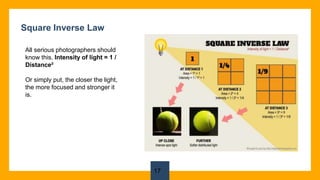
The document provides an overview of photography lighting basics, focusing on natural and artificial light types, their qualities, and how to use them effectively. It emphasizes the impact of different light conditions at various times of the day, highlighting the importance of the 'golden hour' for photography. Additionally, it covers essential concepts such as the laws of light, measurement of light intensity, and the characteristics of hard and soft lighting.