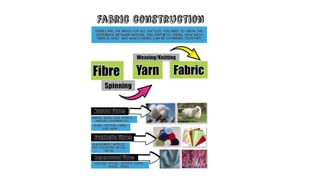
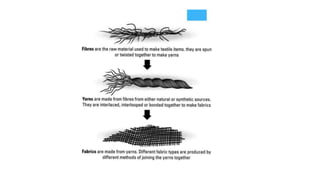
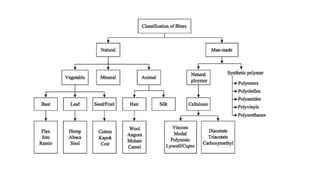
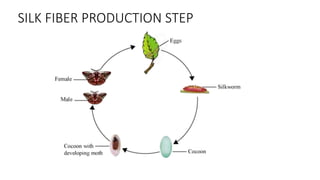
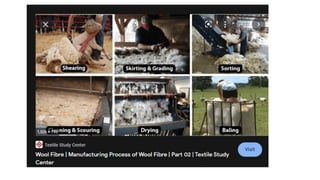
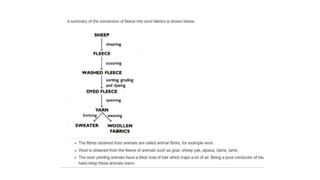
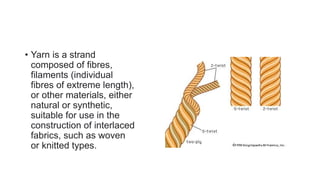
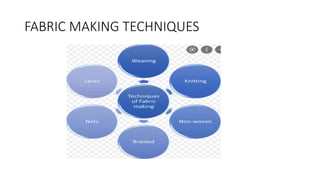
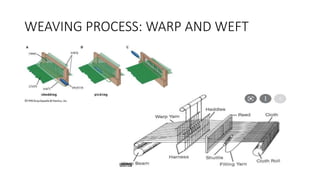
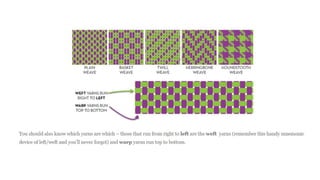
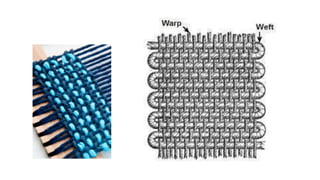
The document presents an extensive overview of textiles and fibers, detailing their historical significance, categories, and manufacturing processes. It covers natural and synthetic fibers, emphasizing the production and properties of cotton, silk, and wool, as well as weaving techniques like plain, satin, and twill weaves. Additionally, it explains different methods of yarn manipulation, including knitting and braiding, showcasing the complexity of textile creation.