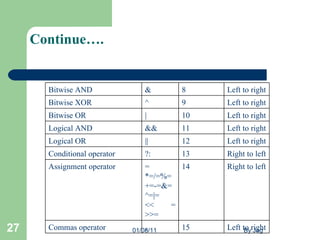
The document discusses various operators in C programming language. It classifies operators into arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, assignment and special operators. It provides examples of using different operators and explains their precedence rules and associativity.
















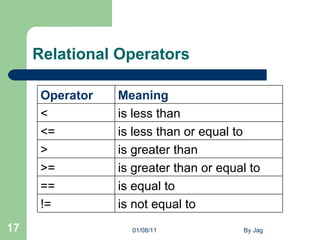








![Summary of C operator 01/08/11 By Jag Description Operator Rank Associativity Function call Array element reference ( ) [] 1 Left to right Unary plus Unary minus Increment Decrement Logical negation Ones complement Address Size of an object + - ++ -- ! ~ & Sizeof 2 Right to left Multiplication Division Modulus * / % 3 Left to right Addition Subtraction + - 4 Left to right Left shift Right shift << >> 5 Left to right Less than Less than equal to Greater than Greater than equal to < <= > >= 6 Left to right Equality Inequality = = |= 7 Left to right](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppt-110108071910-phpapp01/85/C-ppt-26-320.jpg)