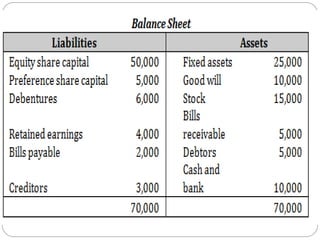
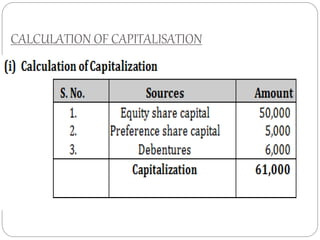
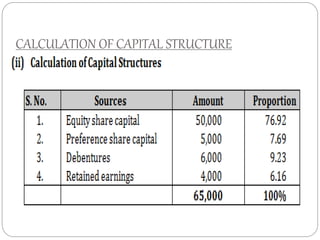
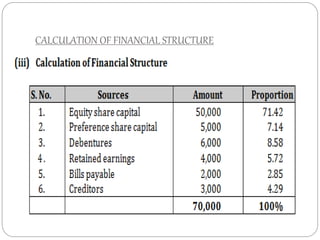
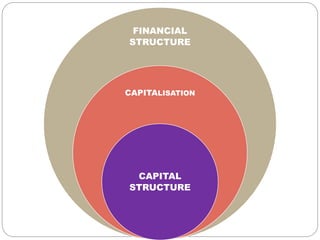
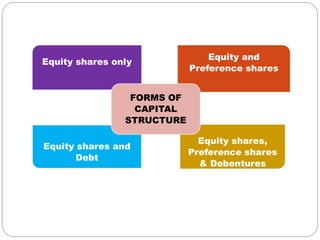
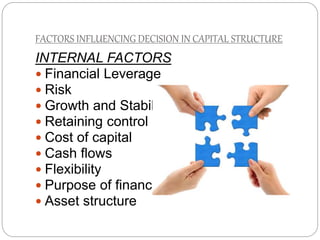
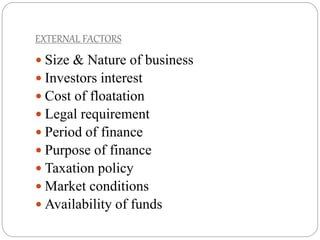
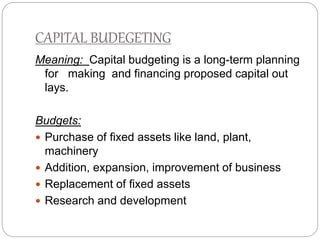
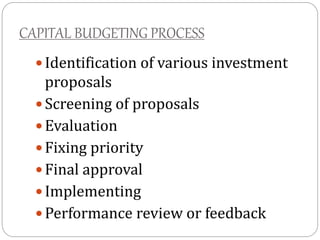
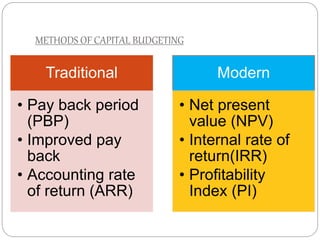
This document discusses capital structure and financing decisions for businesses. It defines capital structure as the composition of a company's long-term capital, including debt and equity. The capital structure determines how a company finances its assets through different sources of funds. The document lists several factors that influence a company's capital structure decision, such as financial leverage, risk, growth opportunities, and costs of financing. It also describes different methods for evaluating capital budgeting proposals, such as net present value, internal rate of return, and payback period.