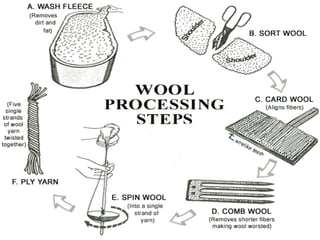
Fibres are the basic unit that make up all fabrics. There are two types of fibres - natural fibres obtained from plants and animals like cotton, jute, silk and wool, and man-made fibres obtained from chemicals like nylon, polyester and acrylic. Wool fibre comes from the fleece of sheep and other animals and is obtained from the soft under-hair. These fibres are converted into yarns through processes like carding and spinning, where they are twisted together into longer, thicker strands to make them stronger for weaving fabrics.