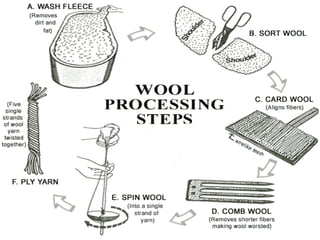
This document discusses the process of transforming natural and synthetic fibres into fabric. It begins by defining a fibre as a thin hair-like strand that fabrics are made from. Natural fibres like cotton, jute and silk come from plants and animals, while synthetic fibres like nylon, polyester and acrylic are man-made. Wool fibre comes from sheep and goat fleece and silk fibre from silkworm cocoons. The document then outlines the steps of collecting, sorting, carding, combing and spinning fibres into yarns, which are thicker strands made strong through twisting. Yarns are then woven or knitted into fabrics.