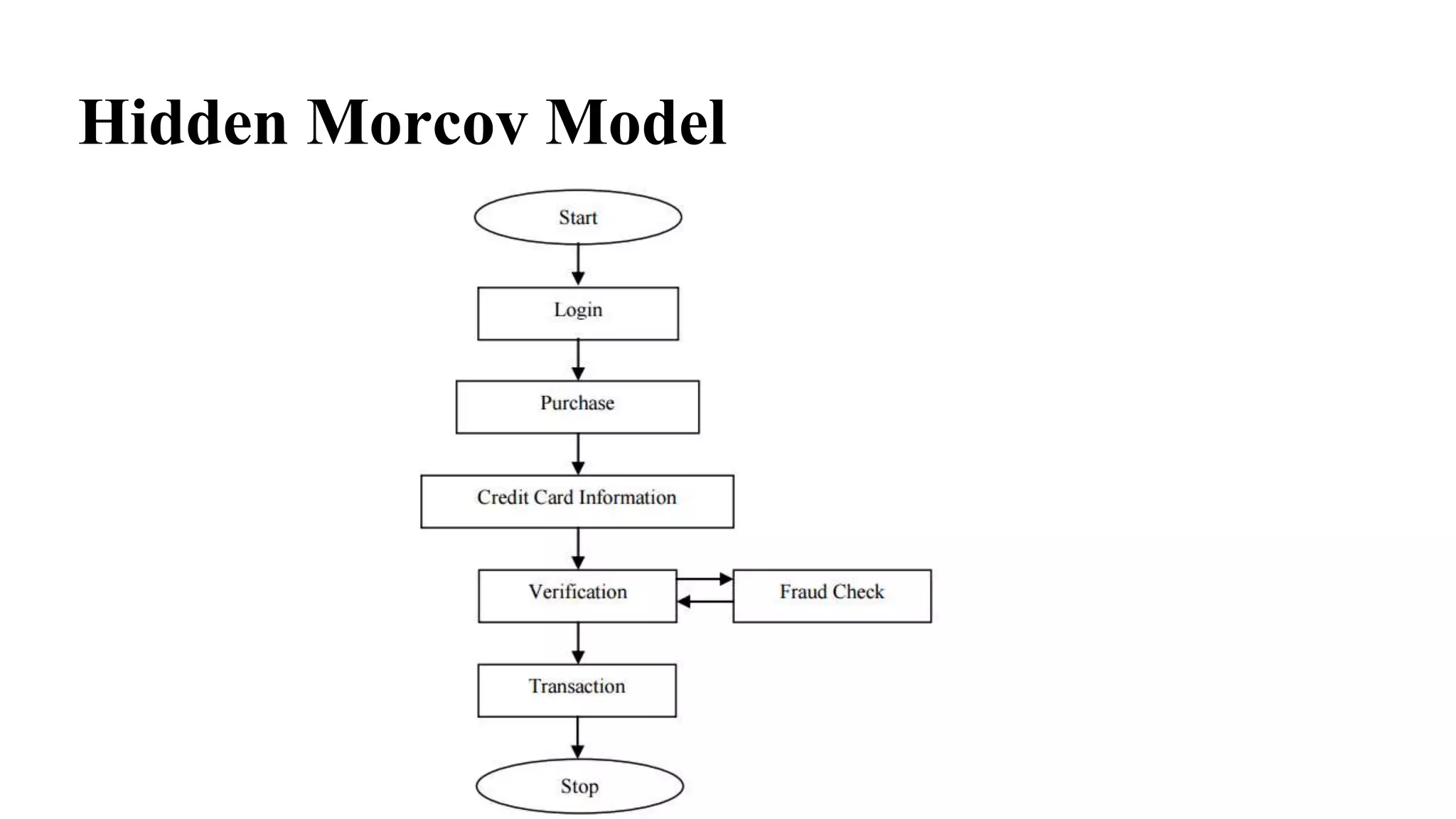
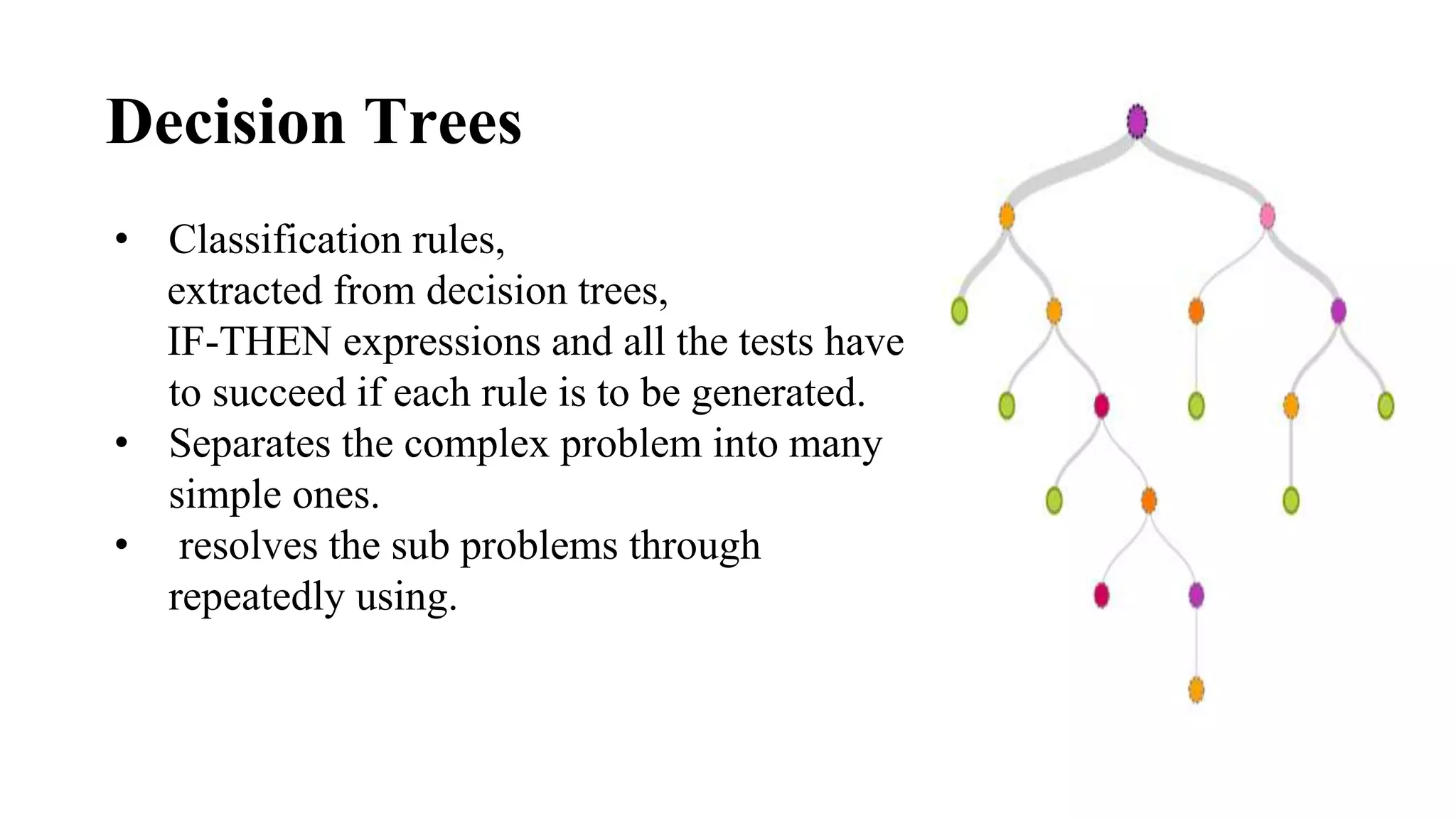
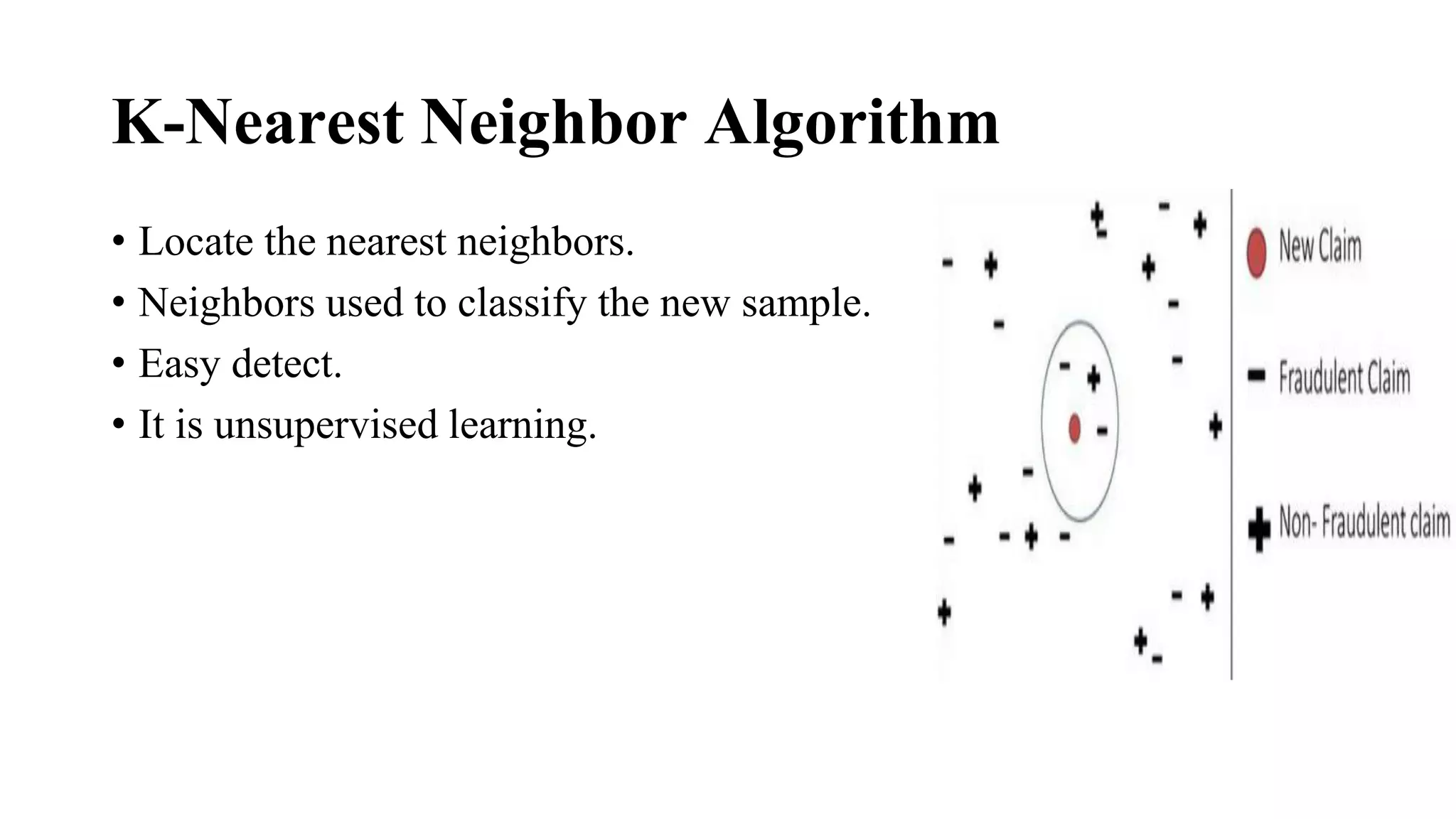
This document discusses advanced credit card fraud detection techniques. It outlines that millions of dollars are lost annually to credit card fraud. It then describes different types of fraud like counterfeit cards, lost/stolen cards, and identity theft. It presents several data mining techniques used for fraud detection, including hidden Markov models, decision trees, k-nearest neighbor algorithm, and logistic regression. Specifically, it notes that hidden Markov models use automatic techniques to take action at precise times, decision trees separate complex problems, and k-nearest neighbor and support vector machines are used for easy detection and kernel representation/margin optimization respectively. The document concludes that logistic regression can minimize fraud rates and is easy to implement.