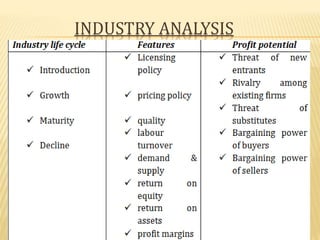
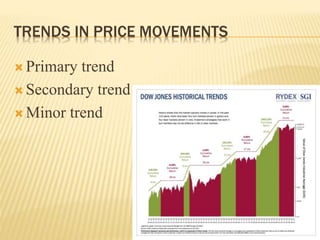
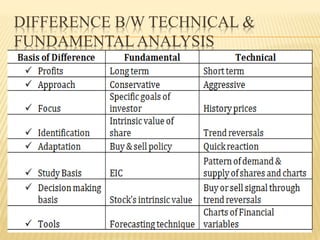
This document discusses security analysis and different types of analysis used for it. Fundamental analysis looks at economic, industry and company factors, while technical analysis examines price trends. Fundamental analysis involves studying economic indicators, industry dynamics and financial statements. Technical analysis relies on the assumptions that market behavior is predictable and share prices discount all information. Different technical analysis techniques are described, including charting price movements over time and identifying support and resistance levels. The limitations of solely relying on technical or fundamental analysis are also noted.