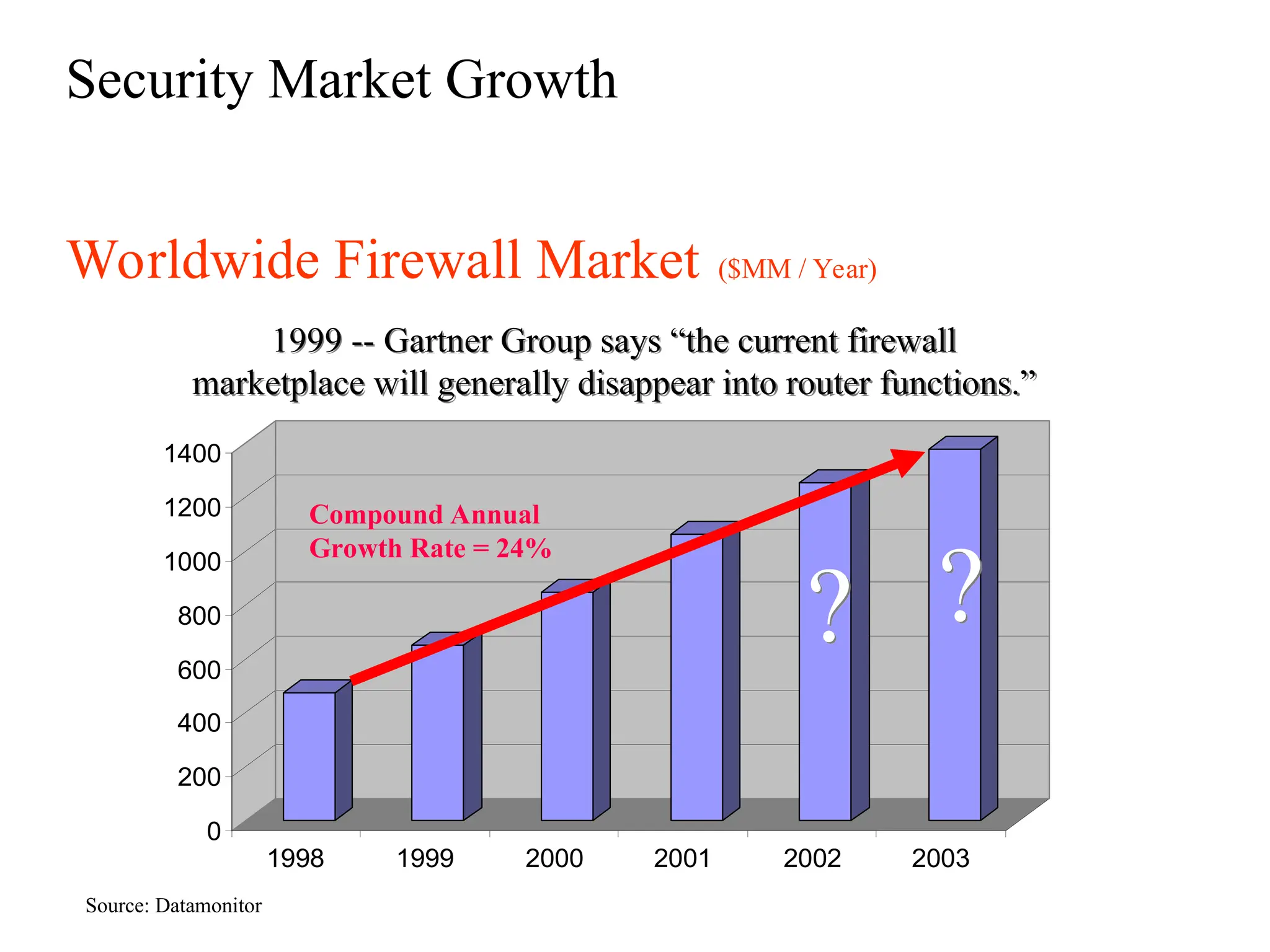
The document outlines the fundamentals of firewalls and their role in information protection, emphasizing the three core components: confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It discusses different types of firewalls, their functions, and critical considerations for implementation and management within a security framework. Additionally, it highlights that while firewalls are essential tools for network security, they are not a complete solution and require ongoing management and monitoring.