1. Fire insurance is a contract between a policyholder and insurer where the insurer agrees to compensate the insured for loss or damage to property caused by fire.
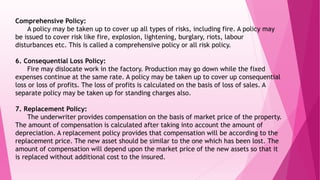
2. There are various types of fire insurance policies that can be purchased, including valued policies, specific policies, average policies, and floating policies.
3. Key principles of fire insurance include insurable interest, utmost good faith, indemnity, and loss being caused directly by fire and not an excluded peril like war or earthquake.