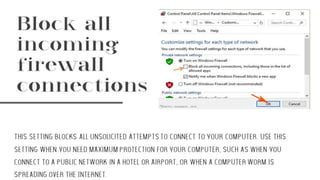
The document defines different types of firewalls and their purposes. It discusses firewall design principles like establishing controlled links and protecting networks from internet attacks. There are four main types of firewalls: proxy, stateful multilayer inspection, packet filtering, and circuit level gateway. Proxy firewalls act as gateways for specific applications. Stateful multilayer inspection firewalls monitor active connections to determine which network packets to allow. Packet filtering firewalls work at the TCP/IP layers to filter packets. Circuit level gateway firewalls rely on packet headers to filter sessions. More complex firewall configurations beyond single systems are also possible.