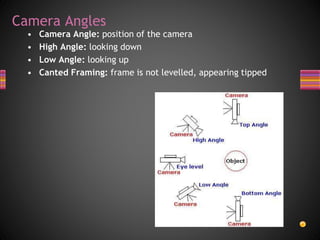
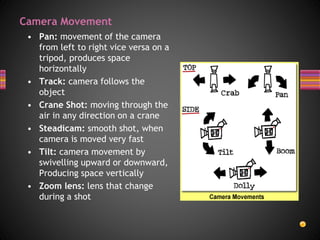
This document provides an overview of key concepts in media studies related to textual analysis. It defines media texts and various production elements like camera shots, angles, and movement that can be analyzed. Examples are given of different shot types like close-ups, establishing shots, and angles like high and low angles. Camera movement techniques such as panning, tilting, zooming, and tracking are also outlined. The purpose is to introduce students to the technical codes that will be examined in their media studies course and mock exam.