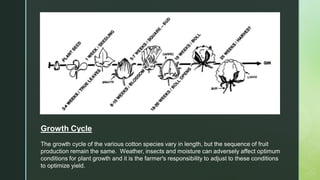
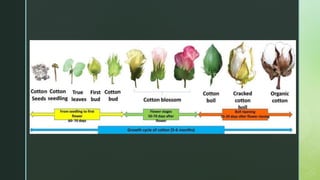
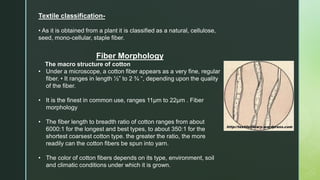
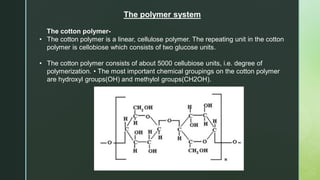
Cotton is a natural cellulose fiber that grows in bolls around seeds and has been cultivated for over 5,000 years in various regions globally, including the Americas, Africa, and India. The document outlines the growth cycle, historical context, fiber morphology, physical and chemical properties, and the manufacturing processes involved in turning cotton into textiles. Additionally, cotton's end uses span from clothing and household textiles to industrial applications and food production.