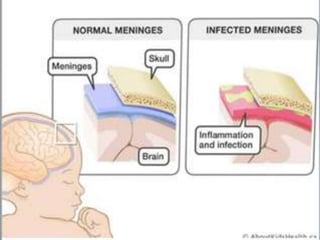
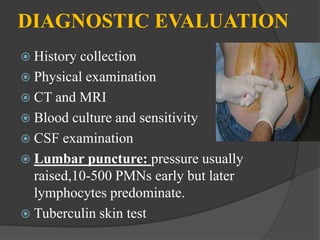
Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges that cover the brain and spinal cord. It can be life-threatening due to its proximity to the brain and spinal cord. Meningitis is usually caused by a bacterial or viral infection that enters the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Diagnosis involves examination of cerebrospinal fluid obtained via lumbar puncture. Treatment focuses on antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals depending on the cause. Vaccines can help prevent certain types of meningitis.