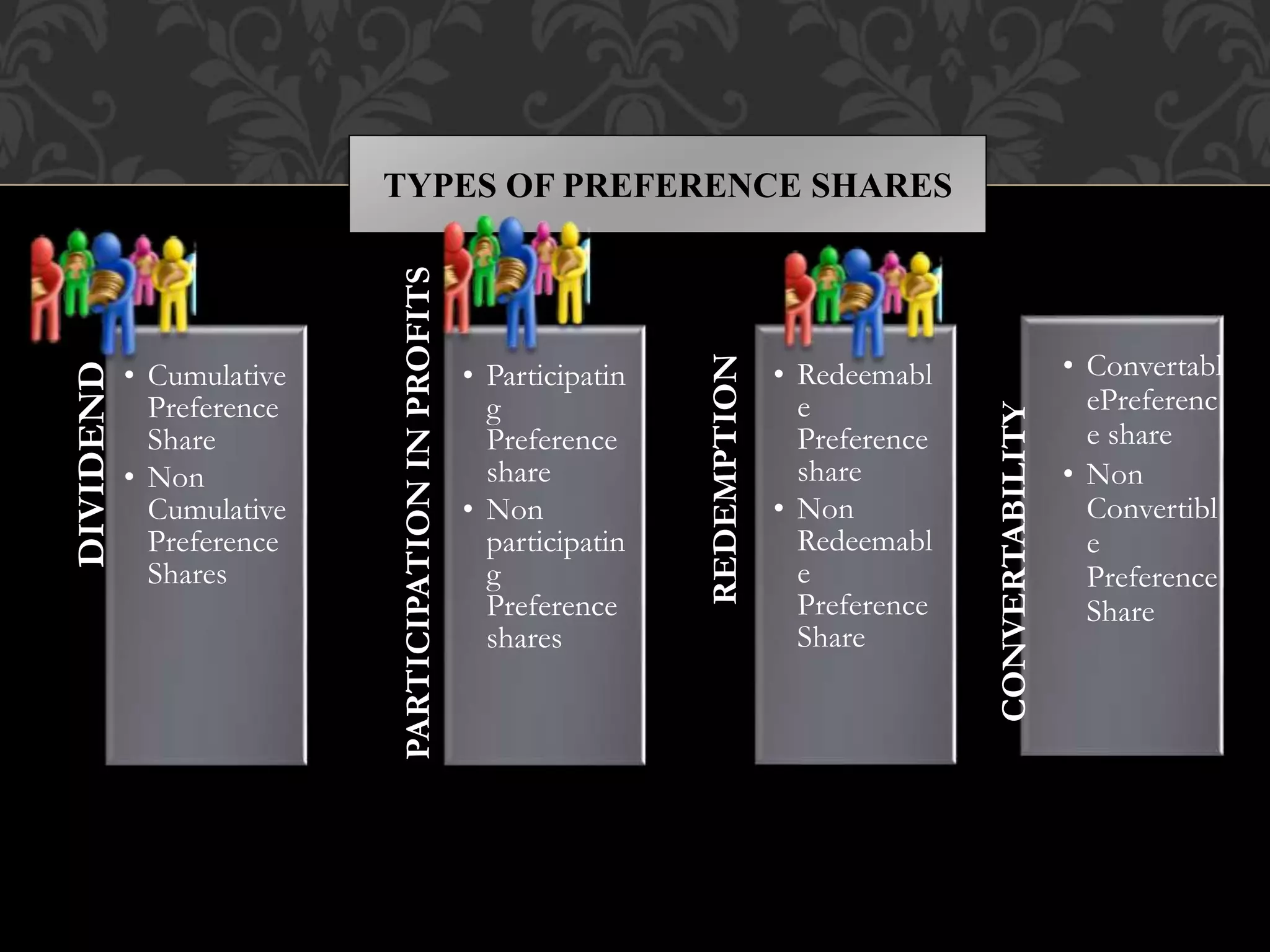
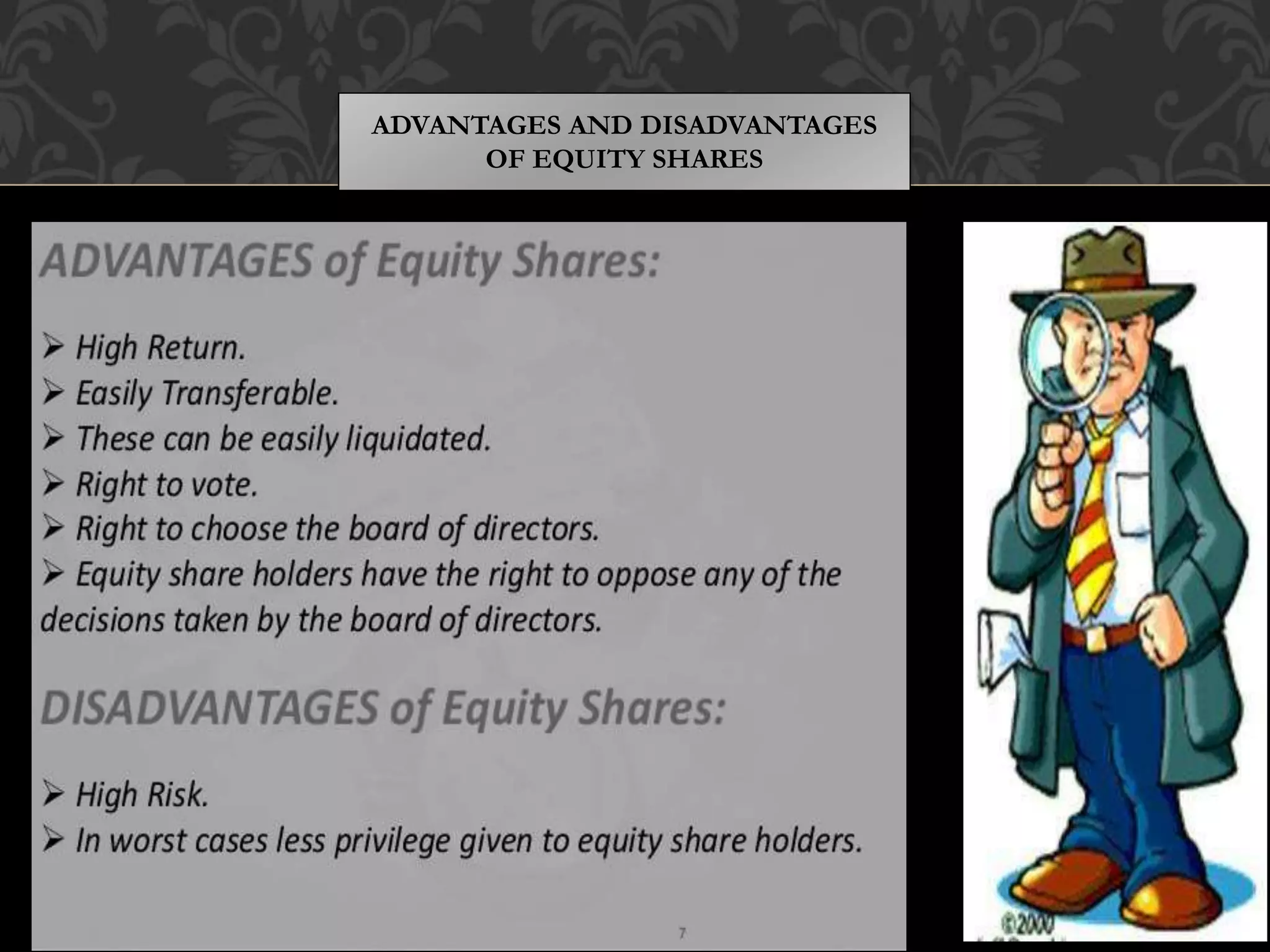
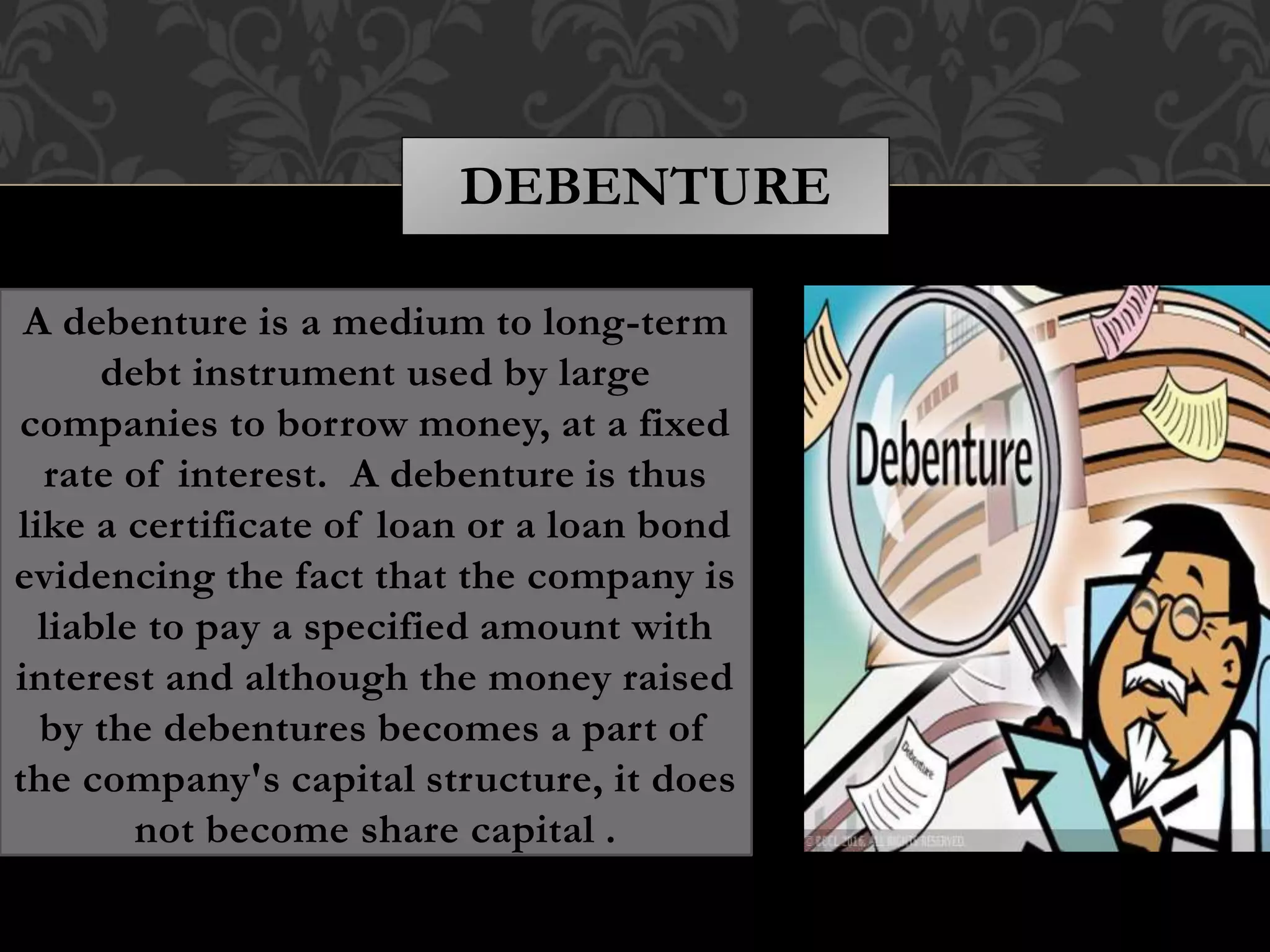
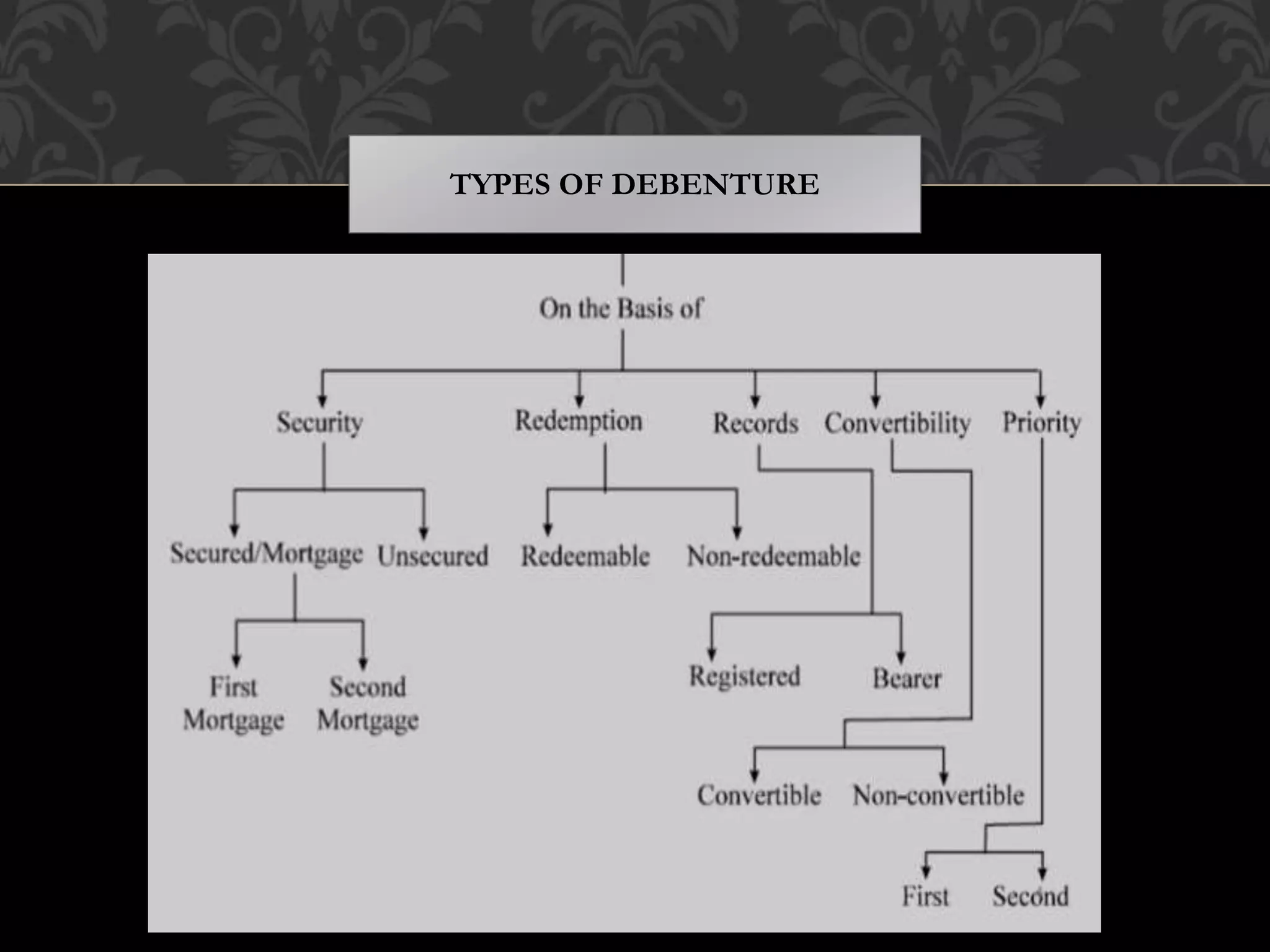
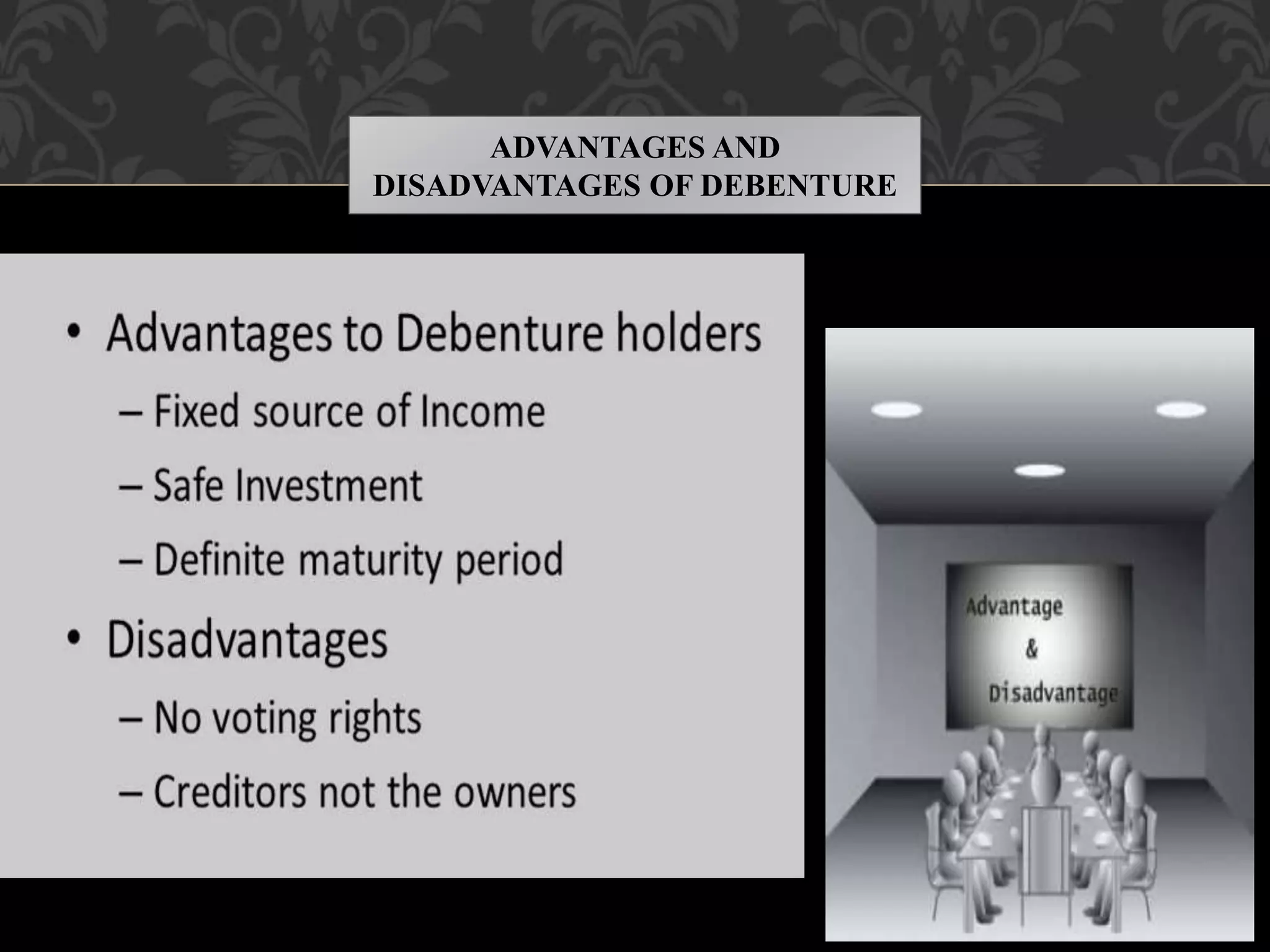
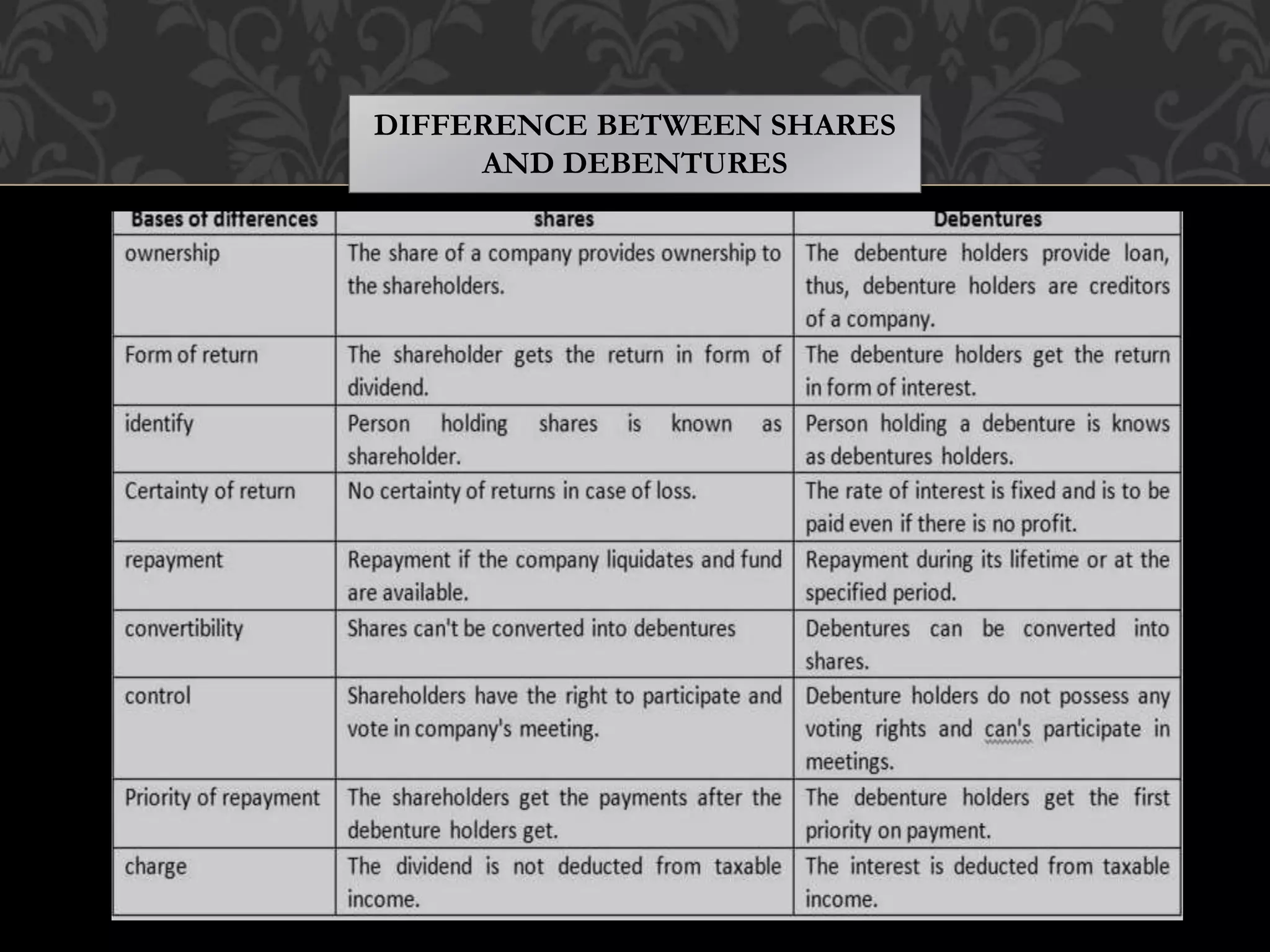
This document provides an introduction to shares, share capital, debentures, and the differences between them. It discusses key terms like IPO, FPO, equity shares, preference shares, debentures, and issuing shares. The main types of each are outlined, along with their advantages and disadvantages. Shares represent ownership in a company and allow shareholders to share in profits as dividends, while debentures are like loans that pay interest but do not provide ownership. This introduction covers the basic concepts for investors regarding the capital structure of companies.