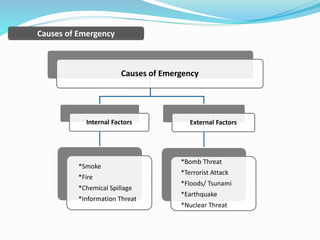
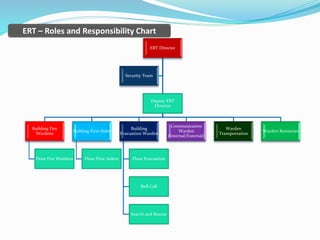
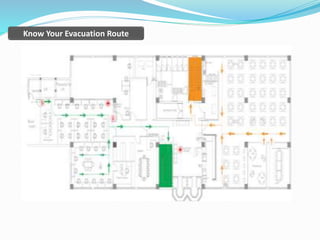
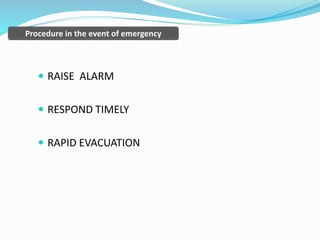
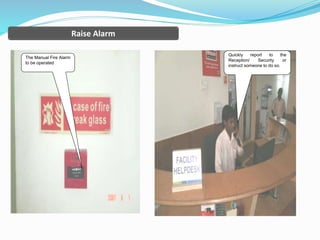
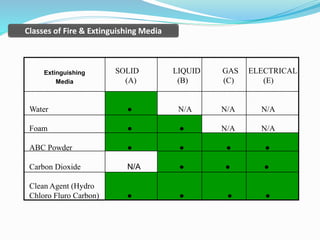
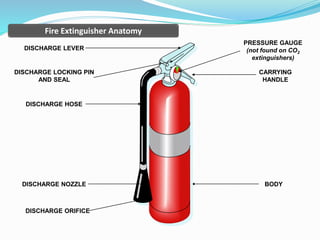
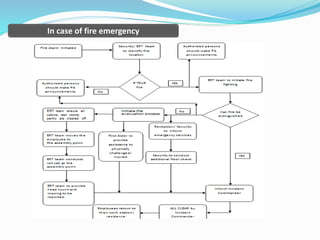
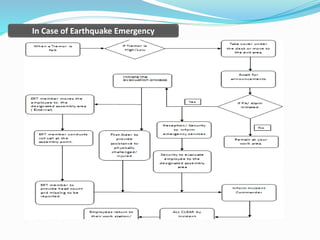
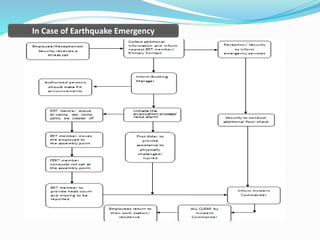
The document outlines an emergency response program that details terminology, causes of emergencies, and procedures for different types of incidents such as fires, earthquakes, and bomb threats. It emphasizes the importance of preparedness, response, and recovery, as well as the roles and responsibilities of emergency response teams and equipment. The document serves as a comprehensive guide to help organizations manage emergencies effectively and protect critical assets.