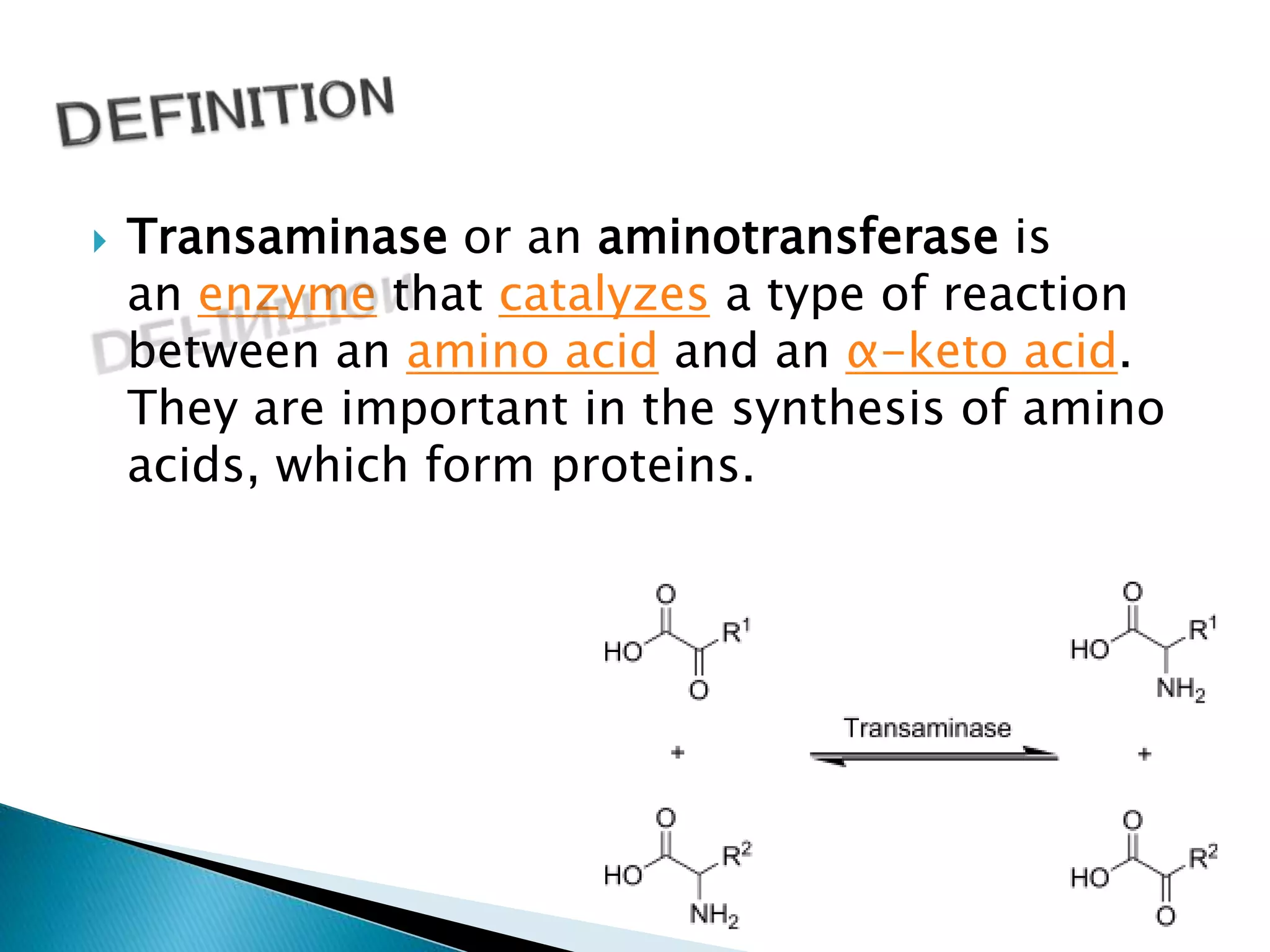
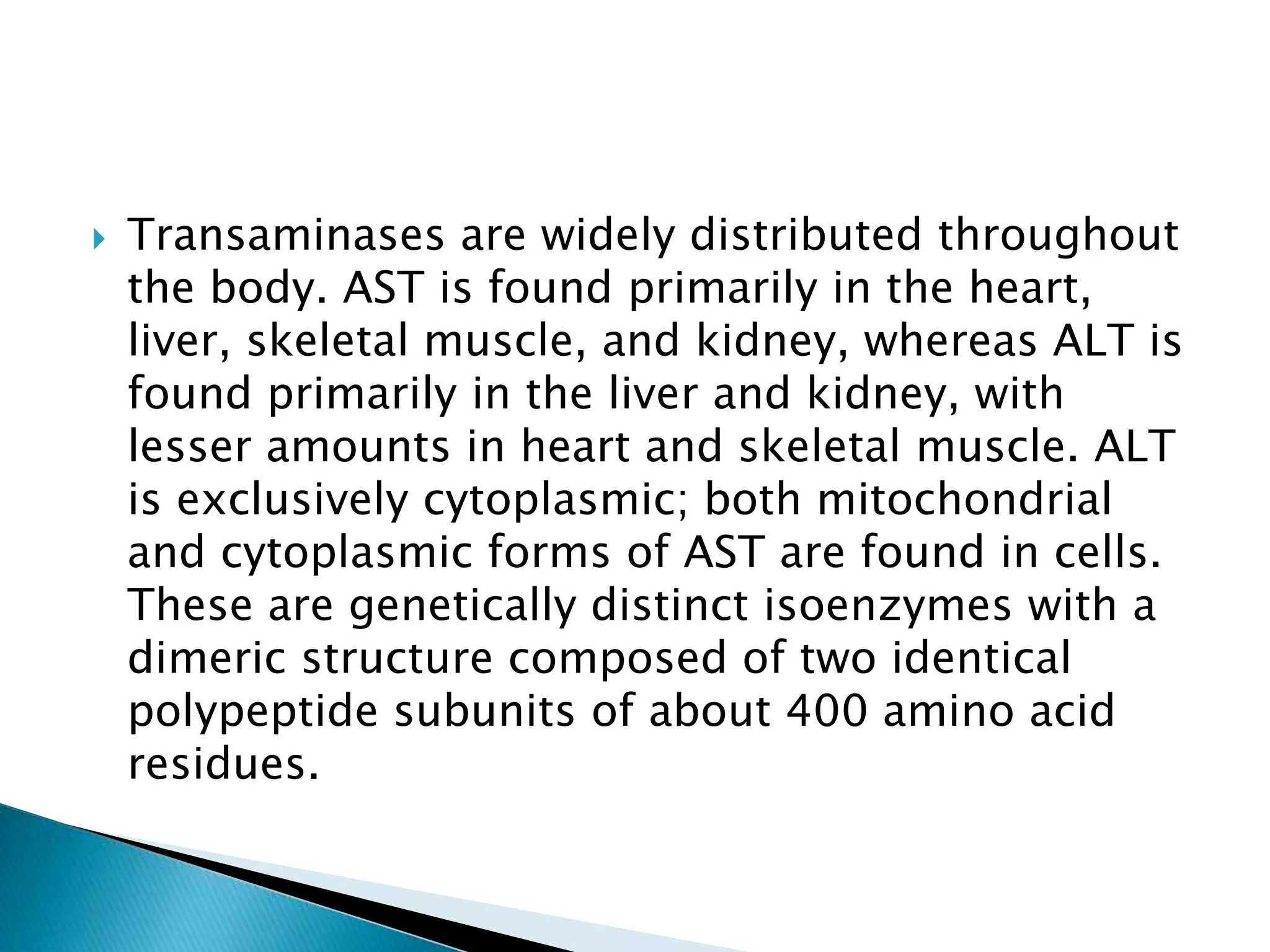
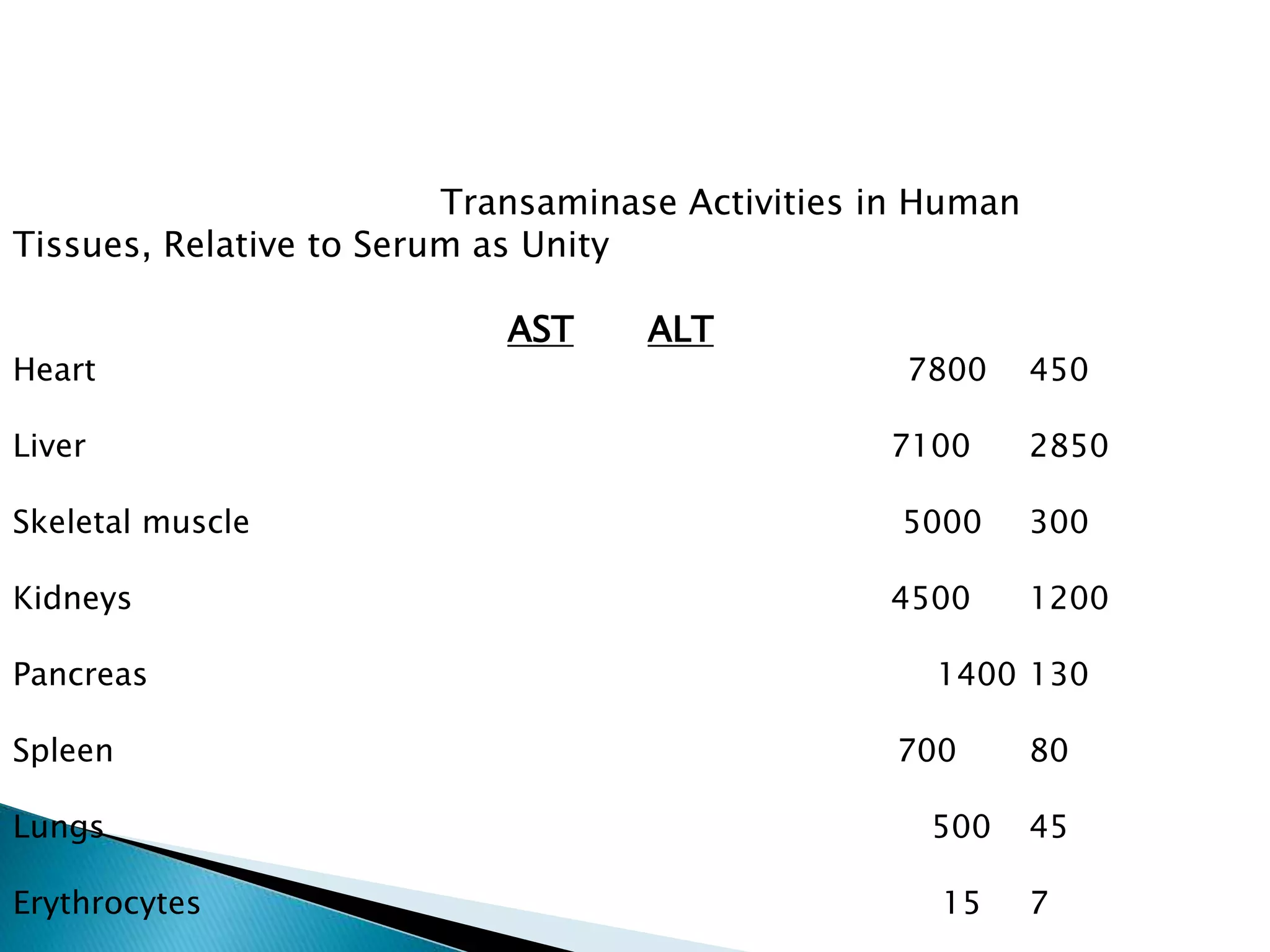
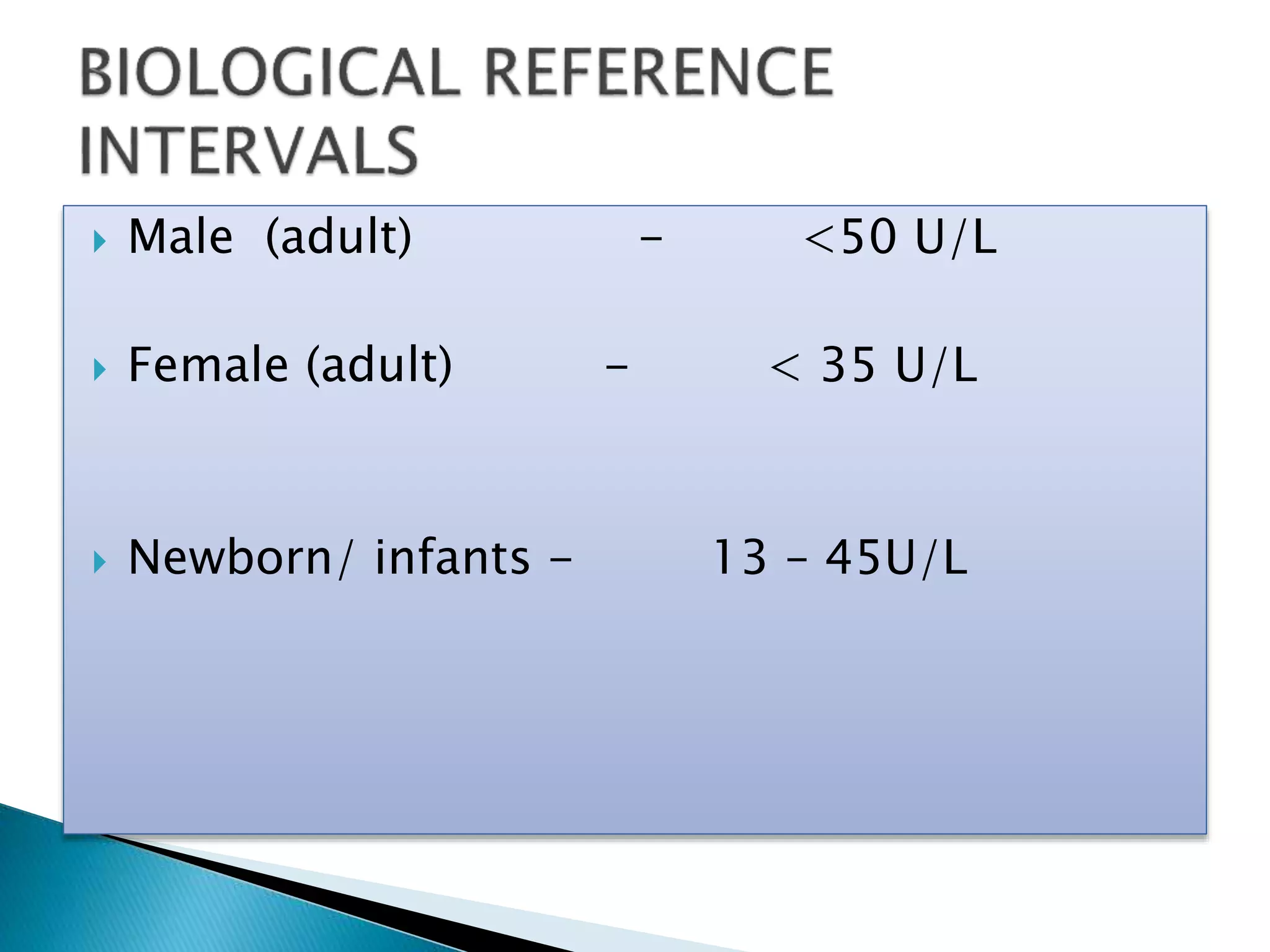
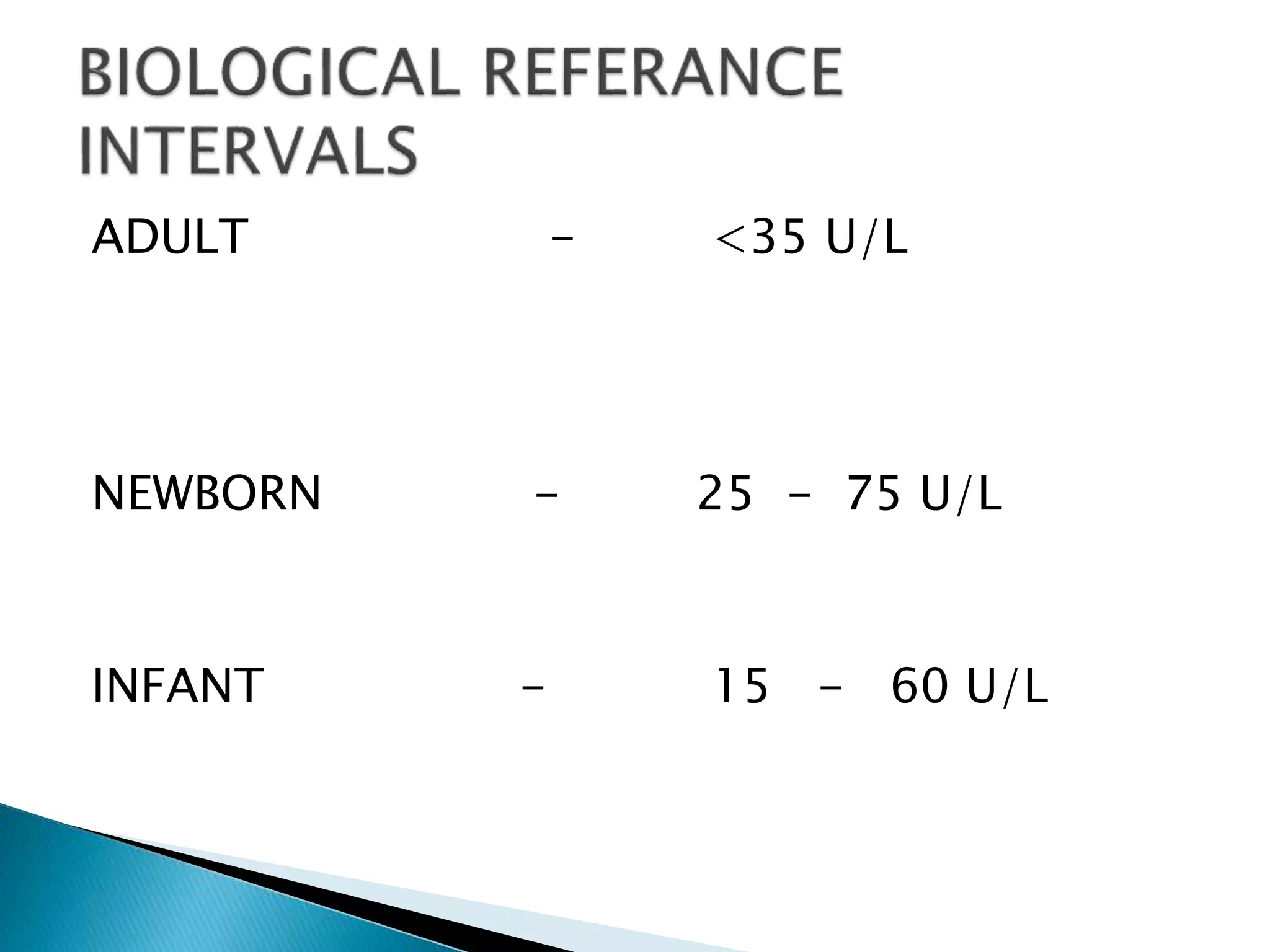
Transaminases are enzymes that catalyze reactions between amino acids and alpha-keto acids, and are important for synthesizing amino acids and proteins. They require the coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) are examples that are clinically significant. Measuring levels of different transaminases in the blood can help diagnose and monitor diseases, as AST and ALT are found at highest levels in liver and other tissues. Common assays involve measuring the decrease in NADH absorption that occurs during transamination reactions.